:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/neurocranium/HnTYr2LCEDwW1SRBnNTH3g_Parietal_bone_02.png)
Parietal
Center Point for Lateral Skull
2 inches (5 cm) superior to EAM
...or halfway between the glabella and inion
CR 1½ inches (4 cm) inferior to
mandibular symphysis is for what x-ray view?
SMV
All four sutures
Coronal, Squamosal, Lambdoidal & Sagittal
Equalizes pressure
Eustachian tube
The two sections for Cranial bones
Calvaria & Floor
Center Point for AP Axial (Towne Method)
2½ inches (6.5 cm) above glabella
Lift chin and hyperextend neck if possible until IOML is parallel to IR is for what Skull x-ray view
SMV
The posterior part of the sella turcica
Dorsum sellae
auditory ossicle that picks up sound vibrations from the tympanic membrane
Malleus (hammer)
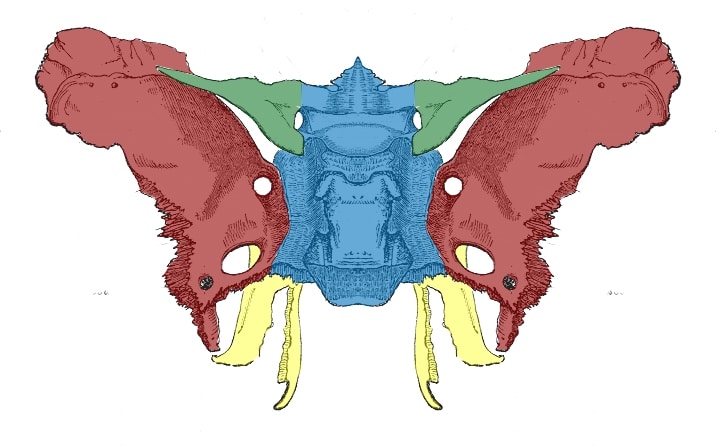
Sphenoid
For a PA and AP Skull x-ray what is perpendicular to the plate
OML
External Landmark that corresponds with the level of the petrous ridge
Top of the Ear Attachment (TEA)
Three aspects of temporal bones
Squamous, Mastoid & Petrous
Opening in the temporal bone that serves as a passageway for nerves of hearing and equilibrium
Internal Acoustic Meatus (IAM)
sella turcica
If the tube angulation for a Towne Method is 37° what positioning line is perpendicular to the IR?
IOML
Junction Points
Asterion, Bregma, Lambda & Pterion
Inferior to the zygomatic process
and anterior to the EAM
temporomandibular fossa, into
which the mandible fits form the
TMJ
Thin plate of bone that separates the mastoid air cells from the brain
Tegmen tympani
The inferior portions of this anatomy:

lateral & medial pterygoid process, & pterygoid hamulus
For a PA without angulation where does the CR exit at?
Glabella
Line used in positioning to ensure that the skull is in true lateral position
Interpupillary line
Five foramen:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/foramina-and-fissures-of-the-skull/RP56K1uPyUzofhiFsB4mCQ_Skull_base_-_superior_view.png)
optic, rotudum, ovale, spinosum, magnum
contains small openings or foramina that olfactory
nerves pass through
cribriform plate