The distance between two consecutive crests or troughs in a wave.
What is Wavelength
This type of energy is at its maximum when a pendulum is at its highest point.
What is Potential Energy?
These waves require a medium to propagate.
What are mechanical waves?
If a wave's frequency is 5 Hz, its period is this many seconds.
What is 0.2 seconds?
The primary factor affecting a pendulum's period.
What is length?
This term describes how many wave cycles occur in one second.
What is frequency?
The wave property most closely associated with the loudness of sound.
What is amplitude?
In this type of wave, particles vibrate parallel to the direction of wave propagation.
What are longitudinal waves?
A wave with a frequency of 10 Hz and a wavelength of 2 m has this speed.
What is 20 m/s?
In a spring-mass system, this determines how quickly the system oscillates.
What is the spring constant and mass?
The time required for one complete wave cycle.
What is period?
When waves combine to increase their amplitude, this type of interference occurs.
What is constructive interference?
These waves can travel through a vacuum.
What are electromagnetic waves?
If a pendulum swings 30 times in 1 minute, its frequency in Hz is this.
What is 0.5 Hz?
For small angles, this type of motion describes a pendulum's swing.
What is simple harmonic motion?
This wave property is shown here.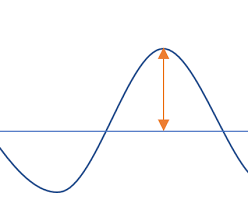
What is Amplitude?
As amplitude increases, this property of a wave also increases.
What is energy?
A wave where particles vibrate perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
A sound wave traveling at 340 m/s with a frequency of 440 Hz has this wavelength.
What is 0.773 m?
The presence of this bringing back something to equilibrium is the defining characteristic of Simple Harmonic Motion?
What is the restoring force?
This is how fast the motion of a particle travels through a given medium.
What is wave speed?
In simple harmonic motion, this energy remains constant (assuming no friction).
What is total energy (sum of kinetic and potential)?
A type of wave formed by the superposition of two waves traveling in opposite directions.
What are standing waves?
If a harmonic oscillator's mass is doubled, its period increases by this factor.
What is sqrt2
(or approximately 1.414)?
The formula for period of a pendulum.
What is T=2pisqrt(L/g) ?