These cells, shown above, are in the Lateral Geniculate Nucleus.
What are Cone Opponent Cells?
Painters use this contrast technique to give mountain ranges in the distance a sense of distance.
What is the Atmospheric perspective?
or
What is Aerial perspective?
*Study: Static Monocular Depth Cues
In a simple feature search (in contrast to a conjunction search), reaction time remains constant (RT 0) regardless of the number of distracters since the target "pops out" because of this characteristic.
What is salience?
This is a powerful illusion of motion in the visual image caused by prior exposure to motion in the opposite direction
What is motion aftereffect?
This visual condition, also known as double vision, occurs when the brain receives mismatched images from the two eyes and fails to combine them into a single image.
What is diplopia?
Bilateral V4 damage in Ventral Pathway results in this.
What is Cortical achromatopsia?
These are both oculomotor depth cues.
What are accommodation and convergence?
This type of search takes people more and more reaction time as the number of features increase.
What is conjunction search?
This visual challenge occurs when only part of a moving object is visible, making it difficult to perceive its true motion.
What is the aperture problem?
Severe bilateral damage to this area can result in simultanagnosia.
What is the Posterior Parietal Lobe area?
*Simultanagnosia: Inability to perceive multiple objects at once, disrupting scene comprehension. One of 3 main symptoms of Balint's Syndrome.
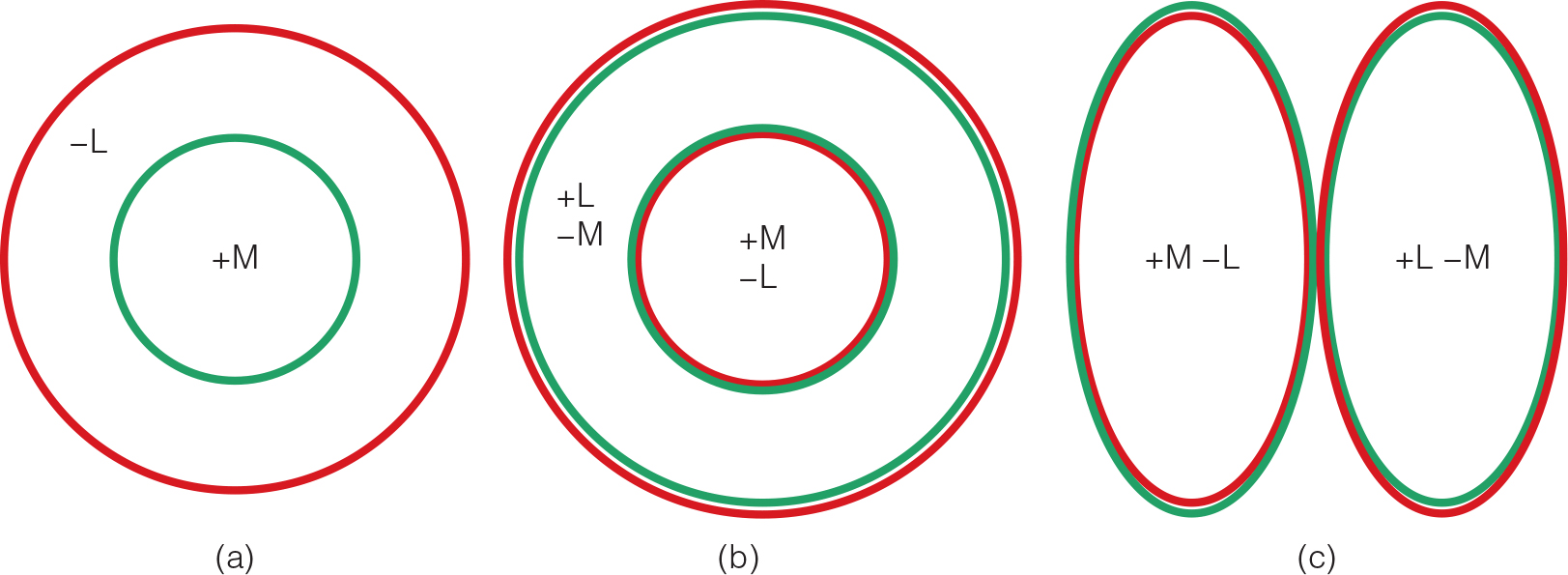
Any pair of stimuli perceived as matching in color, but having different (nonmatching) spectral power distributions, such as a red-green light mix that looks yellow.
What are metamers?
While walking past a fence, nearby objects like fence posts seem to move quickly across your field of vision, while distant buildings appear to move much slower. This phenomenon helps provide depth information.
What is motion parallax?
*Study: Dynamic monocular depth cues
This type of attention impairs performance when trying to focus on multiple tasks at once, regardless of how much practice you have.
What is Divided Attention?
This aspect of optical flow remains stationary while everything else moves outward from that point as a person moves through space.
What is Focus of Expansion?
This apparent motion illusion turns a "hole' into an object.
What is Phi Phenomenon?
This principle explains why a single photoreceptor cannot differentiate between changes in intensity and changes in wavelength, leading to color vision deficiency if only one type of cone is available.
What is the Principle of Univariance?
In a random dot stereogram, this process allows you to perceive depth by matching points once between the two retinal images.
What is correspondence matching?
or What is correspondence point matching?

You are focused on organizing your papers on your desk into seperate piles, and you fail to notice a mouse on a nearly empty plate that is clearly visible. This is an example of
What is inattentional blindness?
In a study on motion perception, monkeys with lesions to this brain area required ten times as many dots in a correlated dot motion display to correctly identify motion direction.
What is the MT (middle temporal) area?
This is the most salient of all features.
What is motion?
This term refers to how much energy a light source emits at each wavelength across the visible spectrum—it's what determines the color quality and appearance of the light.
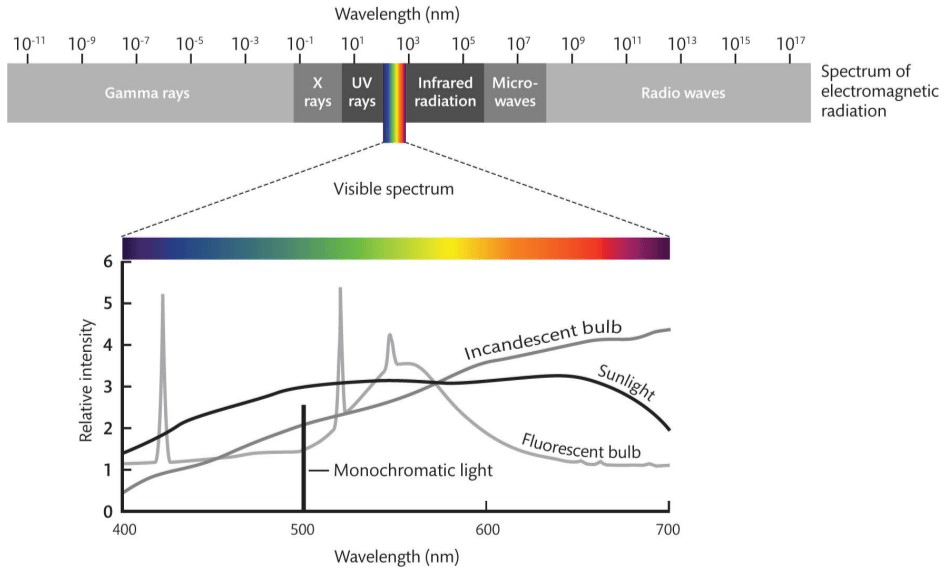
What is Spectral Power Distribution?
or
What is the Distribution of Spectral Density?
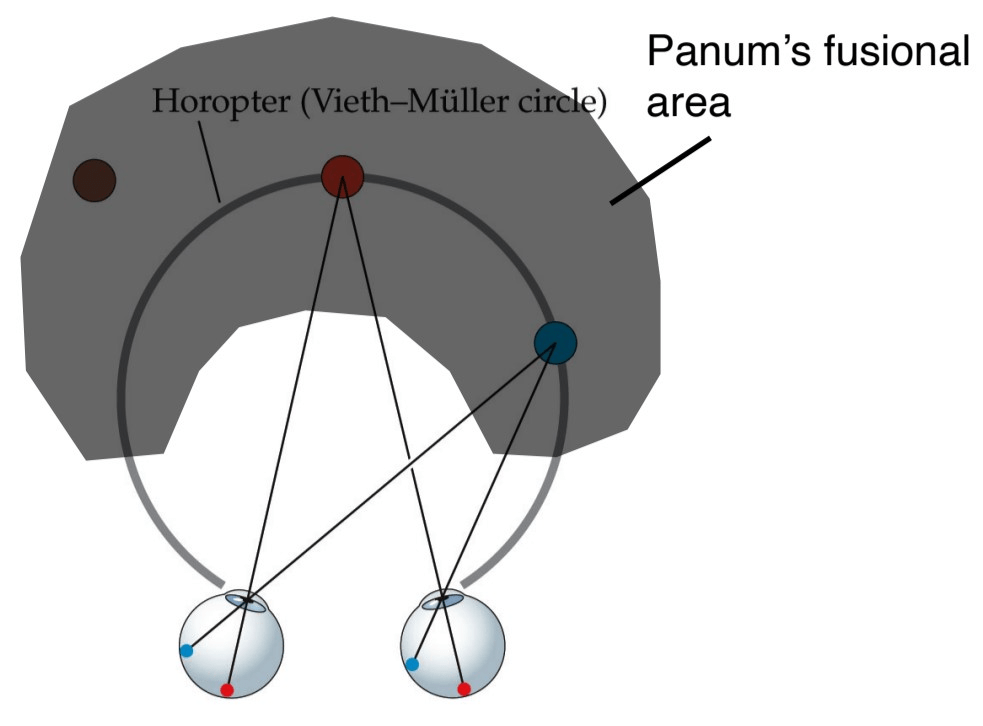
The region of space, in front of and behind the horopter, within which binocular single vision is possible.
What is the Panum's Fusional Area?
Initiating and guiding reflexive eye movements are controlled mainly by this brain structure.
What is the Superior Colliculus?
Severe bilateral damage to Media Temporal (MT) area results in this.
What is Akinetopsia?
Or
What is an inability to perceive motion?
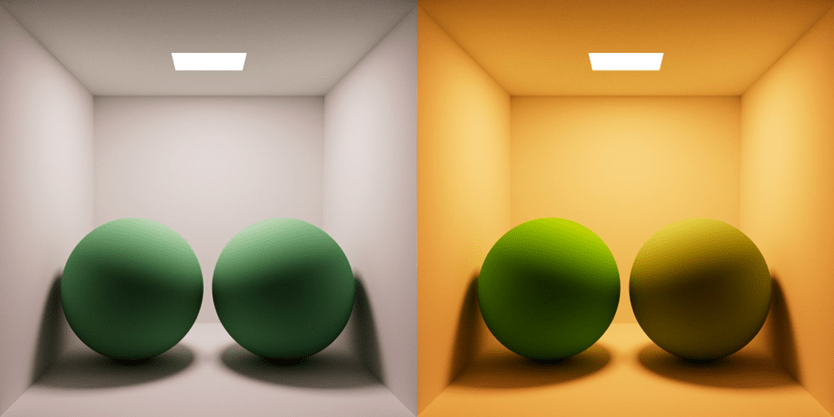
The M-Path relies on this since it cannot see color very well.
What is contrast?