Brilliant
This enzyme controls iron absorption, storage, and distribution by inhibiting ferroportin.
Hepcidin
Upregulated by increased iron stores and inflammation (notably via the IL-6–JAK2–STAT3 pathway), and downregulated by erythropoietic drive, hypoxia, and pregnancy.
Acute intermittent porphyria is the most common acute hepatic porphyria with a symptomatic prevalence of approximately 1 in 100,000. What enzyme is affected?
Porphobilinogen deaminase/hydroxymethylbilane synthase (PBGD / HMBS)
Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer (HDGC) is an inherited syndrome with a high risk of diffuse stomach cancer and lobular breast cancer, caused by mutations in the _____ or CTNNA1 genes.
CDH1
Prophylactic gastrectomy ages 20-30 as screening EGD insufficientWhich tool predicts risk of venous thromboembolism in multiple myeloma?
IMPEDE-VTE
Immunomodulatory agent;
Body Mass Index ≥25 kg/m2 ;
Pelvic, hip or femur fracture;
Erythropoietin stimulating agent; Dexamethasone/Doxorubicin;
Asian Ethnicity/Race;
VTE history;
Tunneled line/central venous catheter;
Existing thromboprophylaxis
This trial demonstrated T-Dxd can be used in metastatic gastric or GEJ if IHC 3+ or (+)FISH and has received prior Herceptin.
DESTINY-Gastric01
40 yo F w iron deficiency anemia s/t menorrhagia received IV iron last week. Her fatigue has significantly worsened with diffuse bone pain. Phosphate = 1. Which IV formulation did she receive?
Ferric carboxymaltose (Injectafer) → hypophosphatemia via upregulation of FGF23 → increased urinary excretion and gut absorption. Presents w muscle weakness, bone pain, fatigue.
What treatment is used for an exacerbation of acute hepatic porphyrias, such as acute intermittent porphyria, by downregulating ALAS1 activity?
Hemin (derivative of heme) via negative feedback loop
Glucose also suppresses ALAS1 expression, and this explains the higher incidence of exacerbations while fasting and remissions observed in response to glucose infusions.
A 20 yo M w NF2 p/w worsening balance, tinnitus, and hearing loss. What type of tumor does he most likely he have?
Vestibular schwannoma / acoustic neuroma
NF2 can result in other tumors, such as meningiomas and spinal tumors
75 yo M p/w unexplained anemia. CMP, nutritional studies, epo normal. Diff and platelets normal. What is the most likely diagnosis?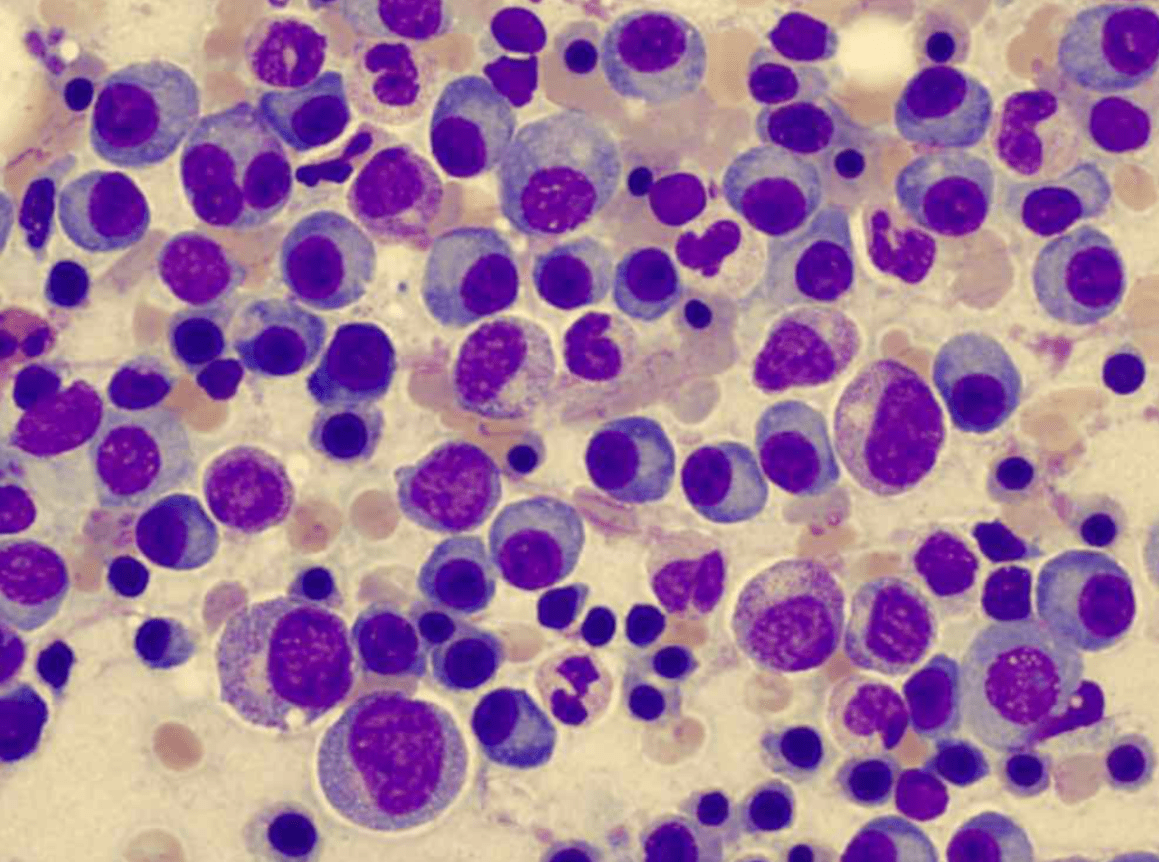
Immature and mature-appearing plasma cells w eccentric nuclei and perinuclear halo of cytoplasm.
60 yo shipyard worker recently diagnosed w metastatic biphasic mesothelioma. What treatment do you offer?
Ipi/nivo (Checkmate 743)
ipilimumab (1 mg/kg every 6 weeks) plus
nivolumab (3 mg/kg every 2 weeks)
(vs carbo/Alimta)
SOC 1st line tx for unresectable MPM, regardless of histology**
22 yo M presents to ED with progressive fatigue, depression, arthralgias, and skin darkening. He drinks beer daily with BMI of 32. CMP and CBC wnl. He's referred to you for outpatient f/up. What do you suspect he may have?
Hemochromatosis
Ferritin >200 in men or >150 in women (+) Tsat >45%
MRI to quantify liver and/or cardiac iron deposition
Always check C282Y and H63D to r/o hereditary hemochromatosis
C282Y/C282Y (homozygous) or
C282Y/H63D (compound heterozygous)
Name this drug:
Subcutaneous double-stranded, small interfering RNA (siRNA) therapeutic specifically targeting ALAS1 mRNA, reducing ALAS1 mRNA levels and leading to reductions in urinary ALA and PBGr, thereby reducing attack frequency and improving quality of life in patients with recurrent AHP.
GIVLAARI® (givosiran)
2.5 mg/kg subQ once monthly
Nausea and increased LFTs
34 yo M reports his sister was recently found to have BRCA2 mutation after breast cancer diagnosis. He completes genetic testing and also has the mutation. When should he begin screening for prostate cancer?
Age 40 (also for BRCA1)
Self and clinical breast exams starting age 35
Pancreatic ca screening age 50
2nd MCC of enzyme-defiencient hemolytic anemia after G6PD resulting in splenomegaly, gallstones, iron overload, jaundice, and leg ulcers. Most do not require treatment.
Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency
Mitapivat (Pyrukynd) for hemolytic anemia. Mutated PK enzymes lead to inadequate ATP production in red blood cells, resulting in a buildup of the upstream intermediate 2,3-DPG, which reduces the hemoglobin's ability to release oxygen. Mitapivat allosterically binds to the pyruvate kinase enzyme (PKR), stabilizing its active form, increasing ATP levels, improving red blood cell survival and function, and reducing the signs of anemia and hemolysis.
50 yo patient w metastatic HR+ breast cancer currently on everolimus + exemestane develops mucositis limiting oral intake. What do you prescribe?
Dexamethasone mouthwash (alcohol-free oral solution 10 mL swish and spit for 2m QID) has been shown to significantly reduce the incidence and severity of stomatitis and is considered standard of care in patients receiving everolimus (SWISH trial).
Topical steroid paste like triamcinolone cream
May see sodium bicarb as an option. This is more supportive and should not replace steroid.
Unlike chemo-induced mucositis, which stems from direct toxicity, everolimus-induced mucositis is thought to arise from local inflammation triggered by the drug's action on the mTOR pathway.
The 22 yo M w hemochromatosis didn't follow up. Now he's 26 p/w worsening DOE and found to have pulmonary edema c/f heart failure. His BG is 400 and liver enzymes are elevated. Which gene mutation does he likely carry?
HJV/HAMP
hemojuvelin and hepcidin
Juvenile hemochromatosis (usually <30 yo), autosomal recessive. Specific subtype of HH. Usually severe clinical presentation inc heart failure, diabetes, cirrhosis, and hypogonadism. Hepcidin is usually severely low. Marked increased intestinal absorption.
The timing of presentation helps to differentiate from hereditary hemochromatosis (HFE), which tends to manifest later in life.
The first step in heme synthesis is condensation of glycine and succinyl CoA to form d-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) in the mitochondria. Which enzyme catalyzes this reaction?
δ-Aminolevulinic acid synthase (ALAS)
A 29 yo M w h/o stage 1 RCC presents after recent diagnosis of uveal melanoma. He reports several family members w mesothelioma and RCC. What germline mutation are you concerned about?
BAP1 tumor predisposition syndrome
Not to be confused w Birt-Hogg-Dube or VHL
A 70 yo M w IgG kappa MM is progressing on RVd-Dara. He prefers to avoid IV/INJ with his next line of therapy. His cytogenetics are notable for t(11;14). What do you offer him?
Venetoclax and dexamethasone should be considered in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma harboring t(11;14) translocation.
The t(11;14) subgroup demonstrates BCL-2 dependency, making venetoclax, a BCL-2 inh, particularly effective in this setting, with response rates and progression-free survival superior to those seen in non-t(11;14) patients.
Venetoclax 800 mg orally daily, with dex 40 mg orally on days 1, 8, and 15 of a 21-day cycle (dose reduction for age ≥75 years), as supported by clinical trial protocols.
Perioperative _______ plus FLOT led to significantly better event-free survival outcomes than FLOT alone among participants with resectable gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma
Durvalumab (MATTERHORN)
PD-L1 CPS ≥1 or TAP ≥1%
durvalumab 1500 mg every 4 weeks plus FLOT for 4 cycles (2 cycles each of neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy), followed by durvalumab every 4 weeks for 10 cycles.
Which oral iron chelation requires weekly CBCs w the risk of agranulocytosis?
Deferiprone (Ferriprox)
Characteristic reddish-brown discoloration of urine as it forms a complex with iron, and this iron-deferiprone complex is excreted in the urine, resulting in a reddish or brown discoloration (chromaturia)
Name that drug:
An α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone analogue that is FDA-approved to increase pain-free light exposure and reduce phototoxic reactions erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP).
SCENESSE (afamelanotide)
SubQ implant by certified porphyria center
_________ syndrome is a rare, genetic, autosomal dominant disorder caused by mutations in the GATA2 gene, characterized by primary lymphedema (swelling, often in the legs and genitals), sensorineural hearing loss, and an increased risk of MDS and AML.
Emberger
It can also involve immune deficiencies, leading to recurrent infections, heart problems, cirrhosis. Physical exam findings may have hypotelorism, skin folds of inner corners of the eyes, long fingers, neck webbing, warts, leg infections.
This CXCR4 inhibitor can overcome stem cell mobilization failure with inadequate response to G-CSF w/wo chemo, resulting in a rapid, significant increase in peripheral blood CD34 count within 4-9 hours after single dose.
Mozobil (plerixafor)
The CXCR4 receptor on stem cells binds to a protein called stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha (SDF-1α), which helps anchor the stem cells in place.
70 yo M w metastatic NSCLC w MET exon 14 skipping mutation starts capmatinib. sCr was normal, now 2. What do you check next?
Cystatin C
MET inh therapy can cause asymp. rise in sCr which must be distinguished from AKI with more accurate, non-Cr-based methods. This could spare invasive testing or possible early discontinuation of TKIs.
The first cancer hospital established in the United States was the ___________, which opened in 1884. It is now known as Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
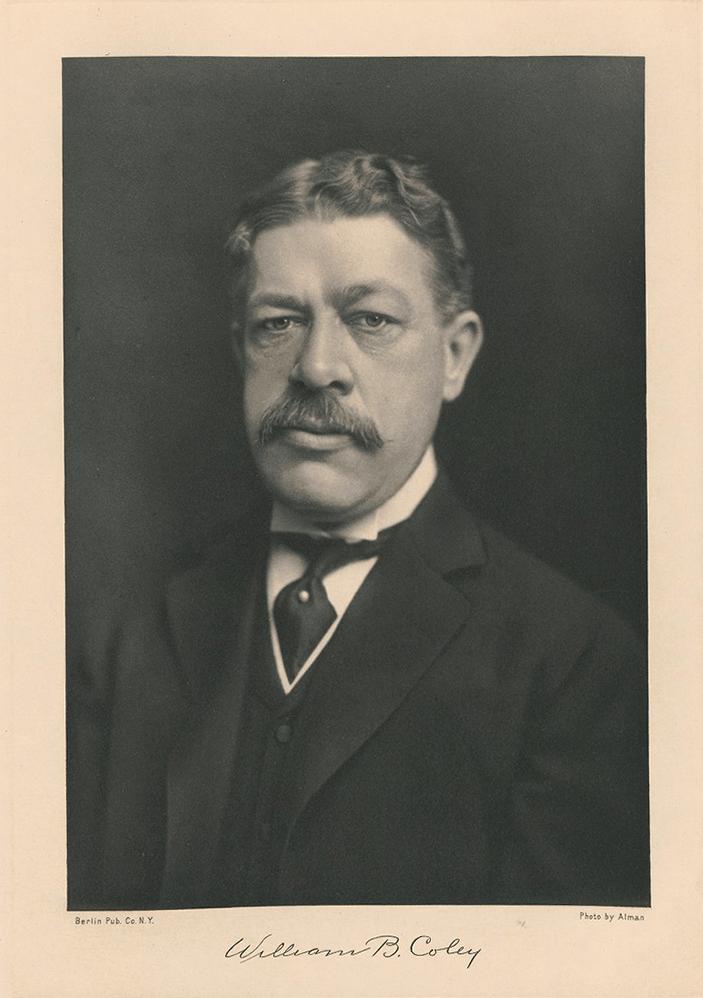

New York Cancer Hospital
William B. Coley was one of its most renowned physicians. Known as the "Godfather of Immunotherapy" for his pioneering work in cancer immunotherapy. Developed "Coley's toxins," a mixture of heat-killed bacteria, including Streptococcus pyogenes and Serratia marcescens, that were used in an attempt to stimulate the immune system to fight cancer. These were first used in 1891 to treat a patient with inoperable sarcoma. The patient had a spontaneous regression of their tumor after developing a fever and other symptoms of infection.