Motion with a restoring force to bring something back through equilibrium. It occurs over and over in regular time intervals.
What is simple harmonic motion?
Waves meet up and subtract
What is destructive interference?
Length, gravity, NOT the mass
What factors affect the simple harmonic motion of a pendulum?
The equation for wavelength of a wave
Lambda = velocity/frequency
Waves meet up and add up.
What is constructive interference?
What is a mechanical wave?
Five ________________ are depicted.
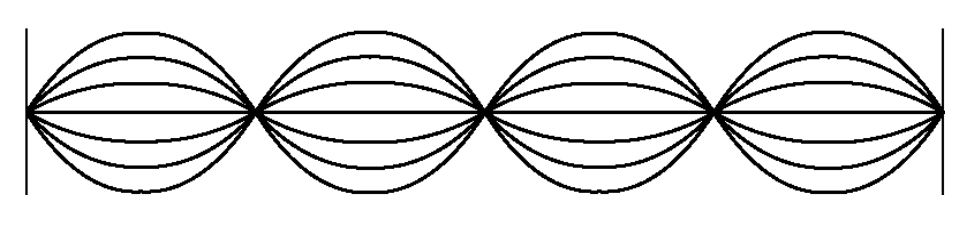
What are nodes?
Mass and the spring constant
What factors affect simple harmonic motion of a mass-spring system?
The ________________ of sound is fastest in solids and slowest in gases.
What is the speed?
A metronome
What is an example of Simple Harmonic Motion?
The greatest speed is here (A, B, or C)
What is point B?
Waves are transmissions of energy, and that travels differently in different materials
What is the speed of sound (or waves) through different media?
The period of a spring is affected how when the mass is halved.
What is the square of 1/2?
At ________________ boundaries, waves are inverted.
What is fixed?
A 53 N spring stretches 0.25 m, what is the spring constant?
What is 212 N/m?
All waves are mechanical except __________________ waves.
What are electromagnetic waves?
Waves per second
What is the frequency?
What is a longitudinal wave?
Particle motion is perpendicular to wave motion, like with a string.
What are transverse waves?
Height of a wave measured from equilibrium
What is the amplitude?
The negative sign in F=-kx only means that the restoring force is in the ________________ direction of displacement
Because _______________ never changes from medium to medium, speed and wavelength change to compensate
What is the frequency?
The greatest acceleration (A, B, or C)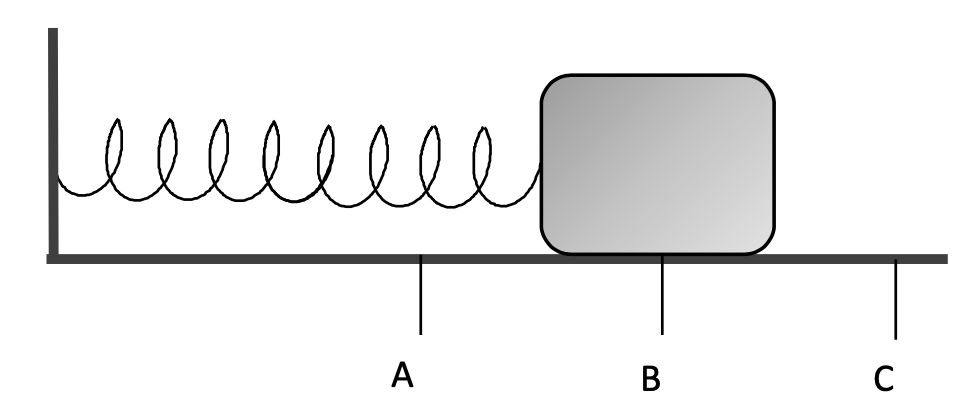
What is A or C?
Remember: restoring force is greatest the furthest away from equilibrium. This means when F is largest, F=ma is the largest. Mass doesn't change, so big F means big A.
What is the Doppler Effect?
A mass is attached to a vertically hanging spring and at rest and hangs 12 cm below its un-stretched position. What two equations can you use to find spring constant?
What are Newton's 2nd Law (F=ma) and the force of a spring (F=-kx)
Remember: set forces equal and then you have ma=kx