Name the 4 phases of wound healing
Inflammation
Proliferation
Contraction
Maturation
This staph infection presents with honey-crusted lesions. 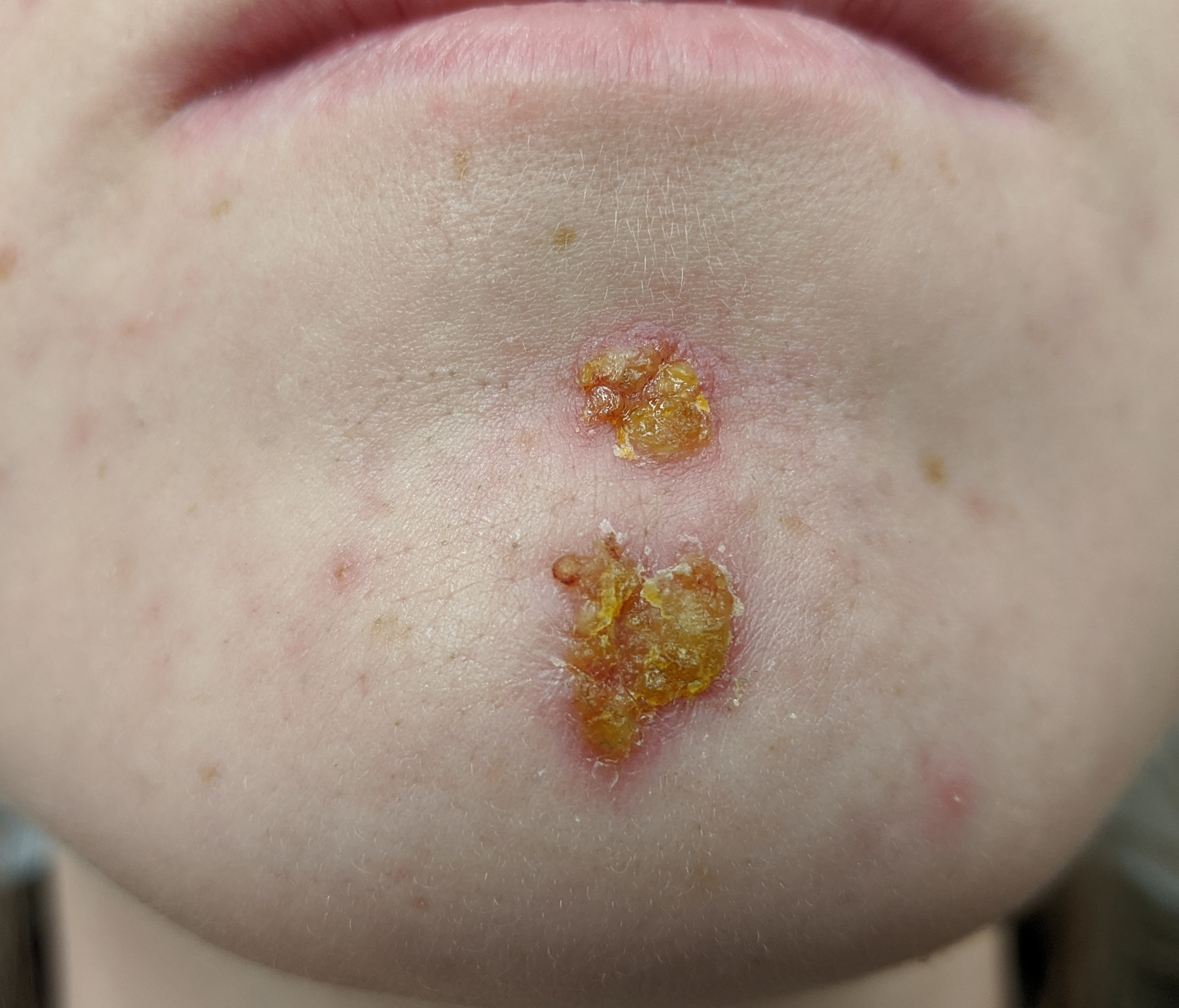
impetigo
This viral skin infection causes warts.
veruca
This fungal infection affects the scalp.

tinea capitis
This condition is caused by lice and managed with permethrin or pyrethrin.

pediculosis
What classification of wound requires debridement to facilitate removal of debris, cells, and exudate because the healing is taking place inward?
Secondary intention
Sandpaper-like skin, wrinkles, and bullae are signs of this staph infection.
scalded skin syndrome
This virus causes cold sores

herpes simplex type 1
Also called "ringworm," this infection affects the whole body

tinea corporis
This tick-borne disease can be treated with doxycycline, or amoxicillin if the patient has no permanent teeth
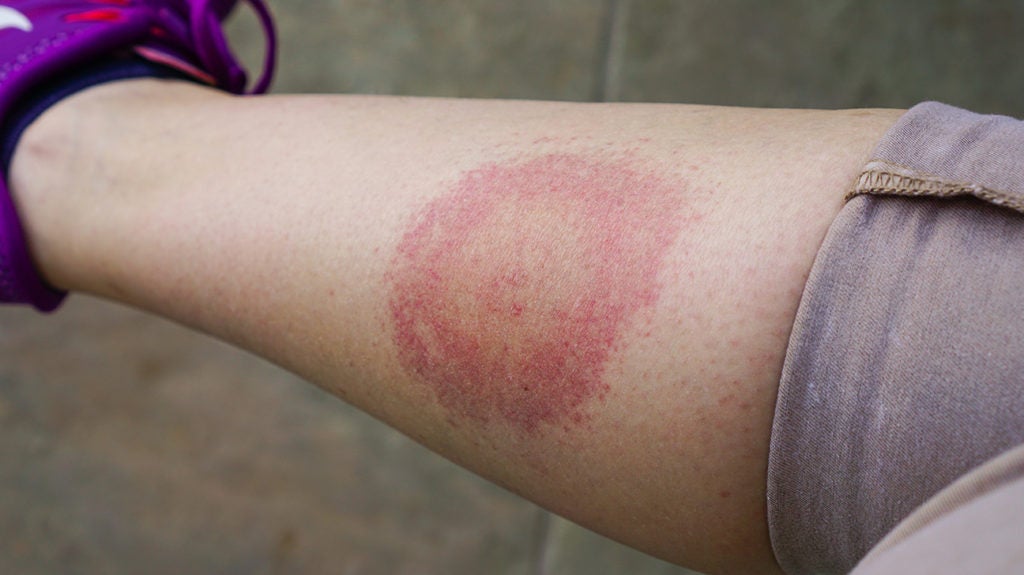
Lyme disease
Wound edges are brought together in this type of healing.
primary intention
This staph/strep infection of the dermis causes fever, lymphangitis, and bullae lesions. 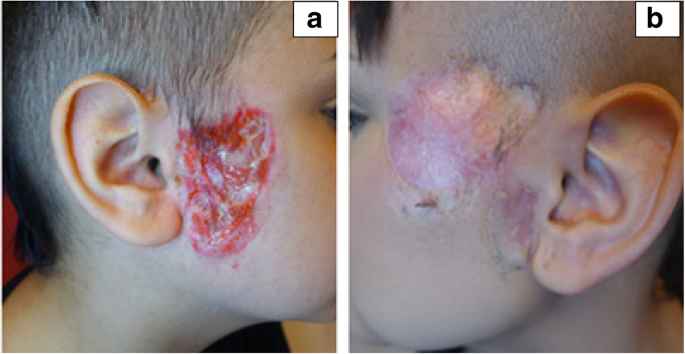
pyoderma
This virus causes genital sores.
herpes simplex type 2
This fungal infection is commonly known as jock itch affect the groin only
tinea cruris
This cradle cap condition is treated with antiseborrheic shampoo.
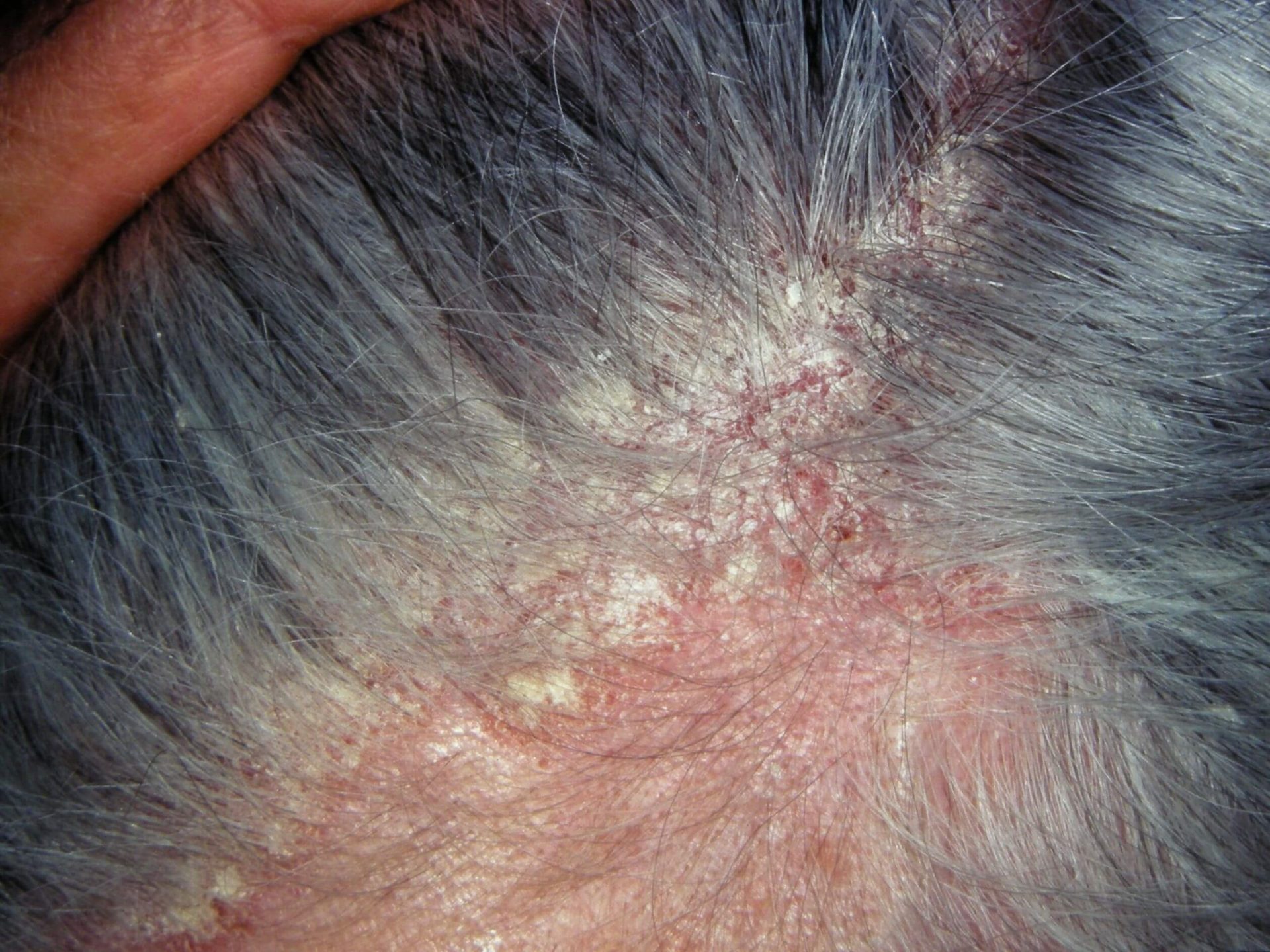
seborrheic dermatitis
Name some signs of wound infection? select all :(
A. increased erythema
B. cool to the touch
C. edema
D. pain
E. increased temperature
F. pallor
Increased erythema
Edema
Pain at site or beyond margins
Increased temperature
This staph/strep/H. flu infection of dermis and subcutaneous tissue is marked by warm, red, painful skin.
cellulitis
This viral infection presents with small dimpled, itchy lesions.
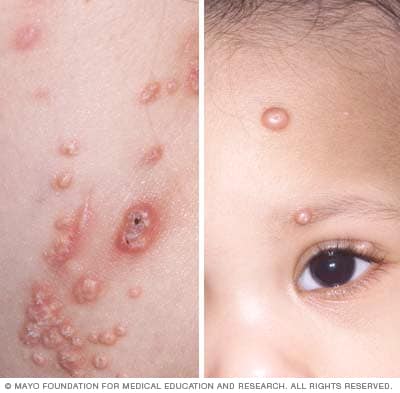
molluscum contagiosum
This itchy, inflamed skin condition is managed with moisturizers, corticosteroids, antihistamines, and immunomodulators.

atopic dermatitis/eczema
This fungal diaper rash is treated with topical antifungals, zinc, and keeping the skin dry.
candidiasis/diaper dermatitis
What can nurses do to prevent scratching?
Short fingernails and/or mittens
Use of antipruritic medications
Wet compresses and use of cleansing solutions
This MRSA follicle infection causes large lesions and requires incision and drainage.
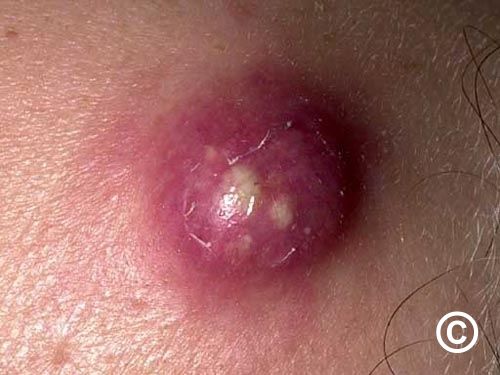
Furuncle/carbuncle
This viral reactivation causes painful blisters in a dermatomal pattern.

herpes zoster or shingles
This contact reaction is caused by urushiol from plants like poison ivy.
allergic contact dermatitis
What is the progression of treating acne?
Starts with non-drying cleaning and OTC options, then moves to Retin-A and oral medications.