A graph that indicates the overall production by businesses in the economy and is affected by wages and cost of inputs...?
What is "Short-Run Aggregate Supply" ?
A name for a set of policies that counteract the business cycle's ups and downs without any new government action required and include social wellfare programs (unemployment benefits)- created by the government ahead of time...
What are "Automatic stabilizers"?
In the short run, prices are __________. In the long run, prices are ___________.
Fill in the blanks: adjustable, sticky, narrow, broad, indifferent
What is "sticky" and "adjustable"?
Increasing the marginal propensity to consume would cause a decrease in...
a - marginal propensity to save
b - spending multiplier
c - savings rate
d - exports
e - aggregate supply
What is " a - marginal propensity to save"?
Which of the following would be counted as consumption for GDP?
1 - The purchase of a stock, 2 - the sale of a bond, 3 - the purchase of a manicure, 4 - purchase of a construction crane, 5 - wages paid to employees
What is #3 - "Purchase of a Manicure" ?
Contracts make it so that wages are fixed in the present. Why is the SRAS curve sloped upward, then? State a solid reason.
What is "As price level increases, producers earn more profit in the short run"?
Each of the following can help end a recessionary gap EXCEPT a(n):
a - decrease in personal taxes
b - decrease in money supply
c - decrease in interest rates
d - increase in government spending
e - increase in net exports
What is "b - decrease in money supply"?
This is not an action for expansionary fiscal policy; rather, one for contractionary policy, when there is high inflation.
When the natural unemployment rate is higher than real unemployment rate--in the absence of the government intervention--1 - what economic state is this economy in, and 2 - how do wages respond long-term? Respond to both parts for full credit.
What is "inflation (gap)" and "wages increase" to restore equilibrium,for which SRAS shifts left?
Which must be true if the marginal propensity to consume is 0.8?
a - average propensity to consume will be less than the marginal propensity to consume
b - the government expenditure mutliplier will be 5
c - a $10 increase in spending will lead to an $80 increase in disposible income
d - wealth will tend to accumulate in the hands of few people
e - the economy will be running a deficit because consumption exceeds savings
Bonus: +100 additional pts
What is "b - the government expenditure mutliplier will be 5" ?
MPS = 0.2
Multiplier for spending = 1/MPS ...1/0.2 = 5
Which kind of unemployment is not present when real GDP is at potential GDP, which is when we are at full employment?
What is "Cyclical unemployment"?
Assume a country is in long-run equilibrium, and this country "A" has a long-time trading partner, country "B". If country "B" goes into recession, what would likley occur in the short run?
a - AD increases, causing PL to increase
b - AD decreases, causing PL to decrease
c - SRAS decreases, PL increases
d - SRAS increases, PL increases
e - SRAS decrases, PL decreases
What is "b - AD decreases; PL decreases"?
This is due to the fact that trade is part of Net Exports, which affects AD, expenditures. Less trade means less Net exports, so leftward shift of AD, and thus PL decreases.
Describe the change that would occur to output and price level when government spending increases--in an economy where the aggregate supply curve is vertical...Answer both with "increase, decrease, or no change".
What is "output: no change; price level: increase" ---as spending increases, AD shifts right. If the SRAS is straight, the output intersects at the same output (real GDP) quantity, and price rises.
Which of the following is illustrated by the long-run aggregate supply curve and the production possibilities curve?
(A) The multiplier effect
(B) The maximum sustainable capacity
(C) The trade-off between inflation and unemployment
(D) Sticky wages and prices
(E) Business cycles
Bonus: +100 additional pts
What is "B - maximum sustainable capacity" ?
When the government decides to increase both spending and taxes by the same amount, what happens? EXPLAIN your answer
a - AS incraeses
b - AS decreases
c - AD is unaffected
d - AD decreases
e - AD increases
What is "e - aggregate demand increases, because the spending multiplier is always greater than the tax multiplier"
Are government transfer payments considered part of GDP? Explain.
What is "no, because those who obtain this money from government do not produce anything to earn the money"?
An increase in government spending would result in which of the following decreasing? Bonus $100 pts - GRAPH and label the change. Graph must have labels for graphs, arrows showing change (if applicable), axes labeled, Y1, Y2, PL1, PL2 (if applicable)
a - interest rates
b - real level of output
c - unemployment rate
d - government's budget deficit
e - price level
What is "c - unemployment rate"
Graph must have labels for AD, SRAS, arrow showing change, PL, Real GDP, Y1, Y2, PL1, PL2
When an economy is operating above full employment, what is an appropriate government response to help stabilize the economy? Respond with:
1 - Taxes (increase or decrease?)
2 - Spending (increase or decrease?)
3 - Aggregate Demand (leftward shift or rightward shift?)
What is "taxes increase" , "spending decreases," and "leftward shift"?
Suppose a nation opened its borders to the free flow of workers from other nations. How would this event likely affect the long-run aggregate supply curve and the production possibilities curve of the nation?
Answer what happens to LRAS: ___________
Answer what happens to PPC: __________
What is "LRAS and PPC shift right"?
1. In 2020, Wendy earned $10,000 at her part time job as a nanny, of which she spent $9,000. If her income increased in 2021 to $11,000, and her propensity to consume is 0.6, how much money did her consumption increase by.....?
2 - Assume the government spends $110 Billion on new schools. What does this spending actually amount to for real GDP? Use the multiplier formula to solve.
What is "$600" and "$275B increase"? Using the MPC formula (change in consumption/change in income = MPC), you can rewrite to solve by multiplying the difference in income by the MPC 0.6.
Assuming X and Y are substitutes, if the cost of producing X decreases and the price of Y increases, what will occur to equilibrium price and quantity of X? Answer each with "increase, decrease, or indeterminate". Hint: Draw a visual
What is "Equilbrium qty will decrease; price is indeterminate"?
Accurately describe the state of the macro-economy if it is operating at the intersection of the AD(1) and SRAS(2) curves:
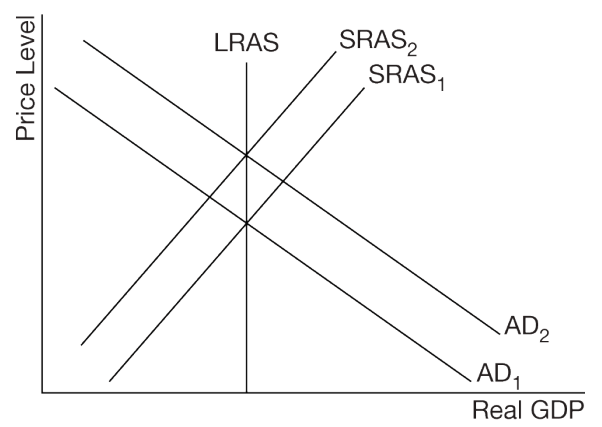
Terms you need to use in the statement to describe it: short run equilibrium, long run equilibrium, recession, inflation, full employment
What is "in short run equilibrium, but not long term, in a recession, not inflation, operatng below full employment" ?
Complete all 4 parts - BONUS~~~600 pts total
1 - An economy of Newland is in short-run equlibrium. Create a graph with Y1 and PL1 labeled.
2 - If the household income increases in Newland, what change will occur? Graph the change on your graph and label all parts
3 - What will be the effect of the change in #2 on unemployment?
4 - Will the change in real output because of income be greater or less in the presence of automatic stabilizers? Why?
1 and 2: 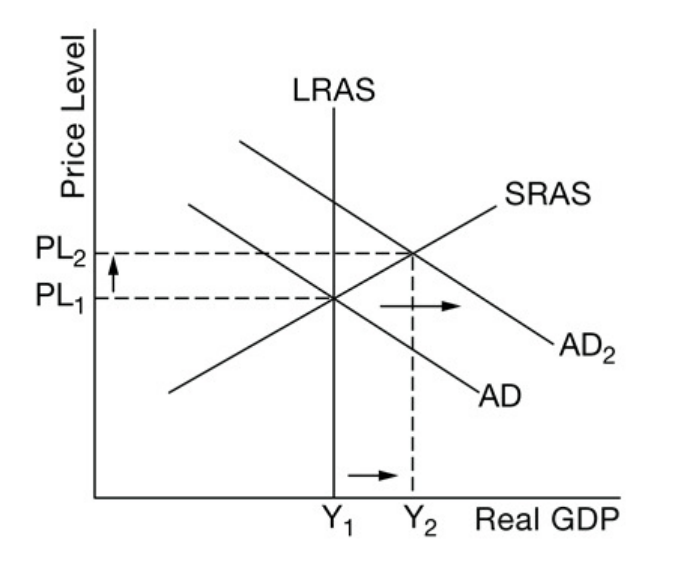 3 - decrease in U%
3 - decrease in U%
4 - Less because when there is high inflation, stabilizers reduce money flow and real GDP through higher taxes and lower qualifications for benefits.
Assume an economy is at full employment. If, after a negative aggregate demand shock, the government does not intervene, what is likely to occur in the long run? Mention the following:
1 - Wages, Inflation rate, Unemployment, and AD and/or SRAS
2 - AND - Draw the graph with complete changes. (+100 pts)
What is "wages decrease, inflation rate decreases, unemployment is lower, SRAS increases (until full employment is restored)"?
Graph must show: lables, SRAS shifts right, PL2 is lower, Y is higher
Country A has a real GDP of $750Billion, and a full employment GDP of $900Billion. Marginal propensity to consume is 0.8.
1 - what economic state is this country in?
2 - Calculate the minimum change and direction (increase or decrease) in spending needed to close the economic gap. (dollar value)
3 - Calculate the minimum change in taxes and direction (increase or decrease) needed to close the economic gap instead of spending. (dollar value)
What is "inflation," "$30b increase in spending" and "$37.5 Billion less taxes"?
gap = 900-750 = $150B
Output gap/multiplier
MPS = 0.2
1/0.2 = +5 .....
$150B/5 = increase by $30b more in spending minimum
0.8/0.2 = -4
$150B/-4 = decrase by $37.5 billion in taxes
Country A and Country B each produce Cocoa (C) and Bananas (B). Country A can produce 100 tons of C or 100 tons of B. Country B can produce 100 tons of C or 25 tons of B. If each country specializes according to their comparative advantage, what would be a mutually benefitial term of trade for 1 ton of Bananas for both countries?
Ex: "Trading 1 ton of Bananas for 25 tons of Cocoa"
What is "Trading 1 ton of Bananas for 1><4 tons of Cocoa"?
Country A's cost per banana = 100C/100B = 1C
Country B's cost per banana = 100C/25B = 4C
Hence, Country A will specialize (has the comparative advantage) in producing bananas, and will be willing to trade with country B to gain more than 1 C back. Country B will be willing to trade for bananas in cocoa tons under 4--their cost to produce alone.