Name three inotropic medications
Dobutamine, dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, milrinone
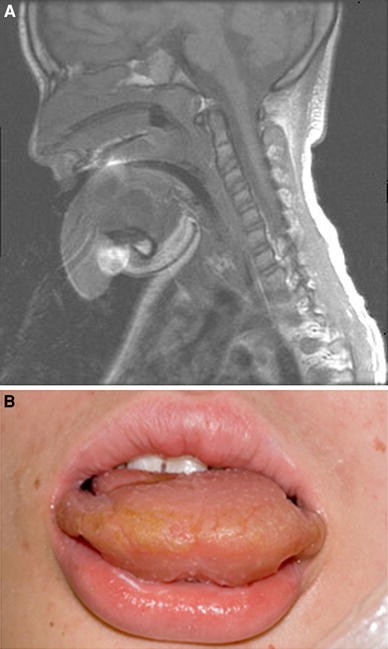
What type of shock should you be concerned about?
Anaphylactic
What is the most common cause of distributive shock?
Sepsis
This type of shock is a life threatening condition caused by irregular blood circulation in the body
Neurogenic Shock
What is this device?
LVAD
What medication can a respiratory therapist administer for stridor?
Racemic Epinephrine
Your patient is diaphoretic, cool and clammy, has a weak rapid pulse and complains they have decreased urine output. What type of shock is this?
Hypovolemic
Cardiogenic
What are potential causes of cardiogenic shock?
CHF
MI
Valvular diseases (Myocarditis, Endocarditis)
Which type of shock can be caused by severe diarrhea?
Hypovolemic Shock
Distributive
Name one crystalloid solution
Isotonic Saline or Ringer Lactate
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1159377189-fb99c16c7e774d63aad95bf6fa50ad3d.jpg)
What is being tested or observed with this image?
Which conditions can lead to an obstructive shock?
cardiac tamponade
pulmonary embolism
tension pneumothorax
Which type of shock is the most common death in ICUS in the US?
Septic Shock

What is this device and what does it measure?
Swan Ganz Catheter
CVP, PAP, PCWP, SVR and PVR
Norepinephrine is what type of medication?
Vasopressor
What does CABG stand for?
Coronary artery bypass grafting
Name three causes of anaphylactic shock
Food allergies
Medication allergies
Allergic reaction produced by basil and mast cells
Insect venom
Latex
Aerobic exercise
Idiopathic
A patient presents to the ED in distress. The patient is having trouble breathing, is hypotensive, and a physical exam reveals pruritis and urticaria. Based on the information above, which type of shock is the patient most likely to be experiencing?
Anaphylactic Shock
Circulation to the vital organs (kidneys, coronary arteries) may be compromised if the MAP falls to below _____ mm Hg
60
What is shock also referred to?
Hypoperfusion
Your patient has an elevated pulmonary capillary wedge pressure. Does this affect the right or left heart?
Left heart
Septic shock results in hypoalbuminemia. Why should RRTs be concerned with hypoalbuminemia?
Low levels results in alveolar flooding causing ARDS
This type of shock is characterized by very low cardiac output and increased systemic vascular resistance
Obstructive Shock
What is the primary problem in patients with septic shock?
Low systemic vascular resistance