This cell is responsible for breaking down bone matrix
Osteoclast
These tiny structures give spongy bone its porous appearance
Trabeculae
Type of bone growth that occurs when osteoblasts in the periosteum and the osteoclasts in the endosteum are stimulated
Appositional growth
Caused by not having enough Vitamin D or Calcium as a child
Rickets
This term refers to the realignment of a broken bone
Reduction
These structures run perpendicular to the lamellae; allow for distribution of nutrients throughout the osteon
Canaliculi
Type of marrow most likely to be found in an adult long bone
Yellow bone marrow
Hormone responsible for stimulating osteoclasts when blood calcium levels get low
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
If you do not produce adequate amounts of growth hormone as a child, you will likely have this condition
Pituitary Dwarfism
 Type of fracture where the bone breaks apart into many pieces
Type of fracture where the bone breaks apart into many pieces
Comminuted
Type of stem cell that undergoes mitosis to become an Osteoblast
Osteoprogenitor cells
This type of bone is characterized by Haversian Systems
Compact bone
Hormone responsible for stimulating osteoblasts when there is increased calcium levels in the blood.
Calcitonin
When your body produces too much GH as an adult
Acromegaly
Fracture that results from a torsional force on the bone
Spiral fracture
Name of the organic part of the bone matrix
Osteoid
The metaphysis of a child's bone is composed of what type of tissue
Hyaline Cartilage
This nutrient is required for osteoblast differentiation and collagen production
Vitamin C
This is due to a genetic mutation that decreases the rate of cartilage growth at the epiphyseal plates
Achondroplasia
Type of fracture that commonly occurs in children; characterized by an incomplete break in the bone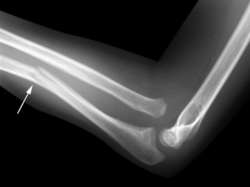
Greenstick fracture
Where blood vessels and nerves are found in compact bone
Central Canal / Haversian Canal
This structure connects adjacent osteons
Volkmann channels
Hormone responsible for bone growth prior to puberty
Growth Hormone
This is associated with the overgrowth of poorly organized bone tissue, usually in older males.
Pagets disease
Forms when the hematoma is invaded by fibroblasts and chondroblasts
Cartilaginous callus
