These are the microscopic bony chambers that house osteocytes.
What are lacunae?
The location of red bone marrow in a long bone (use specific location/vocab)
What is spongy bone in the epiphysis of bones?
This process happens in red bone marrow and produces blood cells from stem cells.
What is hemopoiesis (hematopoiesis)?
During bone remodeling these cell would be active during resorption (when calcium is needed in the bloodstream)
These are the cells that can build themselves into chambers and become mature bone cells. They take calcium from blood to build bone
What are osteoclasts?
What are osteoblasts?
Increased activity of osteoclasts can lead to fragile and weak bones.
What is osteoporosis?
Bone(s) of the pectoral girdle.
What is the clavicle and scapula?
The concentric circles circles of bony matrix that surround the Haversian canal and form osteons.
What are lamella?
This is where yellow marrow is contained.
What is the medullary cavity?
One function of bone is storage of minerals such as calcium. This is the form of calcium that makes up bone
What is calcium phosphate?
These allow for passage through birth canal and brain development, fuse by 2 years old
What are fontanels?
What is rickets?
The zygomatic is an example of this type of bone.
What is an irregular bone?
The horizontal canal that allows blood vessels to run through bone. They run perpendicular to the Haversian canal
What are Volkmann's canals?
This structure reduces friction between bones and allows them to glide.
What is articular cartilage (hyaline)?
The muscular system and skeletal system work together to provide this function of the skeletal system.
What is locomotion?
As a fetus most of your skeleton is made up of ____ and turns into bone through ___
What is cartilage and ossification?
Autoimmune disease that causes deterioration of the joints.
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
The first two vertebrae are called this and allow the head to swivel.
Atlas and axis (C1, C2)
The narrow passageways that contain cytoplasmic extensions of osteocytes. Allows for transfer of materials between cells.
What are canaliculi?
Which is the Proximal Epiphysis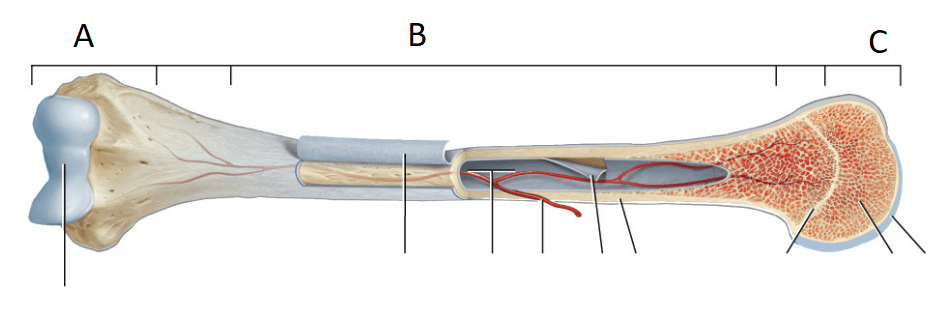
What is C?
These joints have no movement (give one example)
Fibrous (Synarthrotic), Sutures of the skull
The process of cartilage gradually turning into bone.
What is ossification?
Abnormal lateral curve of the spine.
What is scoliosis?
The number of thoracic vertebrae.
What is 12?
Central canal that allows blood vessels and nerves to run through compact bone
What is the haversian canal?
The type of bone that makes up the diaphysis.
What is compact bone?
Your elbow is an example of a _____synovial (diarthrotic) joint and your hip is an example of a ____ synovial (diarthrotic) joint
Hinge, Ball and Socket
This is growth in diameter of the bone.
What is appositional growth?
Fracture that is incomplete, usually because bones are young and pliable
What is a greenstick fracture?
The femur, the coxal bone, the scapula, and the clavicle are all part of the (axial/appendicular) skeleton
what is appendicular
Single unit of compact bone that when combined with others adds to strength of bone.
What are osteons?
The vascular protective outer layer of long bone made of connective tissue
What is the periosteum?
One example of how bones protect internal organs.
Rib cage
Skull
Vertebrae
Longitudinal growth of bone occurs here stops as an adult.
What is the epiphyseal disc/plate
Back pain due to a nerve being pinched by a vertebral disc.
What is a herniated disc?
What bone is part of axial skeleton
...