Without bones, your body would be like the gelatin cubes. Thankfully, the skeletal system provides this function.
What is Support?
This bone encases our brains.
What is the cranium?
Function of the red bone marrow.
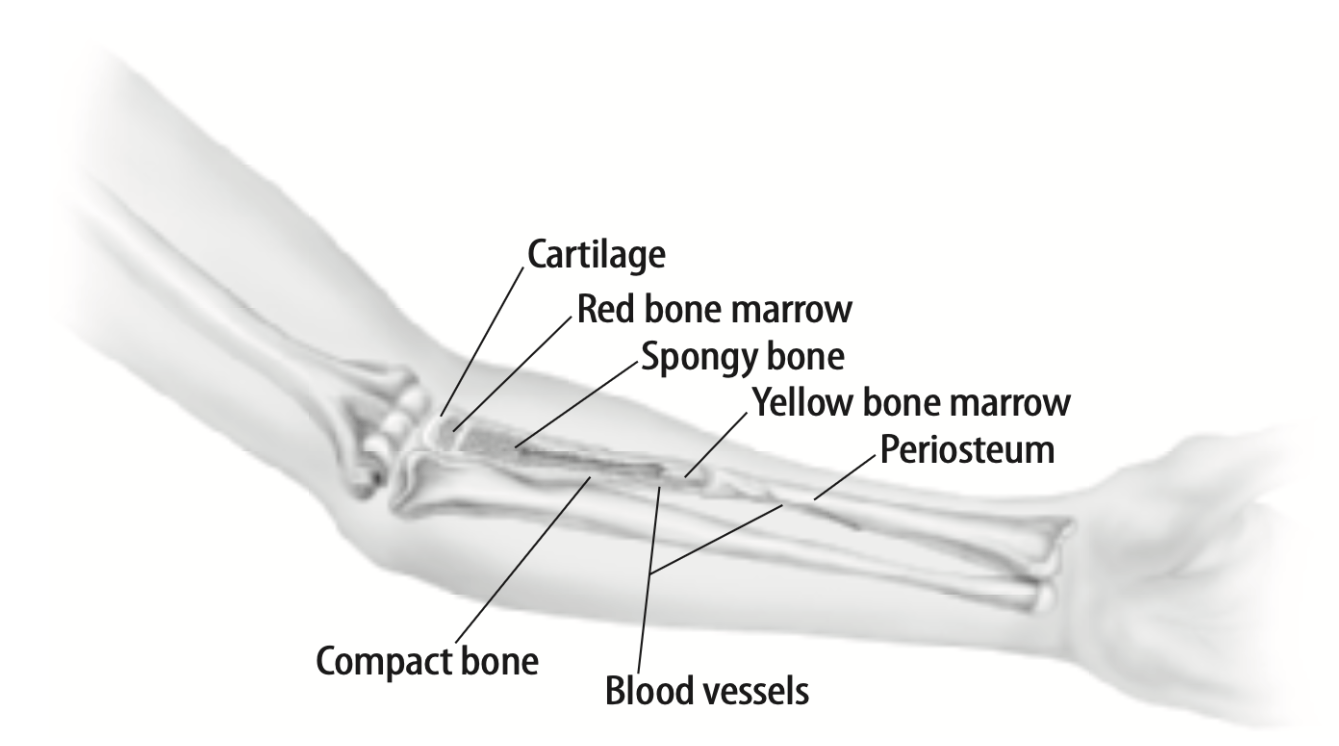
What is the production of red blood cells?
These are the two activities that muscles can perform.
What is contraction and relaxation?
This describes muscles that you can consciously control.
What is a voluntary muscle?
Your skeletal system and your muscular system work together to provide this function.
What is Movement?
This is the longest bone in the leg.
What is the femur.
Function of the yellow bone marrow.

What is the storage of lipids (fats)?
The act of shivering — the rapid contraction-and-relaxation of muscles — serves this function of the muscular system.
What is temperature regulation?
These are voluntary muscles that attaches to bones.
What are skeletal muscles?
Organs like the heart and lungs are easily damaged. Thankfully, structures in the skeletal system — such as the ribcage — can provide this function.
What is Protection?
This is the name of the bones in our fingertips. Or our toes.
What are phalanges?
Function of the cartilage.

What is the protection of ends of bones and joints?
What is protection?
This structure connects muscles to bone.
What are tendons?
Before taking a biology course, most students are unaware that the skeletal system is involved in this function, which involves red blood cells.
What is Production?
This bone holds together our ribcage. Commonly called the "breastbone".
What is the sternum?
Ligaments provide stability as a function, because they connect bones to this type of structure.
What are bones?
This function is enabled by cord-like structures that connect muscle to bones, holding our joints together when the body moves.
What is stability?
This is an involuntary muscle that controls the blood-flow of the human organism.
What is the cardiac muscle?
This instructor was encouraged to drink milk to ensure a healthy external supply of calcium. Otherwise, our body will start obtaining it from our bones. This is because our skeletal system does this function.
What is Storage?
Commonly referred to as our shoulder blade.
What is the scapula?
Tendons provide stability as a function, because they connect bones to this type of structure.
What are muscles?
What is homeostasis?
This is involuntary muscles that lines the insides of hollow organs such as the intestine.
What are smooth muscles?