These macromolecules are hydrophobic and include fats, oils, and steroids.
What are lipids
This type of bond forms between the partially positive hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the partially negative oxygen atom of another.
What is a hydrogen bond
What organelle is identified as D?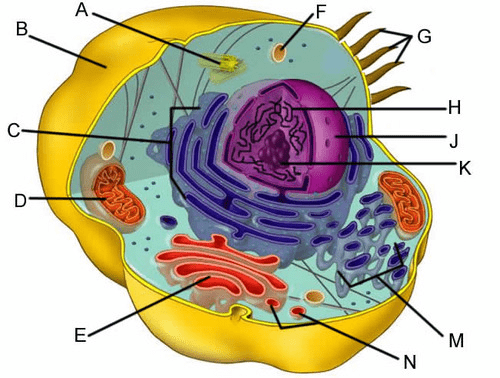
What is the Mitochondria
This is the term for the specific region on an enzyme where a substrate binds.
What is the active site
DNA is composed of two strands that form a twisted ladder shape called a double helix. The sides of this "ladder" are made of alternating molecules of sugar and this molecule.
What is a phosphate group
This macromolecule is responsible for storing genetic information in cells and is composed of nucleotide monomers containing a phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
What is DNA
This property of water allows it to travel up the xylem of plants, defying gravity, due to cohesion and adhesion.
What is capillary action
What organelle is identified as E?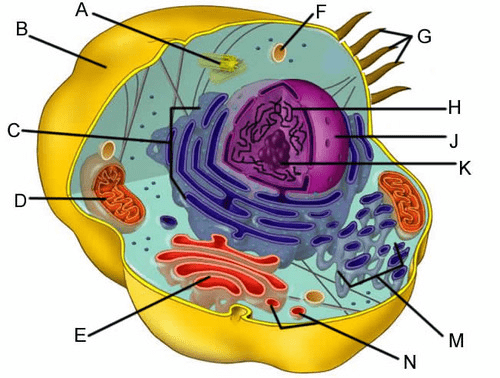
What is the Golgi Apparatus
This environmental factor can denature an enzyme by disrupting its structure, reducing its ability to function
What is temperature
During DNA replication, the two strands of the double helix are separated, and each serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. This ensures that each new DNA molecule contains one original strand and one newly synthesized strand, a process known as this.
What is semiconservative replication
This type of lipid forms the basis of cellular membranes, with a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails that self-assemble into a bilayer in aqueous environments.
What are phospholipids
Water is often called the "universal solvent" because its polarity allows it to dissolve substances that are this type of water-loving molecule.
What are polar or hydrophilic molecules
What is the function of organelle C?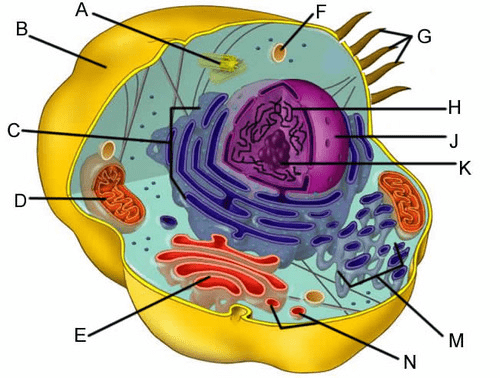
This type of molecule binds to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, causing a change in enzyme shape and reducing its activity
What is a noncompetitive inhibitor
DNA replication occurs in this direction on the new strand being synthesized.
What is 5’ to 3’
This specific type of bond forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another during dehydration synthesis.
What is a peptide bond
This property of water allows aquatic life to survive in winter because ice floats, insulating the water below.
What is water has lower density as a solid than as a liquid
What is the importance of the cellular structure B?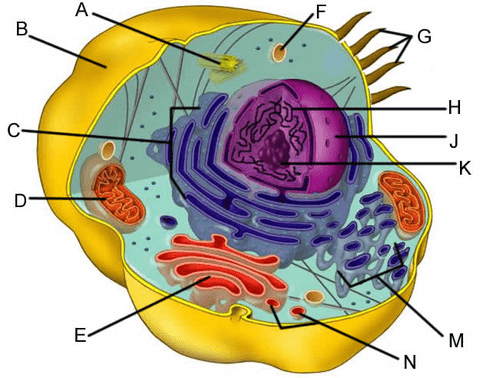
Maintain homeostasis
This model explains how enzymes and substrates fit together precisely and perfectly.
What is the lock-and-key model
These short DNA fragments are synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during replication
What are Okazaki fragments
This level of protein structure is stabilized by R-group interactions such as hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and disulfide bridges, and determines the overall 3D shape of the protein.
What is tertiary structure
This term describes the tendency of water molecules to resist an external force at its surface, creating an effect strong enough to support small objects like insects.
What is surface tension
How does the cellular structure identified as A help cell divide?
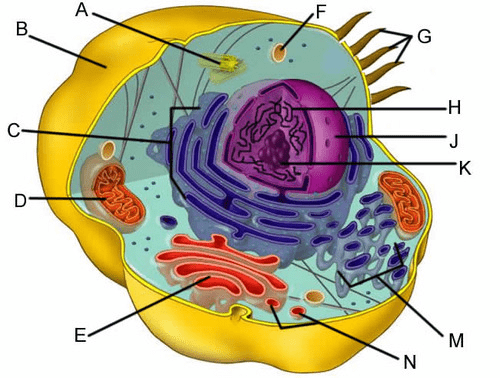
Centrioles create spindle fibers that pull chromosome pairs apart in Anaphase
This term refers to the minimum amount of energy required for a chemical reaction to proceed, which enzymes lower to speed up reactions.
What is activation energy
What part of Mitosis (A.K.A. cell division) does DNA replication occur? Double points for the specific phase within the part.
Interphase - S Phase