List the location(s) of membranes in prokaryotic cells.
outside only (cell membrane)
What is the function of the chloroplast?
photosynthesis
List 5 examples of carbohydrates
cellulose, chitin, glycogen, glucose, starch
What is happening in this diagram? 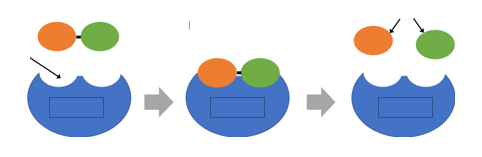
enzyme is breaking a substrate into a product.
List the 3 functions of the roots.
storage, absorption of water, anchor plant in place
What is the function of the excretory system
filter blood and release waste
List 3 locations where DNA is located in a eukaryotic cell
nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplast
What is the function of the nucleus
protect the DNA
what are the functions of starch and cellulose?
starch-energy storage for plants
cellulose- forms the cell wall of plants
If the substrate in this diagram was glycogen, what would the enzyme be named? 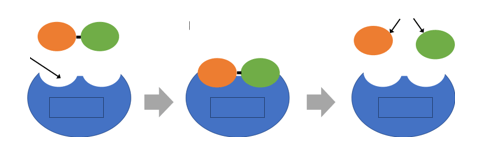
glycoase (begins in substrate-glycogen and ends in ase)
What is the weak bond?
hydrogen
What is the function of the endocrine system
produces hormones and enzymes
What process do all organisms use to make ATP?
cellular respiration
What two structures came from prokaryotic cells?
mitochondria and chloroplast
Hormones can be what two polymers?
lipids and proteins
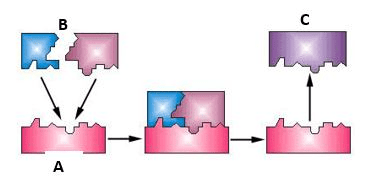 If the substrate in the diagram are amino acids what are the products?
If the substrate in the diagram are amino acids what are the products?
proteins, enzymes, hormones
What property of water allows plants to transfer water from the roots to the leaves?
capillary action which combines adhesion and cohesion
What is the function of the circulatory system
transports nutrients and oxygen
What is endosymbiotic theory?
How eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells.
Where do unicellular organisms perform all chemical reactions?
cytoplasm
What polymer is amylase and how do you know?
ends in ase making it an enzyme which is a protein.
Explain what is occurring in the diagram using a fact of enzymes. 
enzymes are fragile and require specific conditions. the heat denatured the enzyme so it will not work.
What does xylem do?
tissue that transports water from root to stem
What is the difference between hydrolysis and dehydration synthesis.
hydrolysis is adding water to break down polymers and dehydration synthesis is removing water to build polymers
What is the major difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
eukaryotic cells contain membrane bound organelles and prokaryotic do not.
Which structure contains enzymes to break down things for eukaryotic cells?
lysosomes
List the 4 polymers and their monomers.
carbohydrates: monosaccharides
lipids: fatty acids and glycerol
proteins: amino acids
nucleic acids: nucleotides
What is the difference between a exergonic and endergonic reaction?
exergonic reactions release extra heat as light or heat and endergonic reactions absorb energy.
What is the function of the guard cells
open and close stomata to allow gas exchange and release of water
How do the digestive system and the circulatory system work together?
digestive break down food into nutrients which the circulatory system transports using blood