 The bones that make up the spine (100 points for each name you can give for its 4 divisions)
The bones that make up the spine (100 points for each name you can give for its 4 divisions)
Vertebrae (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral)
 The upper leg bone articulating with the pelvis and the tibia
The upper leg bone articulating with the pelvis and the tibia
Femur
A bone that is relatively long and contains spongy bone at its ends is this type of bone. (Double points if you can describe spongy bone and its function)
long bone (contains spaces to make it lighter and to allow some flex)
Joints are held together by these structures (double points if you can use the fancy term for a joint)
Ligaments (articulation)
Bones are dead tissue or a living organ
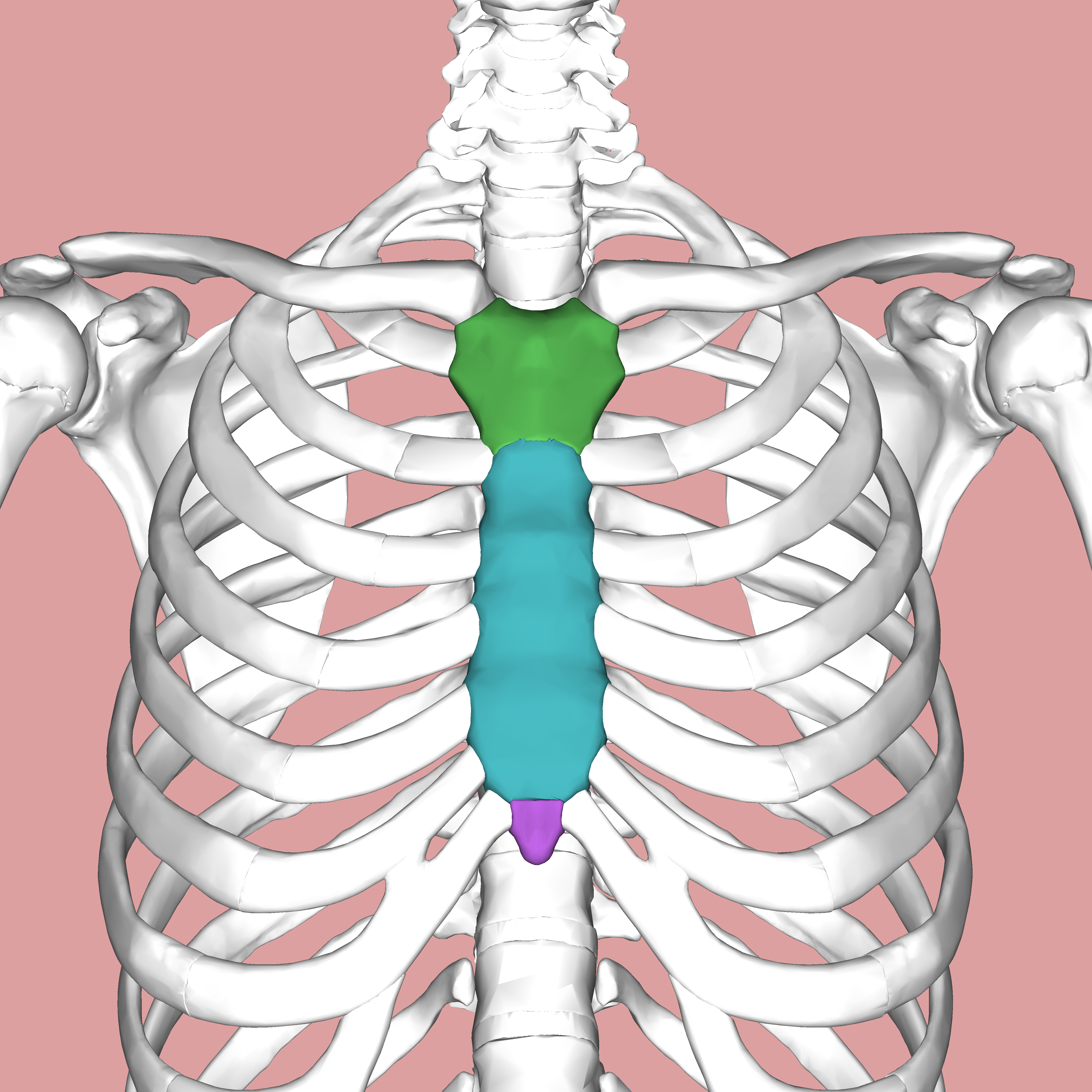 This structure is located on the front of the chest articulating with the ribs (double points for its function)
This structure is located on the front of the chest articulating with the ribs (double points for its function)
Sternum (protecting the heart)
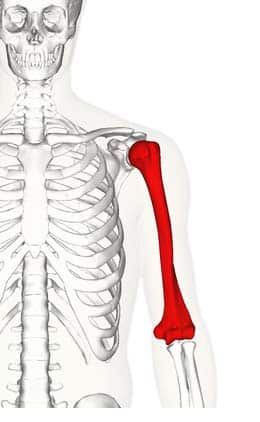 The upper arm bone (double points for the name of its two main articulating bones)
The upper arm bone (double points for the name of its two main articulating bones)
humerus (scapula, ulna)
A bone that is cube like, it is equally long and wide (double points for naming where these bones are usually found)
The tissue on the ends of long bones (double points if you can name its two functions)
Articular cartilage (decrease friction and shock absorption)
Producing blood cells
The axial part of the skeleton consists primarily of these parts (double points if you can name its primary function)
Skull, rib cage, spine (protection)
The medial and larger of the two leg bones (100 points for each of its articulating bones you can name)
Tibia (fibula, femur, patella, talus/tarsals)
This type of bone is thin and curved (double points if you can give an example)
flat (scapula, ribs, skull)
The knee and elbow joints are this type of joint. (double points for its movements)
hinge (flexion and extention)
Bone is responsible for storing and maintaining this mineral (name the other mineral for double points)
Calcium (phosphorus)
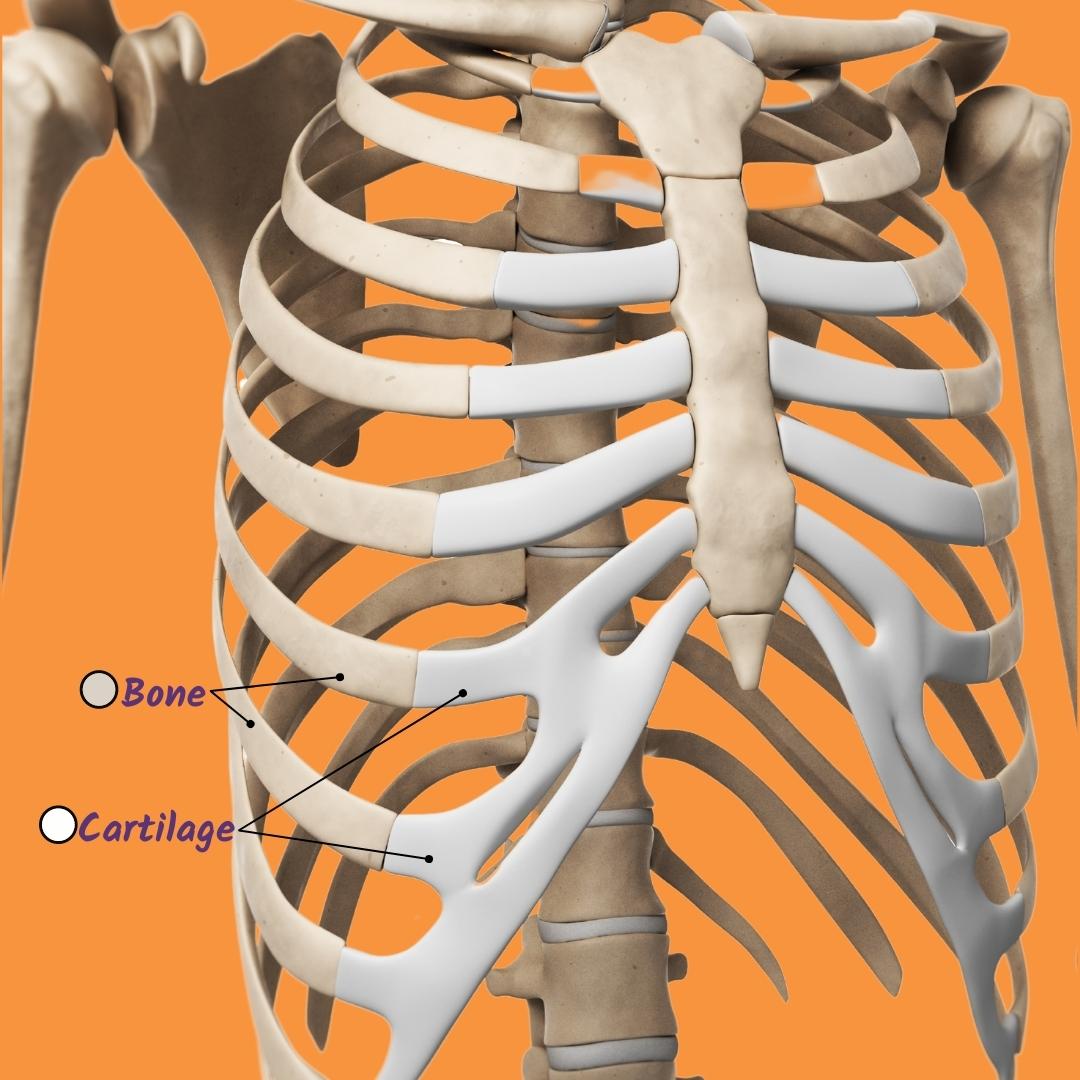 This is the primary function of the rib cage. (double points for describing how its structure lets it do its function)
This is the primary function of the rib cage. (double points for describing how its structure lets it do its function)
(Double points again) This is a secondary function of the rib cage
Protect organs such as the lungs and heart (it is rigid and cage like providing a rigid space for the lungs that is difficult to squish or penetrate)
Helping is breath by changing the pressure in the lungs
Bones of the wrist and hand contain this word. (100 more points if you can name the word for the feet)
Carpal (tarsal)
This type of bone has no clearly defined shape and usually holes or pointy edges. (100 points for each example of this type of bone you can give)
irregular (pelvis, vertebra, sacrum, mandible)
The type of joint that is found at the articulation of the humerus and scapula (100 points for each movement you can name)
ball and socket (flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, circumduction, internal rotation, external rotation)
 Functional unit of compact bone, cylindrical in shape and responsible for much of a long bones strength (100 points if you can name the cells that make it up)
Functional unit of compact bone, cylindrical in shape and responsible for much of a long bones strength (100 points if you can name the cells that make it up)
Osteon (osteocytes)
The appendicular skeleton consists of these parts. (Double points if you can name it's primary function)
Upper/Lower Extremities (limbs, arms legs), Pelvic girdle, shoulder girdle (Movements)
This bone is encased in a tendon and gets its name because it looks like a seed. (Double points for the name of one of these types of bone and its function)
Sesamoid
The radioulnar joint is this type of joint. (double points if you can name the movements associated with it)
Pivot (pronation/supination)
Remodeling is the process by which bones respond to mechanical stress or injury. This is the process by which they release calcium back into the blood. (Double points if you can name the cells that are responsible for remodeling)
Resorption (osteoblasts and osteoclasts)