It is a vector quantity and the object's overall change in position
What is displacement
What is initial velocity
What is g? (Hint: Use the appropriate units.)
The acceleration due to gravity. On Earth it is 10 m/s2
Mechanical energy includes _______ and/or _________ energy.
Kinetic and Potential
Which has the greatest mechanical energy (ME)? Assume no air resistance.
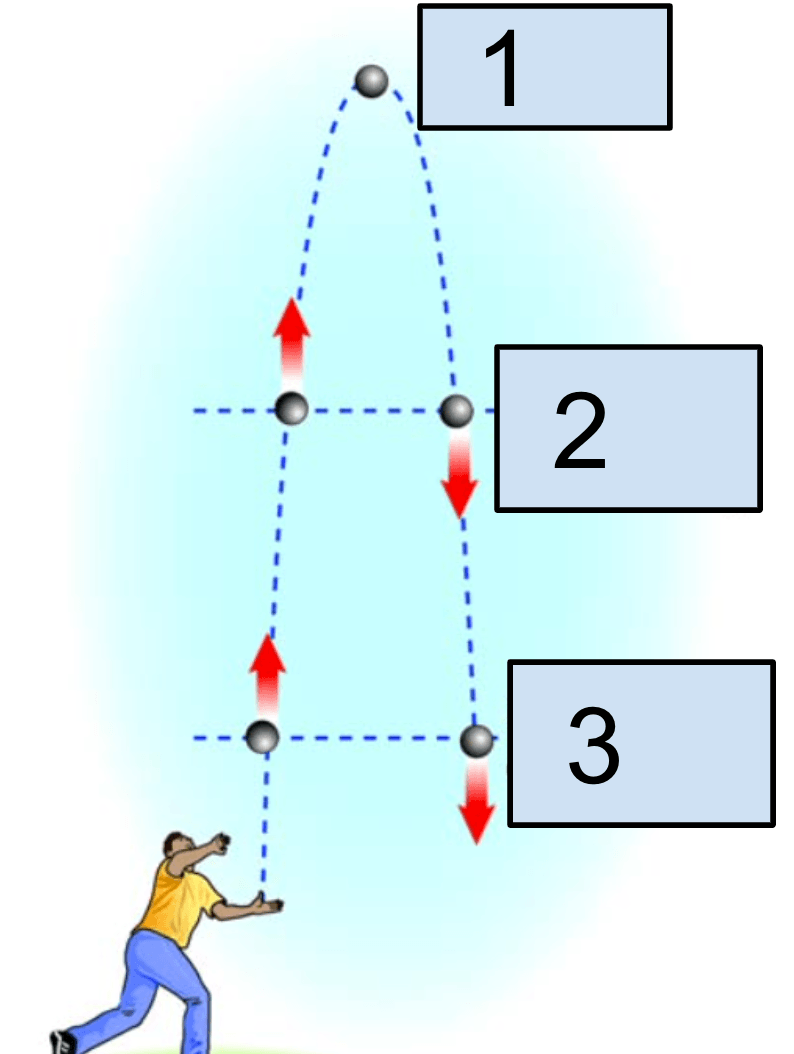
1, 2 and 3 are the same, since ME doesn't change.
The rate at which an object changes its velocity
What is acceleration
If something is thrown upward at 35 m/s it will take approximately this long to reach its max height?
Newton's second law can be summarized using this equation.
F = ma
If the total Mechanical Energy of a system is 10,000 Joules. Half way down the potential energy will be ______?
5000 J
A student is holding a pumpkin at a height of 2 meters. The pumpkin has 50 joules of potential energy and 0 joules of kinetic energy. The pumpkin is released from that height. How much potential and kinetic energy does the pumpkin have right before it hits the ground?
KE = 50 J
PE = 0 J
It is the energy that is possessed by an object due to its motion or due to its position
What is mechanical energy
True or False: The slope of the line of a displacement vs. time graph will be constant when an object is accelerating.
What is false
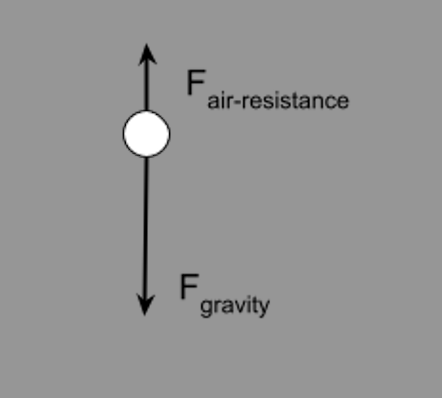
Draw a free body diagram for a baseball in free fall with air resistance.
Which has the greater gravitational potential energy?
A) 10 kg mass that is 20 meters high
or
B) 5 kg mass that is 40 meters high
same
List at least two examples of what is not perfectly conserved in a system.
Answers may vary.
Force, displacement, velocity, acceleration
What are vectors
When an object has negative acceleration with negative velocity is it speeding up or slowing down?
What is speeding up.
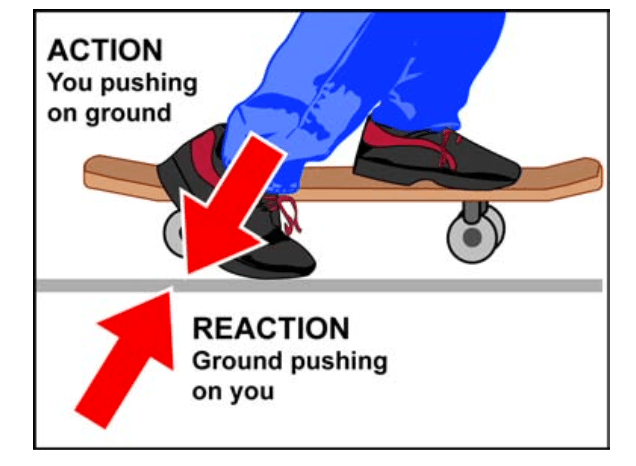
Give an example of Newton's 3rd law.
If you double the velocity of a car how much will the KE increase or decrease by?
4 times
How high up will a ball reach if it is thrown with 12,000 J of energy? (m = 0.145 kg)
h = 8275.9 m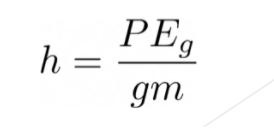
Time, speed, and mass are good examples of this
What are scalars
Describe the motion of this car
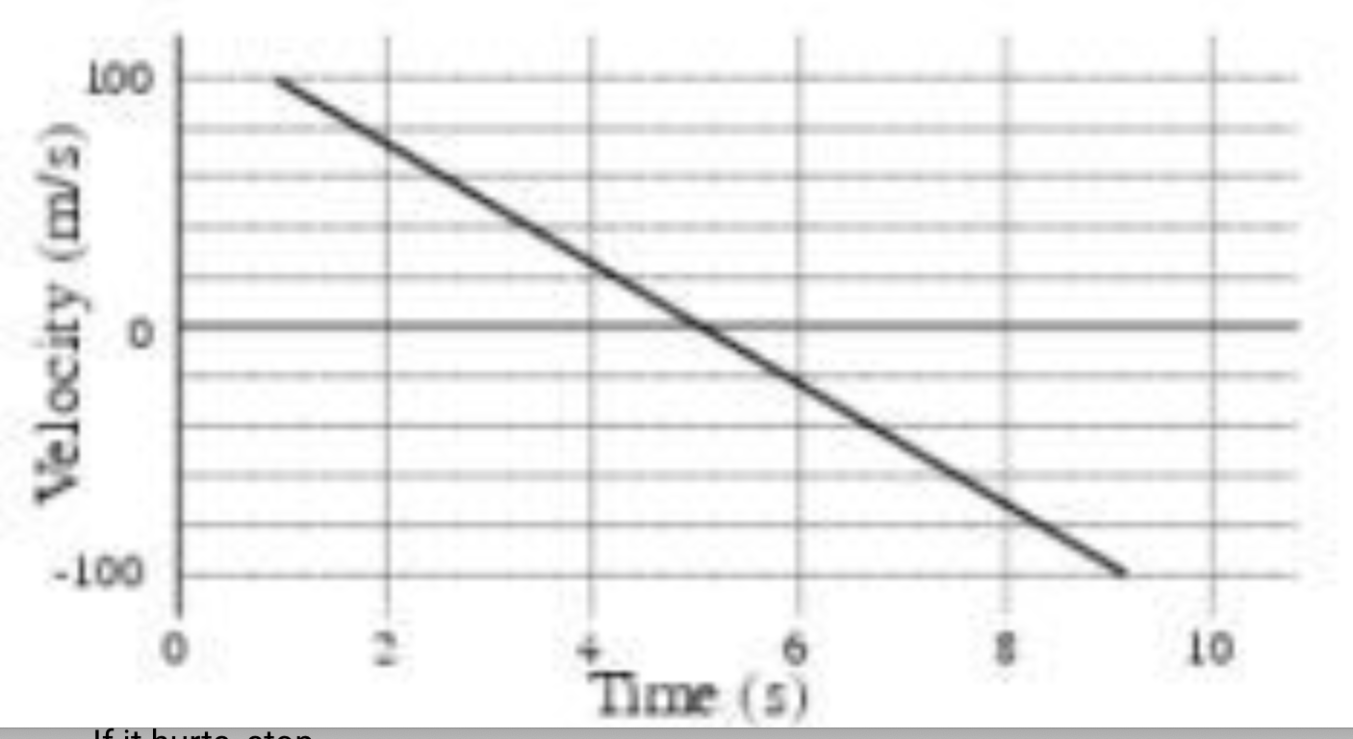
Moving in the positive direction but slowing down until the velocity reaches zero. Then it turns around and speeds up with constant acceleration in the negative direction.
An acrobat is holding onto a rope, and hangs straight down. Draw a free body diagram of this situation.
There should be no net force Fnet=Ftension-Fg=0 since the acrobat is not accelerating. The arrows for force should cancel.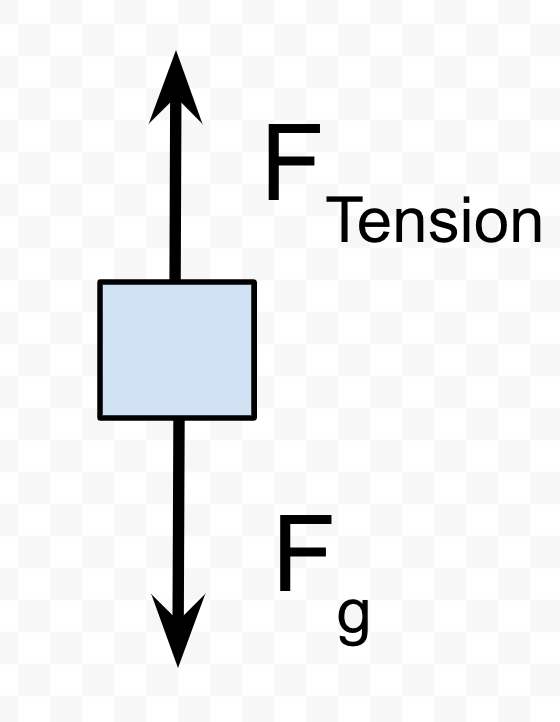
A baseball leaves pitching mound with a mass of .145 kilograms and a velocity of 50 m/s. What is its kinetic energy at the plate if it has lost 10% of its original velocity.
146.8 J
6.3 m/s