A random change in the genetic code of an organism
What is a Mutation?
The process through which organisms best adapted to their environment survive and reproduce, passing on the favorable trait to their offspring
What is Natural Selection?
The law that states that mass cannot be created, nor can it be destroyed
What is the "Law of Conservation of Matter"?
The maximum number of individuals that the environment can sustain for the long term
What is Carrying Capacity?
Animals determined by Dr. Tony Sinclair to be a keystone species in the Serengeti
What are Wildebeest?

The variable that is measured or tested in an experiment to compare results
What is the Dependent Variable?
An inherited trait that gives an organism an advantage in it's environment
What is an Adaptation?
An environmental factor that influences which traits within a population are more advantageous for survival and reproduction
What is Selective Pressure?
An organism that produces its own food/energy
What is an Autotroph/Producer?
In the graph below, Letter C corresponds to this term
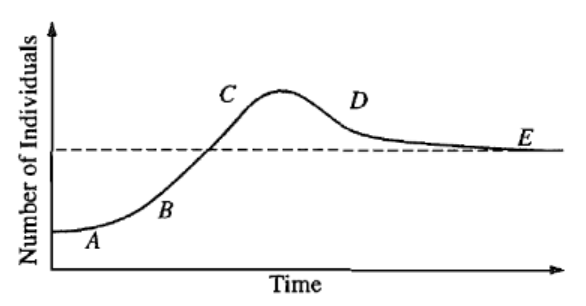
What is population "overshoot"?
A measurement of the variety of species in an ecosystem and their relative population sizes
What is Biodiversity?
In an experiment, a test or baseline that we compare the results to
What is the Control?
Reproduction where there is only one parent and the offspring are typically identical to the parent
What is Asexual Reproduction?
Genetic mutations are the main source of this (from the acronym V.I.S.T.A.)
What is Variation?
The amount of energy available to be stored by consumers in the next highest trophic level
What is 10%?
In the Serengeti, we learned that the wildebeest were kept below their carrying capacity due to this.
What is Rhinderpest?
A species that has a very large effect on its environment both directly and indirectly
What is a Keystone Species?
The location in a cell where you would find DNA
What is the nucleus?
Organisms, such as bacteria, that reproduce by asexual reproduction tend to increase their numbers very quickly. We call this rate of growth __________
What is Exponential?
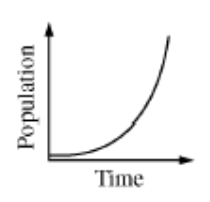
The change in a species over time
What is Evolution?
An organism that obtains energy by feeding on other organisms
What is a Consumer or Heterotroph?
A rapid decline in the population or community of organisms as a result of exceeding carrying capacity
What is "die off"?
Shifts in an ecosystem that occur when a change in the numbers of one species affects multiple trophic levels
What is a Trophic Cascade?
When graphing the results of an experiment, this variable is plotted on the x-axis
What is the Independent Variable?
The first antibiotic that bacteria developed a resistance to
What is penicillin?
In the example of the rock-pocket mice, natural selection favored this trait or variation in mice living on the lava beds
What is dark colored fur?

In the trophic diagram, buffaloes are considered this:
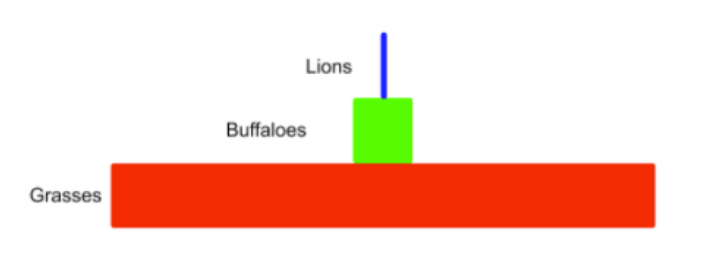
What are Primary Consumers?
When a population of organisms is at its carrying capacity, these two things equal each other
What are birth rates and death rates?
In one ecosystem we learned about, otters had a big impact on kelp forests by eating this organism and keeping that population low.
What are Sea Urchins?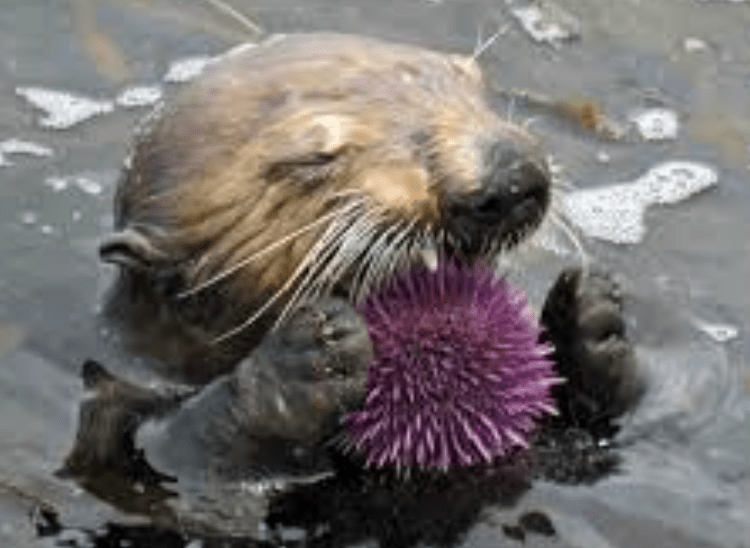
The atom or element that is found in every biological molecule
What is Carbon?