What is the function of the periosteum?
The periosteum contains osteoblasts and osteoclasts to help with bone resorption and growth; contains blood vessels to help with exchange of nutrients and waste; helps anchor ligaments and tendons to the bone.
The end of a long bone is called...
The epiphysis
What is a lacuna?
The fluid filled space that holds an osteocyte.
What are the three types of joints?
1) Fibrous joint
2) Cartilaginous joint
3) Synovial joint
What are the signs of an MSK injury?
Pain, discoloration, limited range of motion, heat, possible deformity, possible change in sensation distal to the injury
What is the process of formation of osteocytes?
Osteoprogenitor cells --> osteoblasts --> osteocytes
Are the pelvic and shoulder girdles part of the axial or appendicular skeleton?
Appendicular skeleton
Where is spongy bone found? What is another name for it?
Spongy bone is found in the epiphysis. Spongy bone is also called cancellous bone.
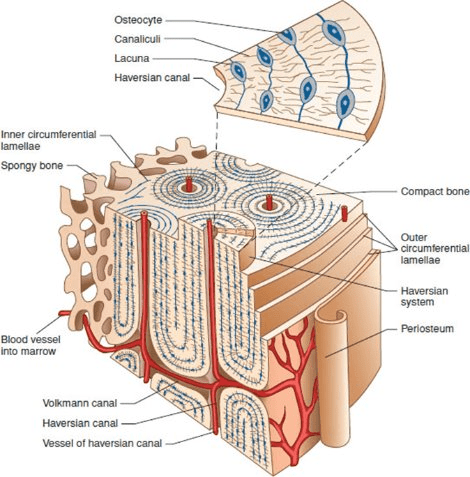
What are lamellae?
Circumferential layers of compact bone.
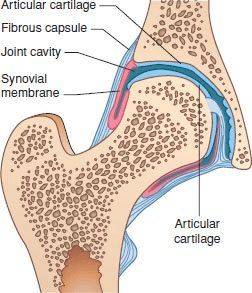
Where is synovial fluid produced? What is its function?
Synovial fluid is produced by the synovial membrane. Its function is to reduce friction between the articulation points and fill the synovial cavity.
What is the treatment for an MSK injury? What are we trying to do by providing this treatment?
RICE
R - rest
I - immobilization
C - cold
E - elevation
We're trying to minimize the inflammatory process and encourage healing.
T/F: red bone marrow is involved in erythropoeisis exclusively.
False - red bone marrow is also involved in the formation of platelets and leukocytes as well as erythrocytes
What are the five structural categories of bones? What is an example of each?
1) Long bones - e.g., femur, humerus, tibia & fibula, radius & ulna
2) Short bones - e.g., carpals in the hand, tarsals in the foot
3) Irregular bones - e.g., vertebra
4) Flat bones - e.g., ribs, sternum, skull
5) Sesamoid bones - e.g., patella
Where is the endosteum found?
The endosteum lines all internal cavities and canals of the bone.
What is a Haversian canal?
A channel running parallel the long axis of the bone that houses nerves and blood vessels.
Where would you expect to find a suture? What kind of joint is it?
A suture would be found in the skull.
Sutures are a type of fibrous joint.
What is the difference between a strain and a sprain? Would you expect them to present the same way?
Strain - a stretched muscle or tendon
Sprain - a stretched ligament
Both present with swelling, pain, heat, and decreased range of motion
A sprain is likely to present with discoloration
A strain will likely present with muscle spasms
What bone cell would be active when blood calcium levels are low? Why?
Osteoclasts - they break down bone and free up calcium when blood calcium levels are low
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
1) Support
2) Protection
3) Movement
4) Mineral storage
5) Hematopoeisis
What is the function and location of red marrow in adults?
What is the function and location of yellow marrow in adults?
Red marrow - functions in hematopoeisis; found in the epiphyses of long bones and medullary cavity of flat bones
Yellow marrow - stores fat; found in medullary cavity of long bones
What is the relationship between canaliculi and lacunae? What's the function of canaculi?
Canaliculi are small channels that run between lacunae to connect osteocytes for the purpose of nutrient and waste exchange, as well as cell-to-cell communication.
What bone is this? What type of joint is highlighted?
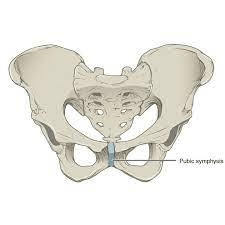
This is the pelvis. The pubic symphysis is a cartilaginous joint.
Describe the treatment for an open fracture.
Determine the presence of possible or confirmed open fracture.
Assess CSM frequently.
Rinse with sterile saline.
Dress and bandage open fracture.
Immobilize and elevate fracture.
Apply cold pack, if tolerable, and provide pain management.
Osteoblasts and osteocytes are found within the...
periosteum and endosteum
What is intramembranous ossification and what bones are formed by it? What is endochondral ossification and what bones are formed by it?
Intramembranous ossification - osteoblasts turn a connective-tissue membrane directly into bone; forms skull and flat bones
Endochondral ossification - a cartilage template is created, then turned to bone; forms long bones (+ pretty much every other bone)
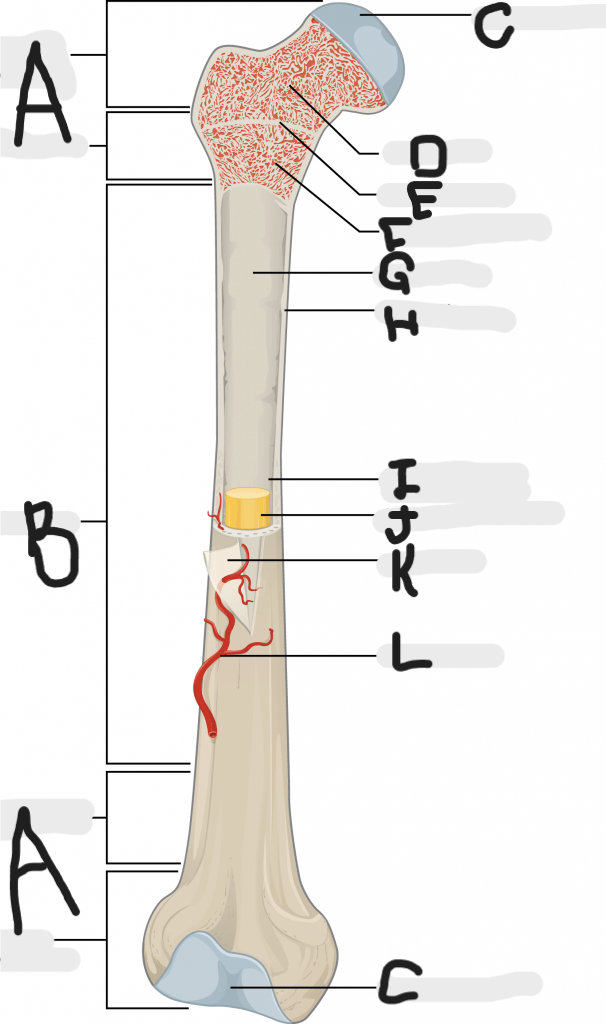 Label at least 7 structures.
Label at least 7 structures.
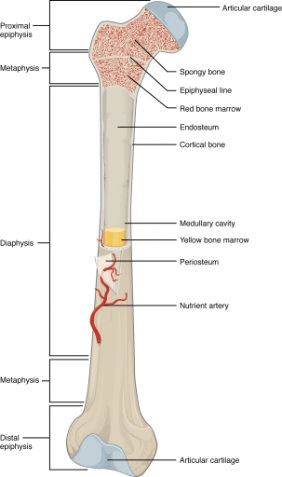
Label at least 5 structures.
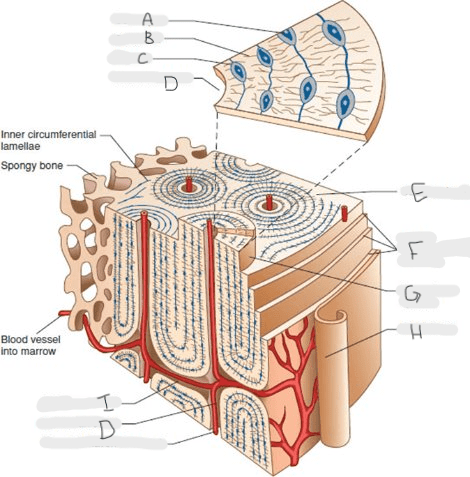
What type of joint is this? Label the structures.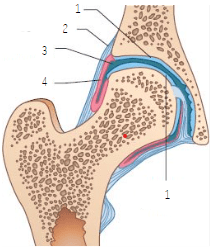
Synovial joint.
How would our bone cells work together to heal a fracture?
Osteoclasts clean up bone chips and fracture edges
Osteoblasts lay down new bone tissue and mature into osteocytes to bridge the fracture
What organelles do osteoclasts contain in high concentration? What are their functions?
Mitochondria and lysosomes
Mitochondria - provide energy
Lysosomes - contains digestive enzymes