This bone of forms the only synovial joint of the skull
Mandible
What is the name of this landmark?

Coracoid process
This joint allows the movement of the shoulder.
Glenohumeral joint
Which ribs are “floating”?
11 and 12
Which one is not a skeletal function: mineral storage, blood cell production, or hormone secretion?
hormone secretion
This bone has a spine, acromion, and forms the glenoid cavity.
Scapula
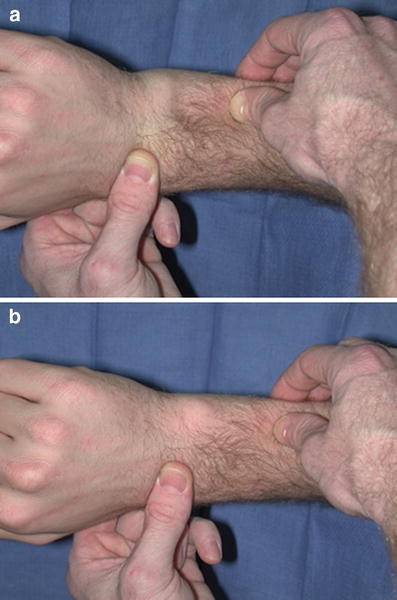 This bony projection is used to attach to the wrist ligaments to stabilize the wrist.
This bony projection is used to attach to the wrist ligaments to stabilize the wrist.
The ulnar styloid
Only true anatomical link of the upper limb to the axial skeleton.
Sternoclavicular joint.
Arrange the ear ossicles from lateral to medial.
Malleus → incus → stapes.
Name the two types of osseous (bone) tissue, and name one of the other tissues commonly housed within its trabecular spaces.
Compact bone; spongy (cancellous) bone. Spongy bone forms marrow.
This bone is the only true joint of the shoulder girdle.
Clavicle

What is the joint is being palpated in the image above?
Temporomandibular joint
Classification of the wrist (radius–carpus).
Condyloid/ellipsoid.
Which lower-leg bone bears most body weight?
Tibia.
These two cell types build up bone and break down bone, respectively
Osteoblasts, osteoclasts
This bone forms the atlanto-occipital joint.
C1 vertebrae
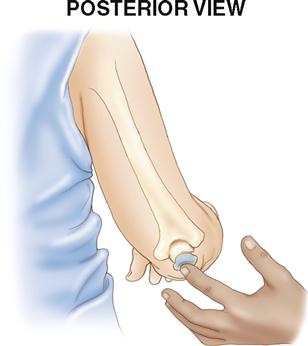 what is the name of the indicated landmark, and on what bone is it located?
what is the name of the indicated landmark, and on what bone is it located?
The olecranon process; ulna
Joint primarily enabling pronation/supination of the forearm.
Proximal radioulnar (pivot).
Which digits have only two phalanges?
Thumb (pollex) and big toe (hallux).
What’s the job and location of the epiphyseal plate?
Longitudinal growth of long bones at the head of the long bone which occurs during development
This bone looks like a cube.
Cuneiform

What is the bone labelled in the # 1 position?
The Talus.
Joint chiefly responsible for foot inversion/eversion.
Subtalar (talocalcaneal).
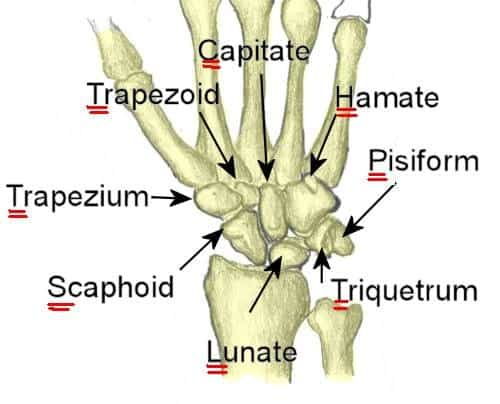
Name the proximal carpal row from lateral to medial.
Scaphoid → lunate → triquetrum → pisiform.
List the four types of bony landmark types
Projections, depressions, openings, articulating surfaces