_______________ planets are rocky, small, Earth-like planets such as Mars and Venus.
Terrestrial
Planets that are found around starts other than our Sun are known as _____________________ planets
Extrasolar
________ waves can move through Earth's interior layers, while __________ waves can only travel across Earth's crust
Body; surface
A ______________ is a volcanic mudslide, caused by precipitation or snowfall mixing with volcanic debris
Lahar
The _______________ refers to all of the rocks and minerals on Earth, including the crust, mantle, and core. The envelope of gases surrounding Earth is known as the ______________
Geosphere; atmosphere
__________ ____________ are large planets composed mostly of gas, such as Jupiter and Saturn. __________ ___________ are planets that have "slushy" mantles, such as Uranus and Neptune.
Gas giants; ice giants
______________ is the curvature of spacetime due to the presence of an object with mass.
Bonus: Gravity increases with increasing _________, and decreases with increasing __________
Gravity; mass, distance
A region where two plates come together is called a _____________ plate boundary. A region where two plates move apart is called a _______________ plate boundary. A region where two plates move along each other is called a ______________ boundary.
Convergent; divergent; transform
_______________ lava is low viscosity and dark, often forming shield volcanoes.
Basaltic
Lower frequency, longer wavelength light is _____________ in energy than higher frequency, shorter wavelength light
Red light is ____________ energy than blue light
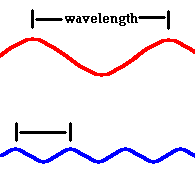
Lower; lower
Identify the three types of galaxies shown below with their correct names:



Elliptical; irregular; spiral
The average distance between the Sun and the Earth is an ___________ ____________. The distance that light travels in one year is a __________ ___________
Astronomical unit; light year
A fault in which the two plates move along each other is known as a _________-__________ fault, which occurs at a transform plate boundary. A fault in which the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall is known as a ___________ fault, which occurs at divergent plate boundaries. At a convergent plate boundary, the hanging wall is pushed above the footwall, making it a ___________ fault.
Strike-slip; Normal; Reverse
___________________ volcanoes are formed from layers of high-viscosity rhyolitic lava and other volcanic debris that builds up steep sides over time. ______________ volcanoes are relatively small and may form after only one eruption.
Stratovolcanoes; Cinder cone
List two pieces of evidence that can be used to support the theory that continents used to be together as a supercontinent called Pangea, and has drifted apart since
Fossil evidence (fossils of the same species of organism are found on continents now separated by oceans)
Mineral/rock deposits (deposits of certain rocks like coal are now found in regions that are no longer near the equator, like Antarctica)
Kepler's ________ Law states that planets move faster when they are closer to the Sun in the course of their orbit
Kepler's _______ Law states that planets orbit in elliptical paths
Kepler's _______ Law states that planets with larger orbits take longer to complete their course around the Sun (p2 = a3)
A ____________ is a chunk of space rock that has entered Earth's atmosphere. A ___________ is a chunk of space rock that is currently found in space. A ___________ is a chunk of space rock that has made it to Earth's surface.
Meteor; Meteoroid; Meteorite
There are two types of surface waves: _____________ waves and ________ waves
P
Rayleigh; Love
In Earth's mantle, warmer material near the core ______________ because it is ____________ dense. Near Earth's crust, cooler material _____________ because it is ________ dense. Movement of heat through a fluid in this manner is called _______________
Rises, less; Sinks, more; Convection
The __________ of the Sun is the hottest layer, where nuclear fusion takes place. The _________________ is the visible surface of the Sun, where sunspots are found. The ______________ produces UV radiation, which is mostly blocked by Earth's ozone layer

Core; Photosphere; Chromosphere
What are two pieces of evidence that support the Big Bang Theory? Briefly explain each theory (one sentence).
Cosmic Background Radiation -- there is leftover radiation spread uniformly throughout the universe, considered a remnant from the Big Bang
Redshifting -- light from celestial objects like galaxies is redshifted, indicating that they are moving away from us (celestial objects expanding outwards)
Many asteroids are found within the asteroid belt, which is found between __________ and __________. Many icy objects are either found in the _________ __________, which forms a disk outside of Neptune, or the ________ __________, which forms a sphere marking the outer bounds of the solar system
Earth's lithospheric plates move through a combination of three mechanisms: _______ _______, which occurs at divergent plate boundaries where new seafloor is made; _______ ______, which occurs at convergent plate boundaries where old seafloor is recycled; and _________ _________, which is a result of temperature and density differences within Earth's interior
Ridge push; Slab pull; Mantle convection
The _____________ of an earthquake is the point within the Earth where a rupture first occurs. The ______________ is the point on the Earth's crust directly above the previous location.
The upper portion of the upper mantle is known as the _____________
Focus; Epicenter
Lithosphere
Red, small stars will live _____________ than large, blue stars.
When a massive star dies, it goes supernova, producing either a _______ _______ or a _________ _______
When a low-mass star dies, it produces both a _________ __________ and a _________ __________
Longer
Neutron star; black hole
White dwarf; planetary nebula
