Practice Problems
Practice Problems
Write the anticodon for 5' - UGA- '3
What amino acid does it code for?
3' ACU 5'
Does not code for an amino acid, just codon that signals stop
5' GGATAGCAG 3'
3' CCTATCGTC 5'
Above is double stranded DNA , top strand is the coding strand, using that limited information write the amino acid sequence, label amino and carboxyl ends with N and C
N- Gly - Ser- Arg -C
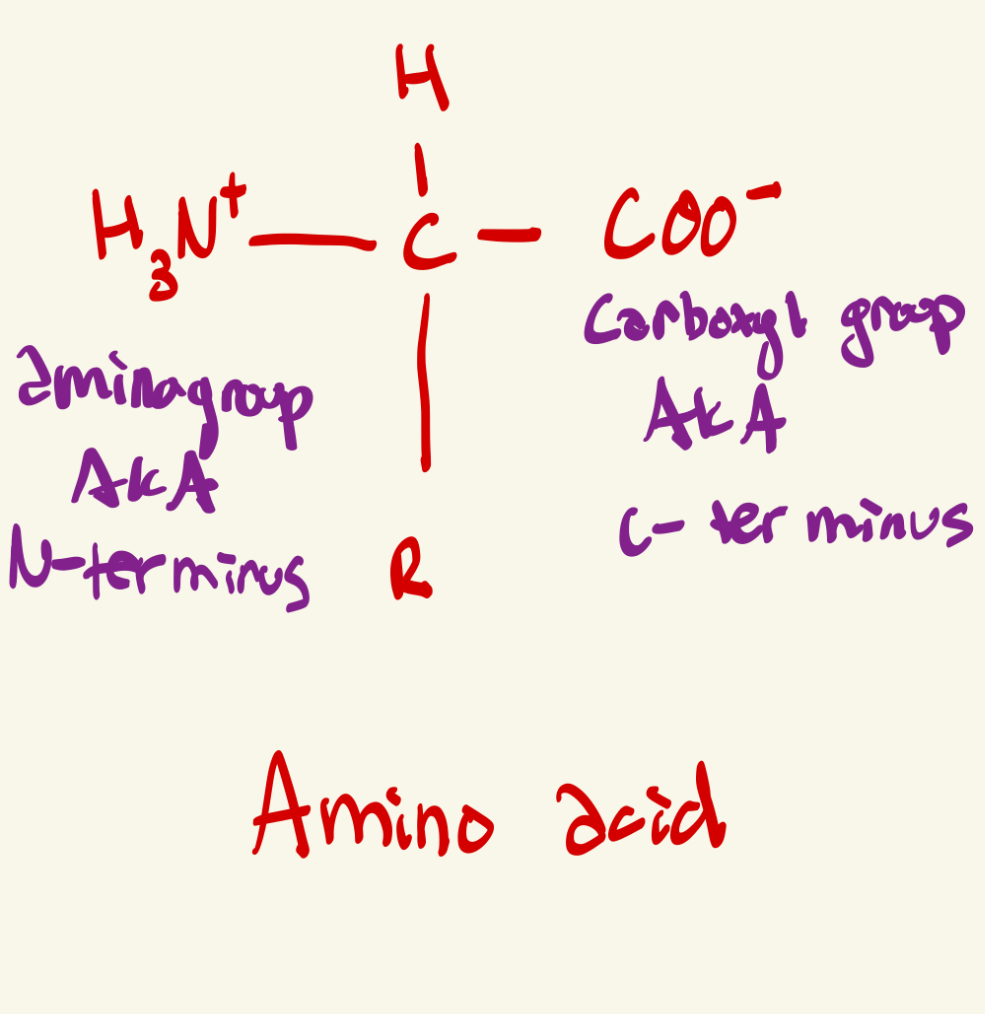
Draw the structure of an amino acid
1. Draw a central carbon
2. Put amino group (NH3+) on the left, and carboxylic acid group on right
3. Hydrogen on top, and the R group on bottom
For this glass, always put amino group on left side, and carboxylic group on right side because a polypeptide chain of amino acids is made going from the amino end to the carboxyl end.
** Extra Note: Amino group side means the N terminus of a polypeptide, and the C terminus is the carboxyl end of a polypeptide chain
Charged tRNA vs uncharged tRNA
Charged tRNA has the amino acid in it, the other one does not
Here is the template DNA strand, write out the polypeptide chain that would result, make sure to label the amino group and the carboxyl group on appropriate side
3' TACCTGTAA 5'
1. First, transcribe into RNA strand, this is the template so, write out complement
5' AUG GAC AUU 3'
2. Write the appropriate amino acid based off of what each codon codes for
NH3+ - Met-Asp-lle -COO-
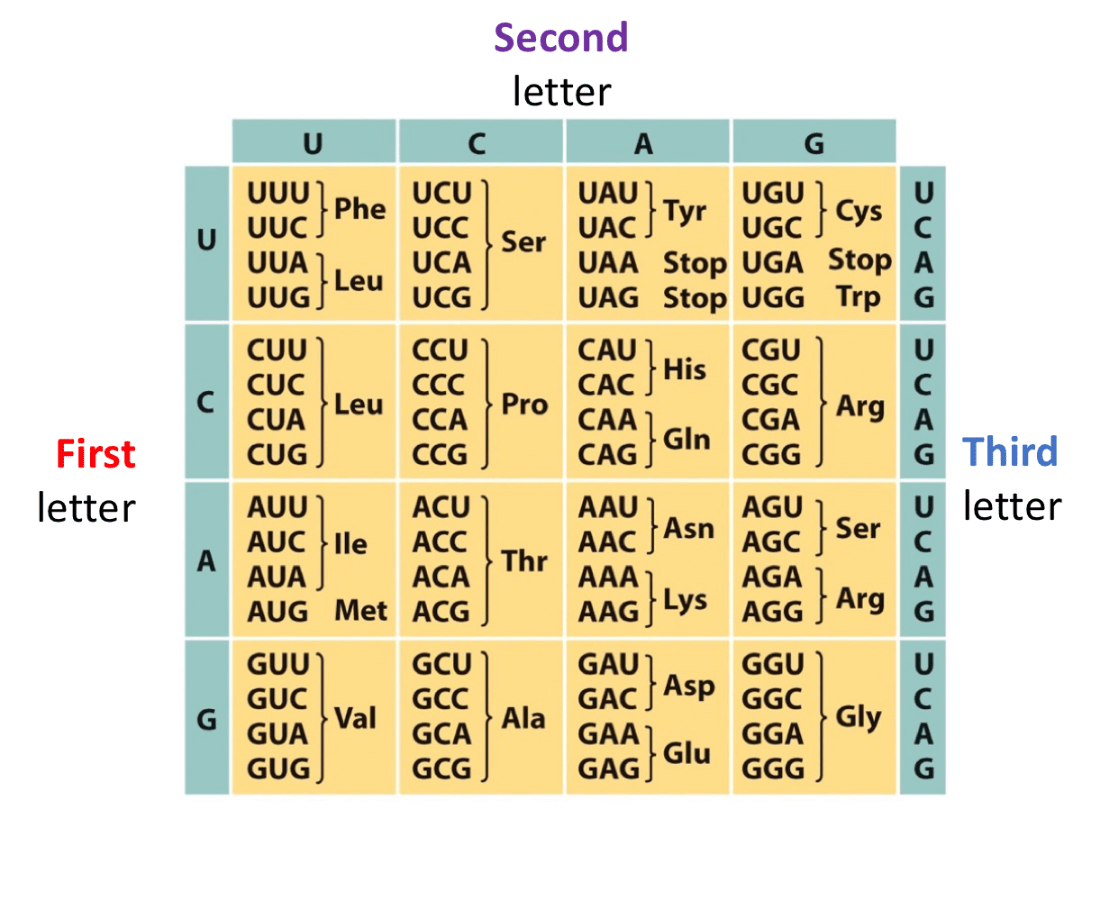
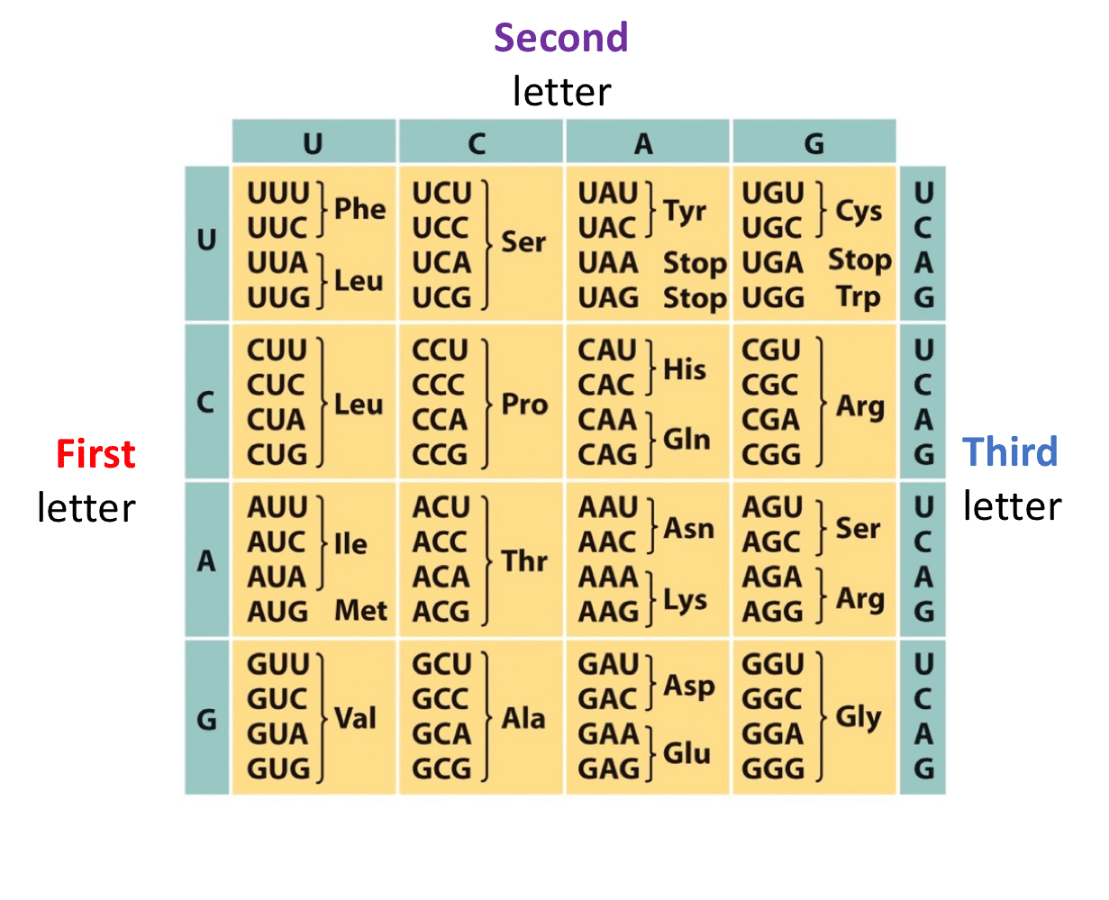
What are the tRNA anticodons for the amino acid, Proline? Make sure polarity is included
Proline has 3 codons that code for it
5' CCU '3 --->>> 3' GGA '5
5' CCC '3 --->>> 3' GGG '5
5' CCA '3 --->>> 3' GGU '5
5' CCG '3 --->>> 3' GGC '5
*** Anticodons run in opposite direction and are complementary.
Which portion of an amino acid remains the same, and which portion varies among each amino acid, and give that each of the 20 amino acids it's unique properties
the R group
How do you do initiate translation in prokaryotes vs eukaryotes?
We need to position the first tRNA (AUG the start codon) at the P-site of the ribosome
Prokaryotes: There is a shine delgarno sequence called 5' AGGAGGU '3 5-6 bases upstream of the first AUG, SO find the shne delgarno sequence and then after that find the first AUG codon (you will have mulitple AUG codons in the sequence but choose the first one after the shine- delgarno) Overall, this shine dalgarno sequence serves as a ribosomal binding site, where it binds to a complementary sequence somewhere on the ribosome, this aligment allows for the AUG codon to be in P-site
Eukaryotes: small ribosome subunit binds to 5'cap of mRNA, and then reads through it from that point till it hits its first AUG. Initiation codon is found within the Kozak sequence 5' CC(A/G)CCAUGG-3'
5' ATGCGTGTCGGA '3
3' TACCGACAGCCT '5
This double stranded DNA is transcribed left to right, in other words mRNA is created from left to right, what is the sequence of resulting polypeptide? Label ends with N and C
1. Template strand is bottom strand because the prompt says it is transcribed left to right, thus mRNA is made left to right , mRNA is made in 5' to 3' direction, 5' would be left and 3' would be right, so antiparallel to that would be the bottom strand
2. Transcribe to create mRNA
5' AUG CGU GUC GGA '3
3. Translate
N-Aug-Arg-Val-Gly -C
There is a codon 5' CGU '3 that is changed to 5' CGC 3' , what is the initial amino acid and final amino acid? What does this tell you about the genetic code? Why is the DNA code like that? (Solve first part of problem, then you will be able to answer the rest)
Arg to Arg
Multiple codons (3 letter codes) code for the same amino acid
This redundancy occurs to help reduce effects of mutations
This redundancy is also great as as cells need huge numbers of tRNA molecules
What are the differences in the primary, secondary, and tertiary, and quaternary protein structures?
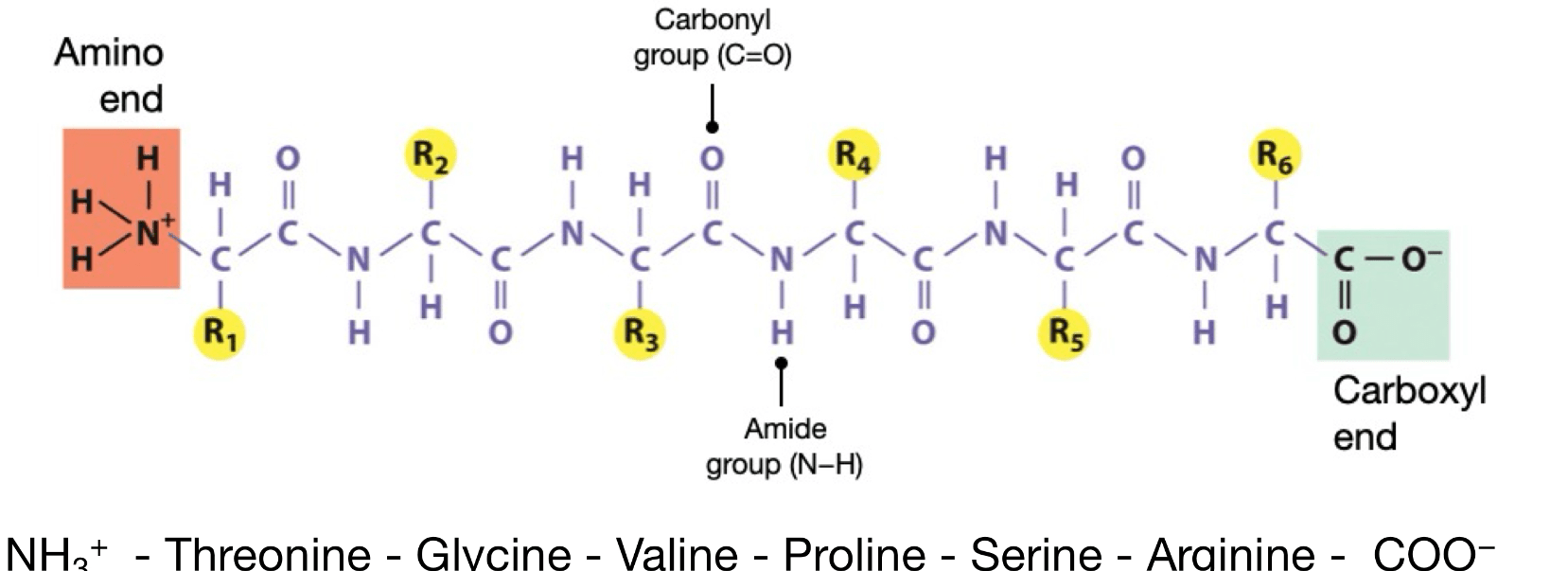
1. Primary structure is simply the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
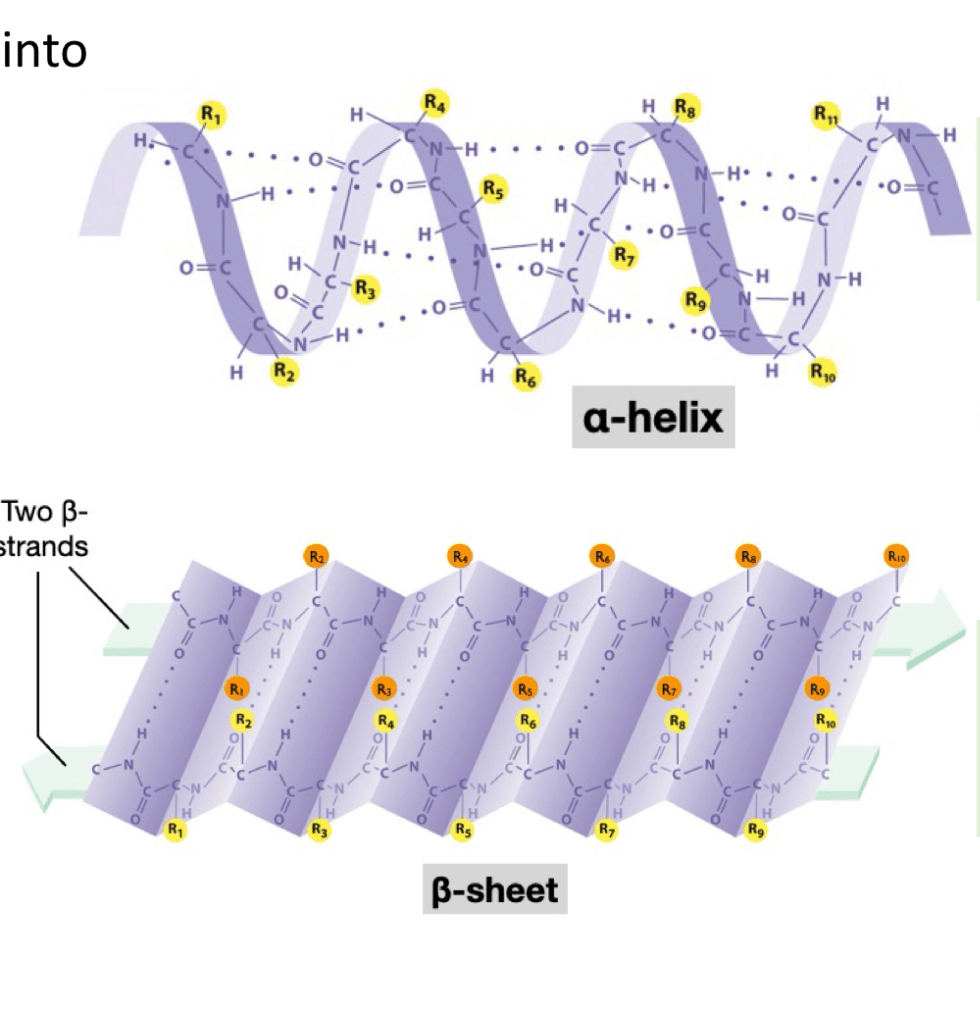
2. secondary structure comes into play when local folding occurs due to molecular interactions between amino acids, like hydrogen bonds/van der waals occuring. Folding results in alpha-helix shapes or Beta- sheet shapes. In alpha, looks like there is an H bond occurs between the H from the amino group to the oxygen from the carboxyl group of an amino acid that is 4 amino acids away. Causing it form loops. In beta, we see that beta strands align in parallel directions, causing h bonds to form
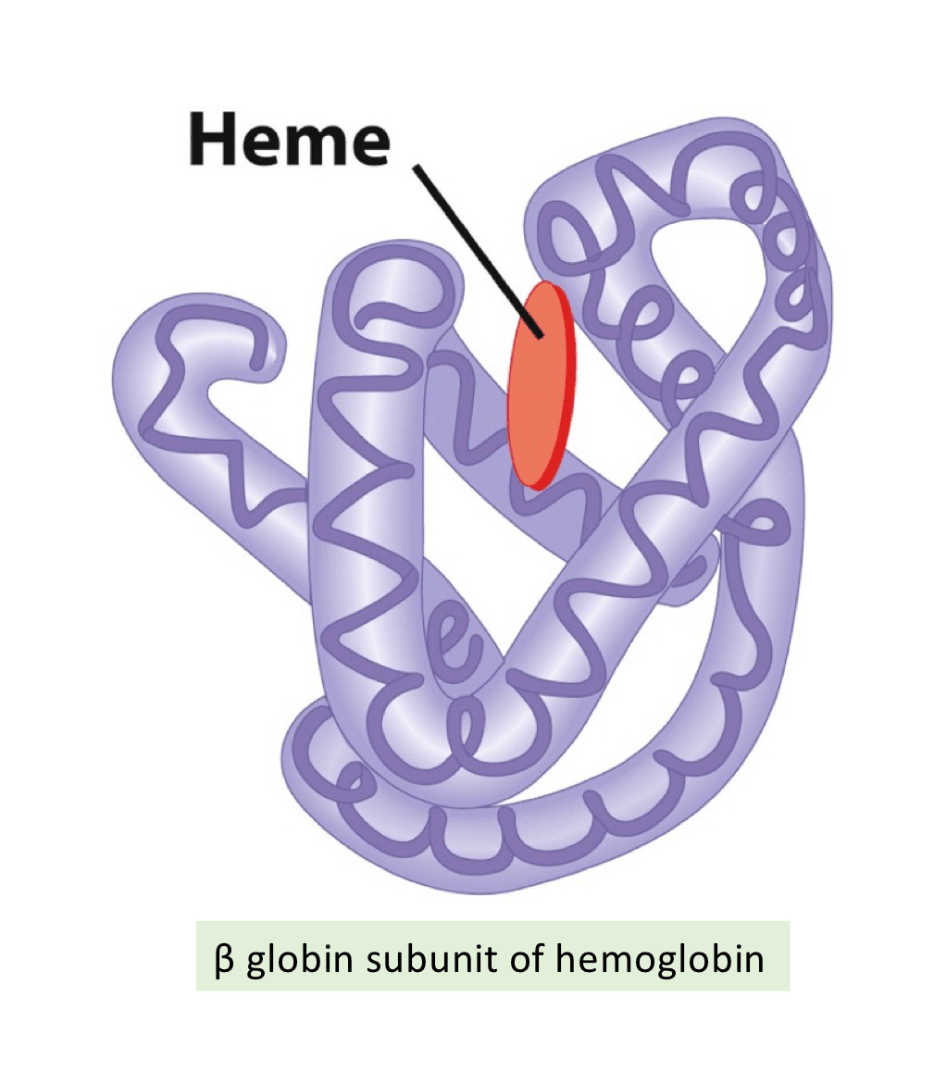
Tertiary: Overall 3D dimensional shape of a single, fully folded polypetide chain formed by further interactions between side of amino acids in the secondary structure
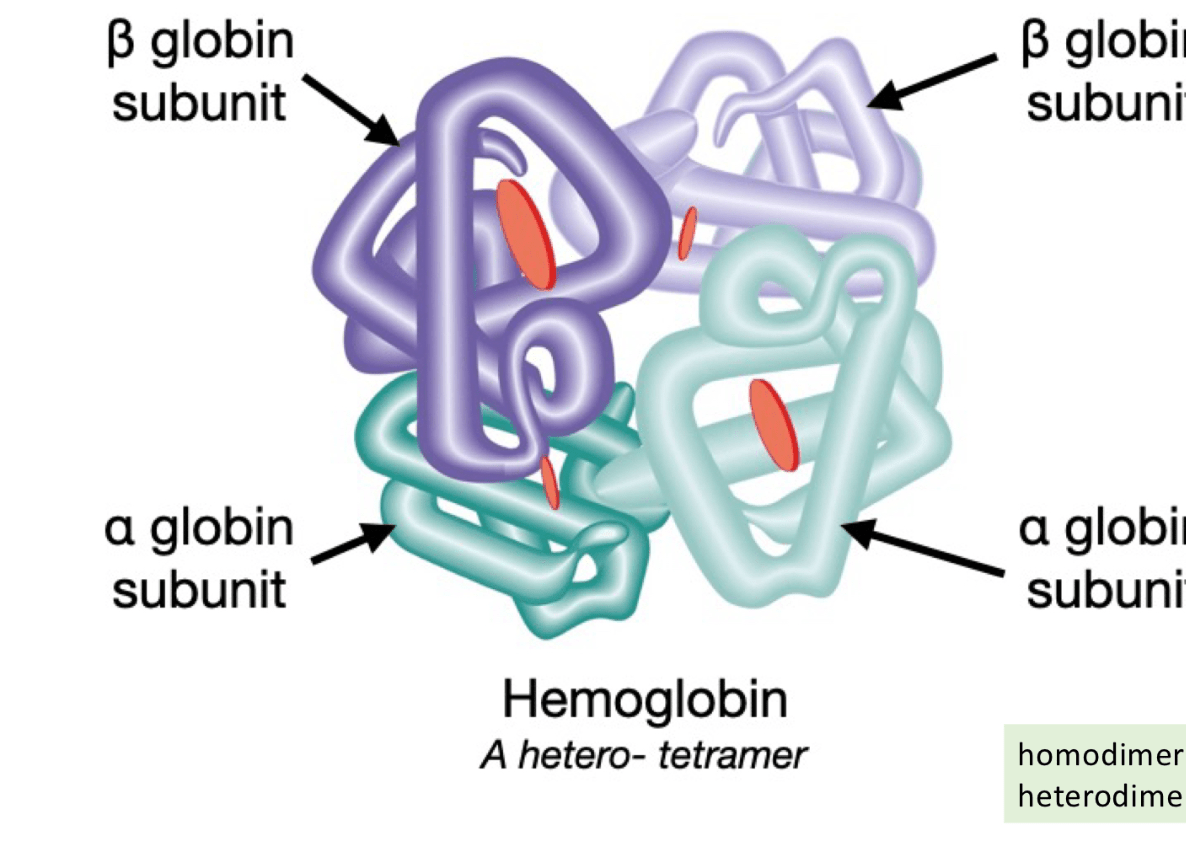
4. Multiple polypeptide chains coming together and interacting
What happens in the three binding sites for tRNAs?
1. A site, also called aminoacyl tRNA binding site
This is the section where charged tRNAs carrying the amino acid come, they use their anticodon to attach to the complementary codon in the mRNA within the A site
2. P or peptidyl site
The amino acid of the growing chain in P site disconnects from that tRNA and connects to the amino acid the tRNA in site A bought
3. The uncharged tRNA leftover from P site goes to the E site, where it exits from the ribosome
Which mutation is more severe?
mRNA 5' AUGGGCUUU '3
Polypeptide chain: N- Met-Gly-Phe -C
1. Substituting the 4th G for a C so sequence becomes
5' AUGCGCUUU '3
2. Adding an A nucleotide after 4th base
5' AUGAGGCUUU '3
Mutation 2 is worse because it causes a frame shift so you would produce
N' Met- Arg- Leu 'C
Result is more amino acids are changed
In mutation 1, just one amino acid is change your just substituting,
N- Met-Arg-Phe -C
Down below is a segment of double stranded DNA, write out the polypeptide chain to result if top strand is template.
5' CCG GAT CAT ATA '3
3' GGC CTA GTA TAT '5
Top strand is template so complement mRNA would be
3' GGC CUA GUA UAU '5
For convenience, reverse it because mRNA is translated from 5' to 3
5' UAU AUG AUC CGG '3
N- Met-Lle- Arg -C
*** Remember that first amino acid will always be the AUG codon
To yield a final, functional protein, a polypeptide chain must generally be (3)
1. Folded into a 3D shape
2. Modified post transitionally
3. Be complexed with other proteins, or with non protein functional cofactors
Which site of the ribosome serves to ensure that the correct tRNA with the correct amino acid is there.
A site, carefully looks at the codon and sees if anticodon on tRNA matches to the codon
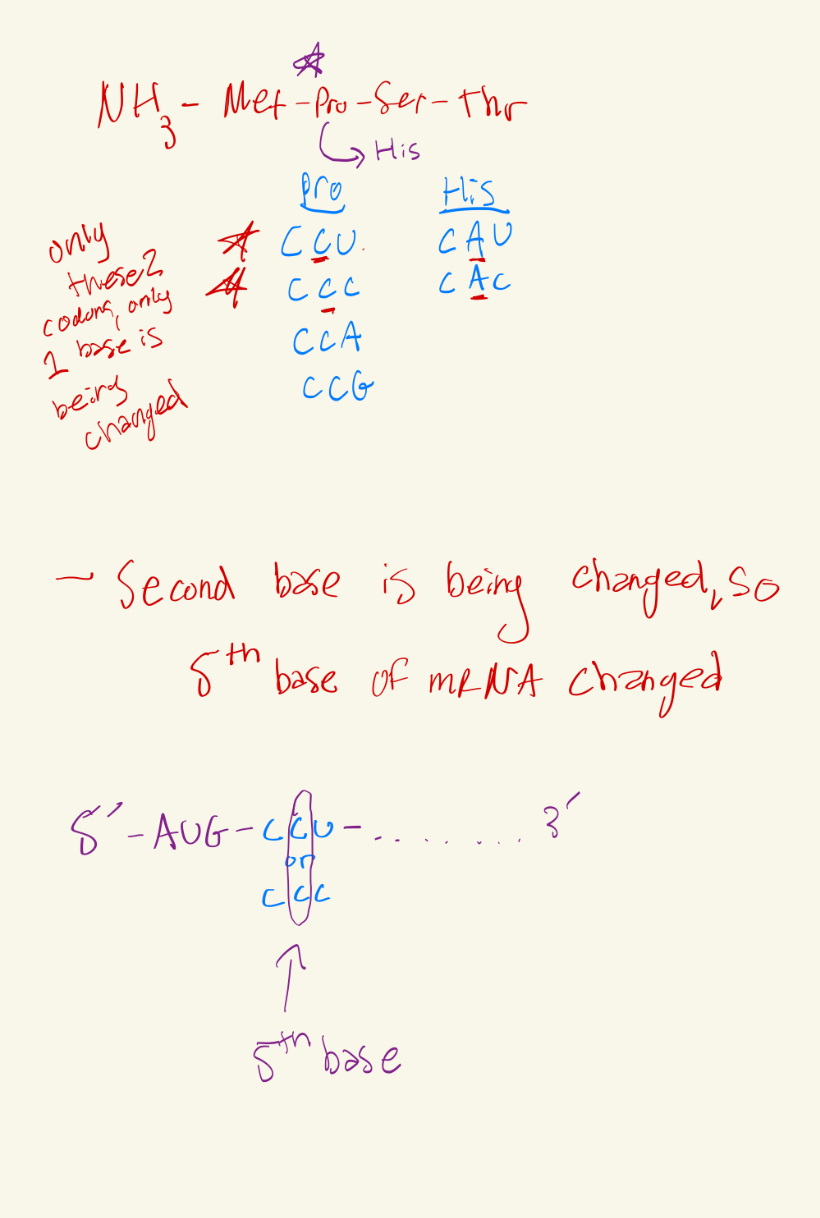
This polypeptide chain is changed due to a mutation due to a single nucleotide being substituted, the base at position __ of mRNA was changed.
NH3 - Met - Pro - Ser- Thr - COO-
to
NH3- Met - His - Ser - Thr - COO-
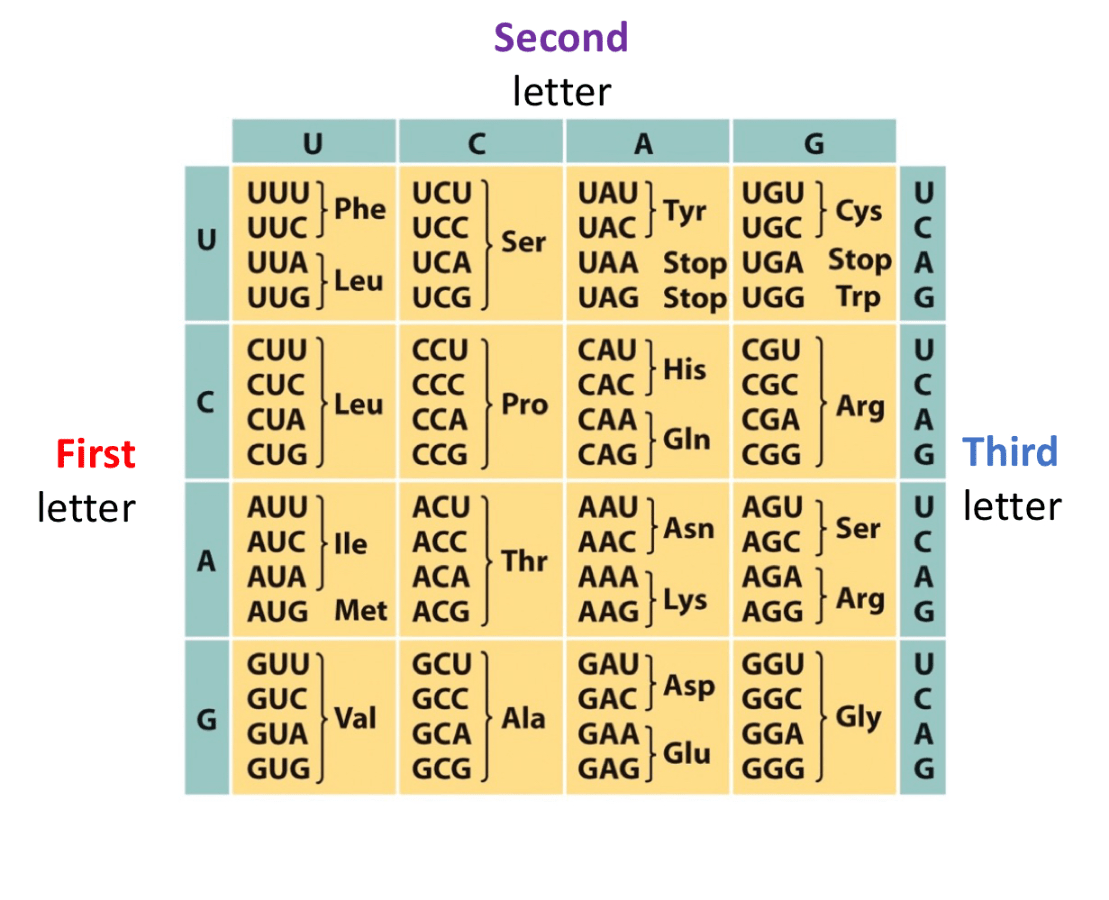
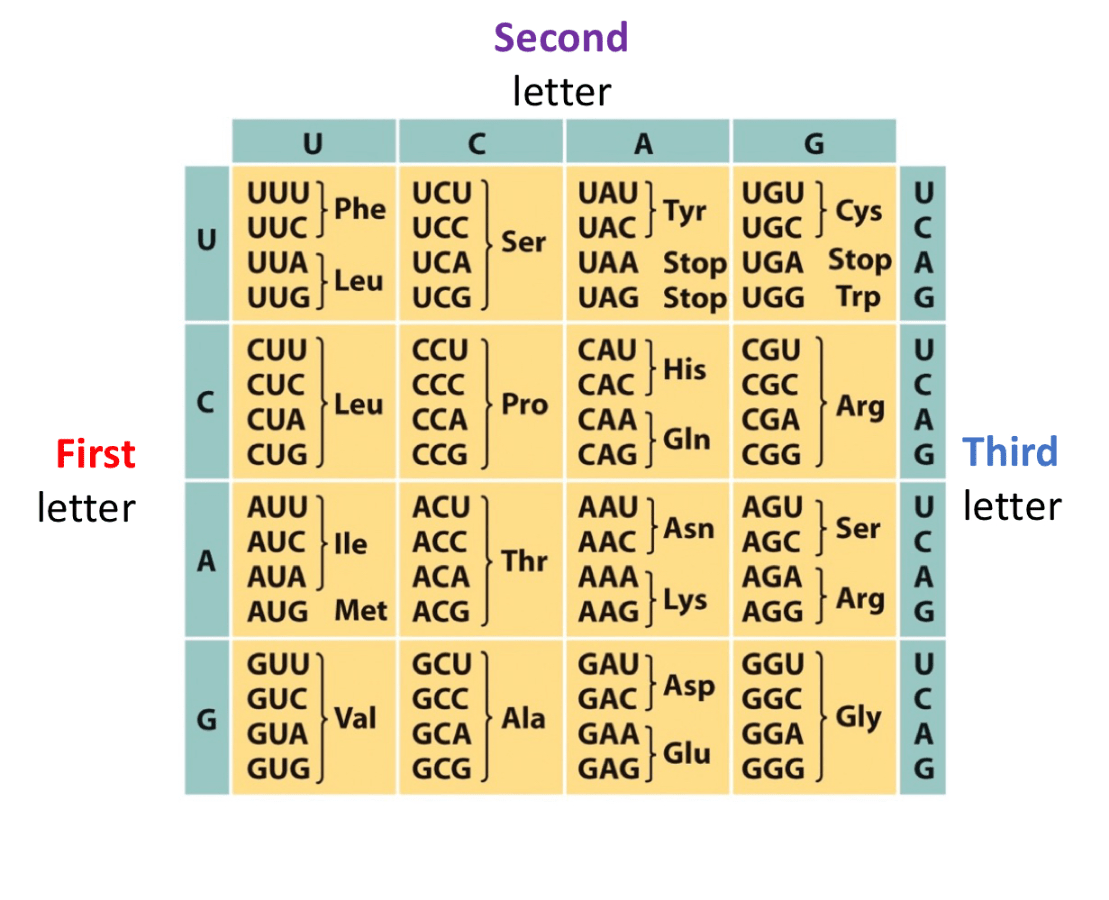
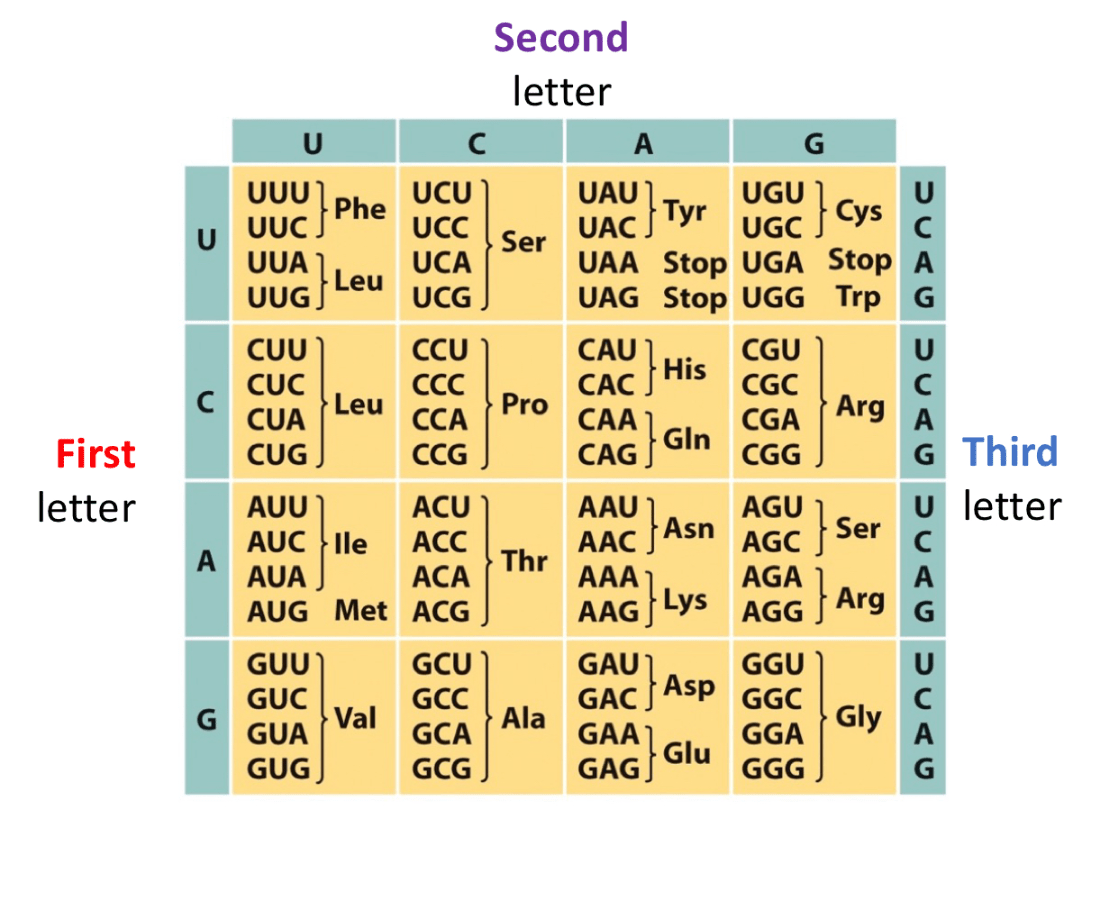
Use Wobble base pairing rules to fill this chart
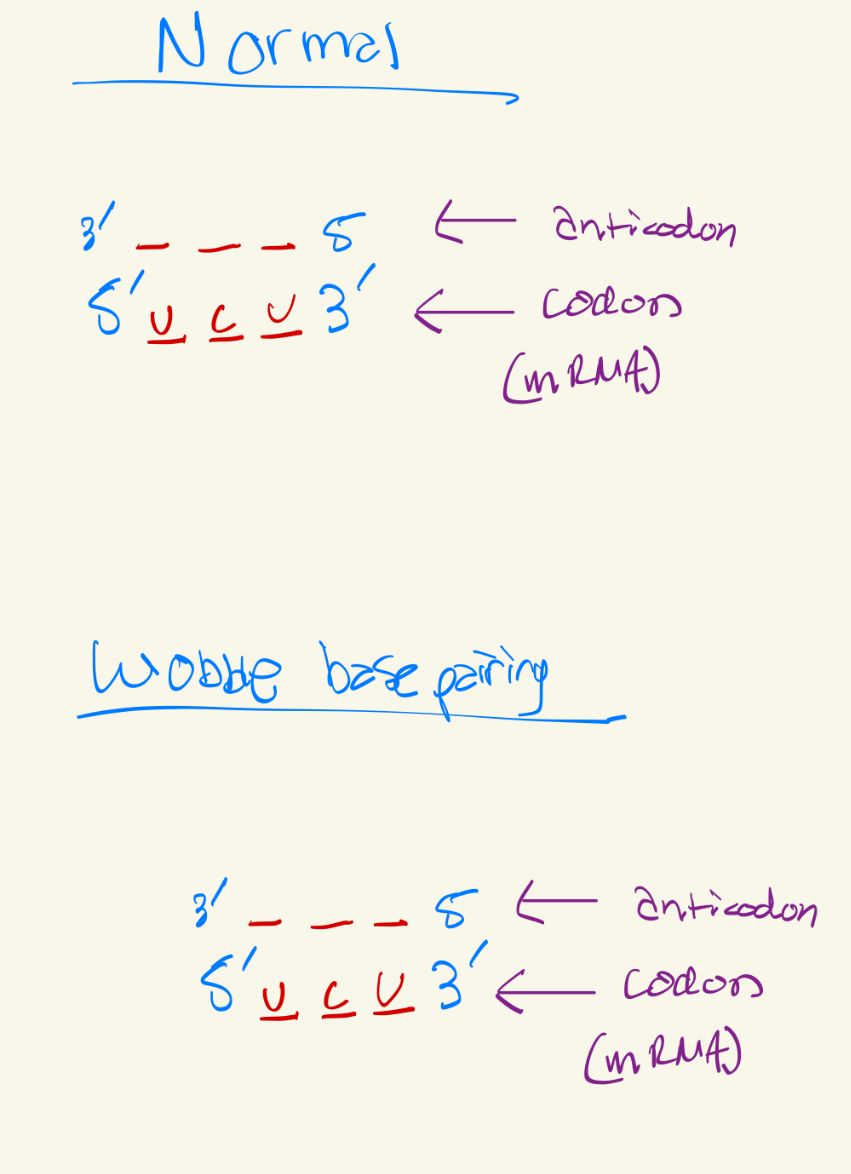
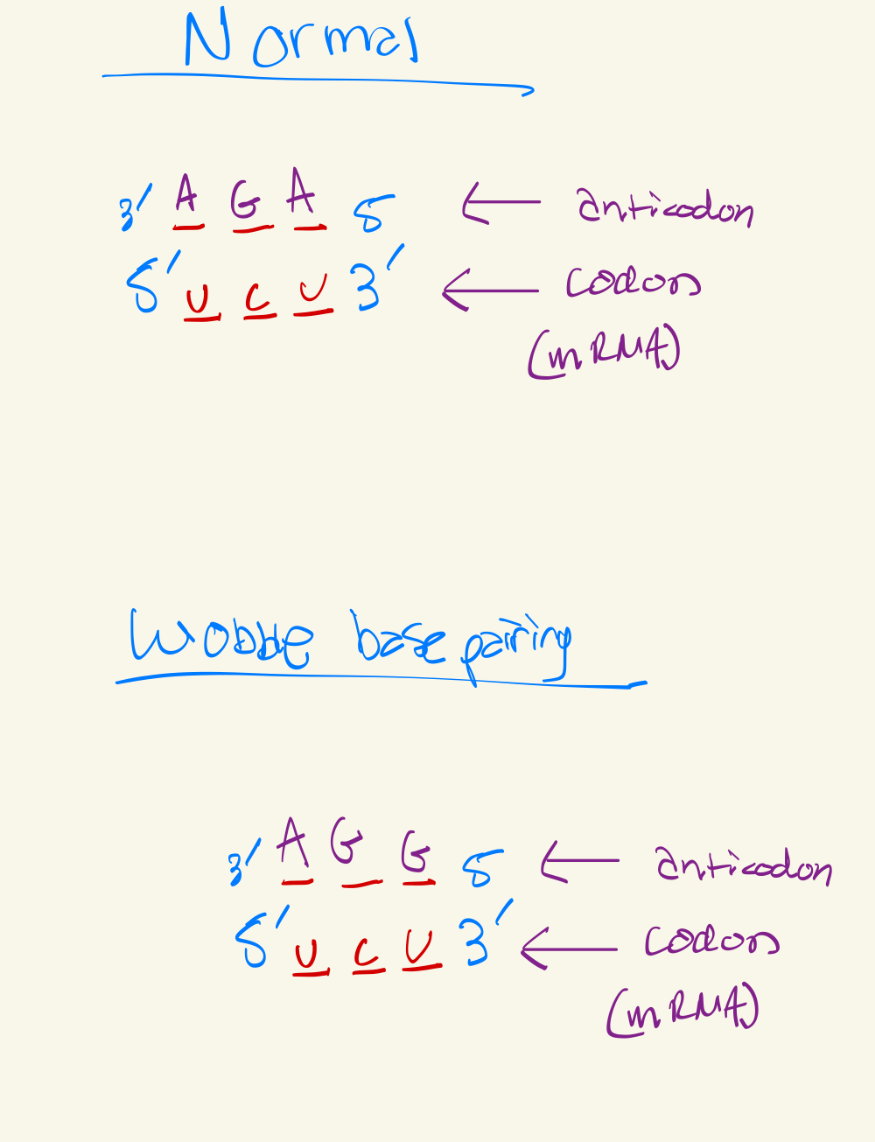
Last base of the codon has more freedom to connect to any base, but it will be slightly looser, this is bc there are not anticodons for every single codon, there are slightly less anticodons so to problem solve that, wobble base pairing occurs.
In some cases of a mutation, a certain amino acid is substituted out for another amino acid, causing the final protein to be slightly different, why so?
Change of protein, means change in R group, thus making the amino acid have a different polarity, charge, size, thus interfering with how amino acids interact and fold to make that functioning protein
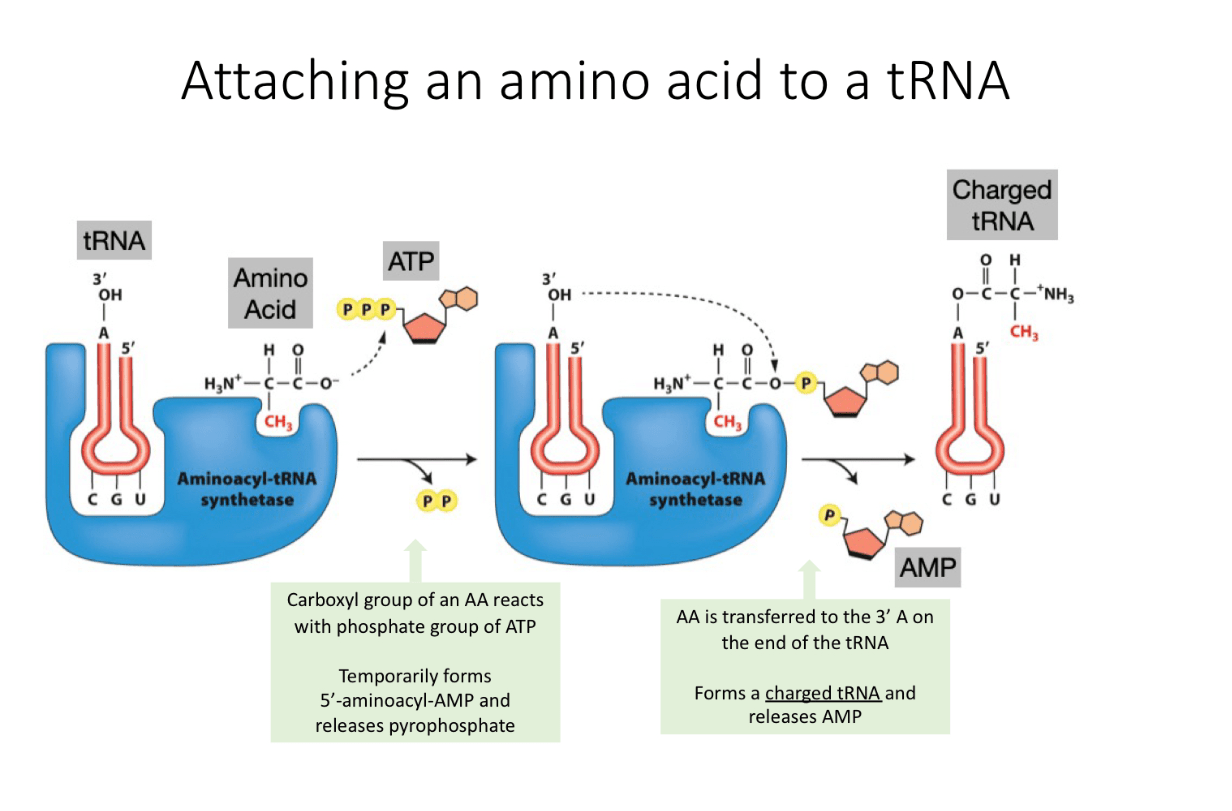
Describe the steps of attaching an amino acid to a tRNA