What is fluency?
What is:
The effortless, rapid, and forward movement of the speech apparatus.
Do children who stutter fluctuate between stages?
What is:
It is very common for children who stutter to fluctuate between the various phases, especially when they first begin stuttering. This can be caused by a number of factors, including demands and capacities, environmental influences, stress, overall development, etc.
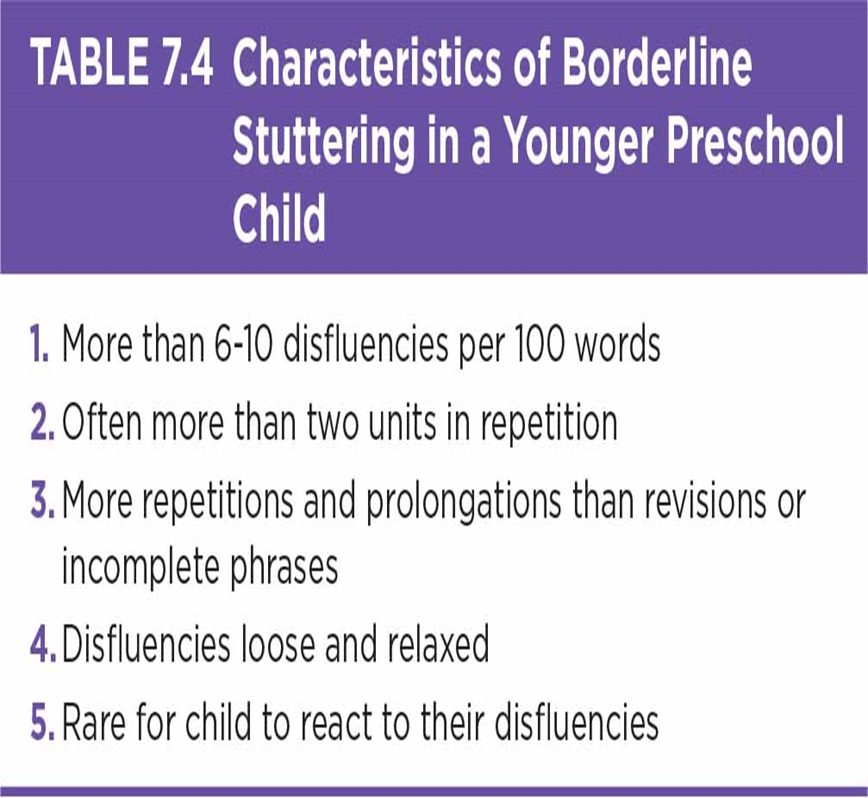
Discuss developmental stuttering.
What is:
Stuttering that occurs in early childhood development. It includes phases that begin early and carry onward into adulthood: borderline, beginning, intermediate, and advanced stuttering phases.
What is the formula for calculating percent of disfluencies stuttered in syllables?
What is:
%SS = total stutters/total syllables X 100.
When counting stutters, each syllable can only be stuttered once (eg, N-n-n-n-n-nuh-nuh…[silent block]…name” = one stutter); If client has obvious avoidance behavior without stutter, count as stutter (eg, “My name is uh…uh…uh…uh…Barry.”).
Differentiate the 4 classifications of stuttering:
borderline; beginning; intermediate; advanced



Guitar, B. (2024). Stuttering: An integrated approach. Wolters-Kluwer.
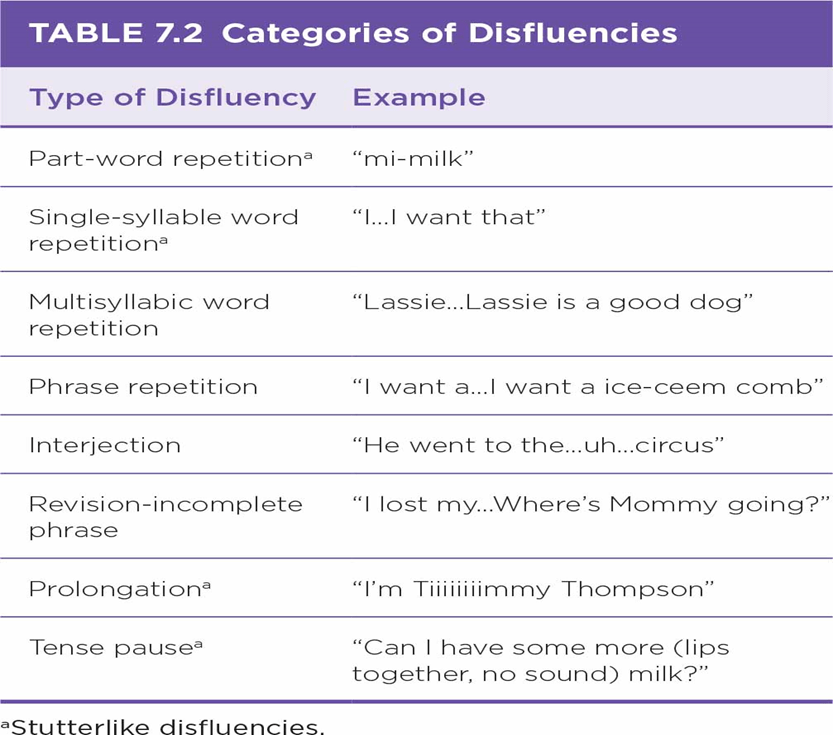
Define the terms disfluency and dysfluency.
What is:
Disfluency - normal (typical) or abnormal (atypical) disfluency.
Dysfluency - abnormal (atypical) disfluency.
List and discuss typical disfluencies (4) versus stuttering-like disfluencies (4).
What is:
Guitar, B. (2024). Stuttering: An integrated approach. Wolters-Kluwer.
Discuss functional (psychogenic) stuttering.
What is:
Functional stuttering usually has a late onset: teens or later; it typically appears after prolonged stress or a traumatic event; unlike malingering, functional stuttering is not a conscious behavior deliberately enacted; it may be accompanied by unusual secondary behaviors; it may occur as a lone symptom or accompanied by psychological or neurological signs.
What is the formula for calculating speaking rate?
What is:
% of syllables/time (in secs.) X 100 = rate of syllables per second
Severe stutterers may produce speech at a very slow rate, decreasing their communicative effectiveness; Individuals who both stutter and clutter may have excessively fast rates of speech, making them somewhat unintelligible.
Differentiate operant conditioning, classical conditioning, and avoidance conditioning.
What is:
Classical conditioning: Learning caused by the association of a neutral stimulus with a stimulus that strongly provokes a response, usually through a physiological or psychological process that occurs without awareness.
Operant conditioning: Learning caused when a behavior is immediately followed by a reward or punishment or the relief from punishment.
Avoidance conditioning: Learning that teaches an individual to engage in behavior that prevents an unpleasant consequence.
What is spontaneous or natural recovery?
What is:
Recovery that occurs without intervention.
Discuss the following avoidance techniques: circumlocutions, postponement, substitutions, and starters.
What is:
starters (beginning a word by saying another word or sound, such as “well” or “uh” just before saying it);
substitutions (substituting a word or phrase for another when stuttering is expected, as in “he’s my unc-unc-unc…my father’s brother”);
circumlocutions (talking all around a word or phrase when anticipating stuttering, as in “well, I went to…yes, I really had a good time there, I saw the Empire State Building”);
postponements (waiting a few beats or putting in filler words before starting a word on which stuttering is expected, as in “My name is………Bill”);
Discuss neurogenic acquired stuttering.
What is:
Neurogenic stuttering is caused or exacerbated by neurological disease or damage; the typical onset is after childhood; some etiologies include stroke, head trauma such as combat-related brain injury, tumor, disease processes such as Parkinson’s, drug toxicity; should be distinguished from increased normal disfluencies that sometimes accompany neurological problems.
When counting disfluencies, what is the percentage of SLD’s required to be atypical? What is the percentage for typical speech?
What is:
If child has more than 50% stutter-like disfluencies, more likely to be stuttering than normally disfluent; If child has more than three stutter-like disfluencies per 100 words, more likely to be stuttering.
What is trial therapy? When would you engage in it?
What is:
Trial therapy is a brief treatment for stuttering carried out during the evaluation to identify treatment techniques that seem particularly effective. Some trial therapies may take longer to have an effect than others. If the client immediately becomes fluent with trial therapy, functional stuttering may be suspected.
Name and define the (3) core behaviors.
What are:
1. repetitions - may be single-syllable word or part-word repetitions; word or syllable repeated more than two times, li-li-li-like this.
2. prolongations - sound or airflow continues but movement of articulators is stopped; prolongations as short as 0.5 second may be perceived as abnormal.
3. blocks - inappropriate stoppage of airflow or voicing; movement of articulators may be stopped; blocks may occur at any level—respiratory, laryngeal, and/or articulatory; blocks may be accompanied by tremors of lips, tongue, jaw, and/or laryngeal muscles; on average, stutterers stutter on about 10% of words while reading; on average, stutters last about 1 second.
What is a critical response? How does it relate to stuttering?
What is:
A negative response from a listener. Critical responses can increase anxiety and self-consciousness when in turn increases disfluent behaviors and may lead to avoidance behaviors. Critical responses undermine the PWS confidence and self-esteem.
Discuss cluttering.
What is:
Cluttering is sudden bursts of rapid speech that is difficult to understand and somewhat disfluent; people who clutter may have excess of normal disfluencies or co-occur with developmental stuttering; with effort and attention, speaker may be able to speak without cluttering; cluttering often accompanied by disorganized language (mazing) as well as learning and neuropsychological problems.
What is a stuttering event? How do you count it?
What is:
Stutter-like = part-word and single-syllable whole-word repetitions, tense pauses, and dysrhythmic phonations
Normal = multisyllable word repetitions, phrase repetitions, interjections, and revisions
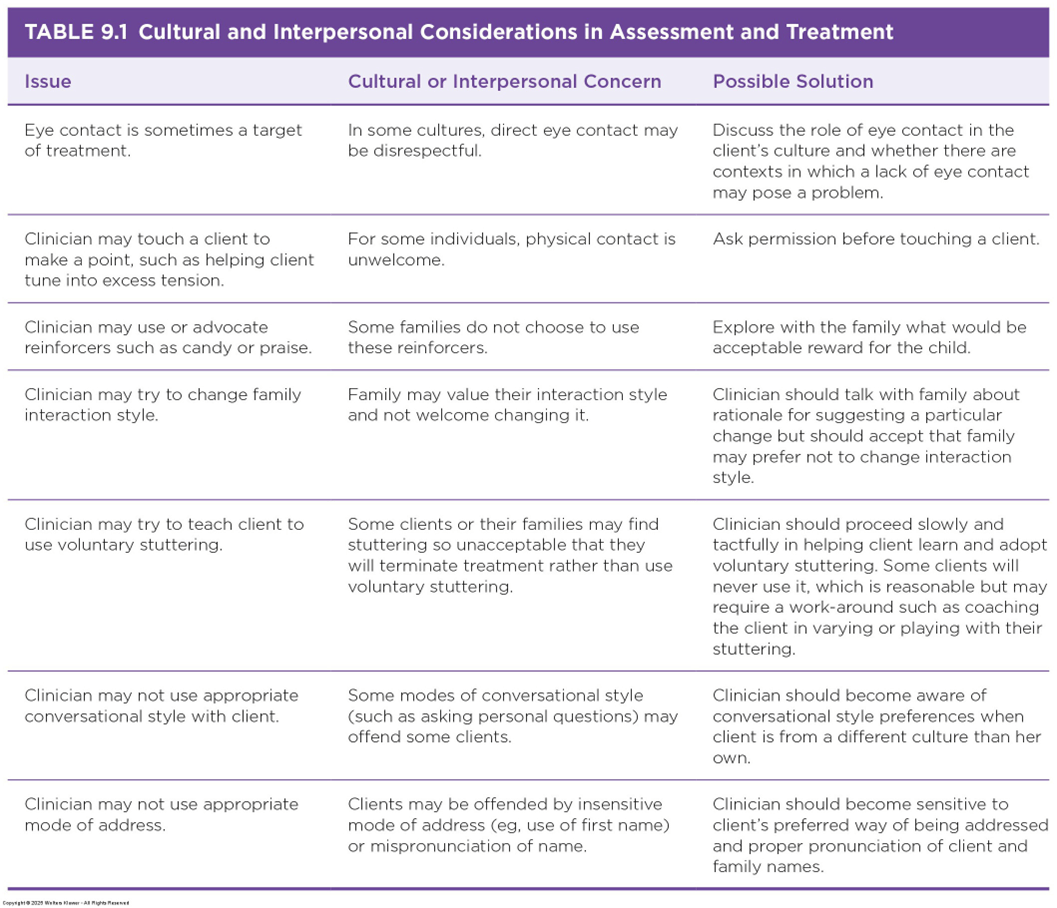
How might culture influence/impact the disorder? What are the implications in your professional practices?
Guitar, B. (2024). Stuttering: An integrated approach. Wolters-Kluwer.
Discuss the following avoidance techniques: anticipation, consistency, and adaptation
What are:
Anticipation: People who stutter can predict which words they will stutter on in a reading passage.
Consistency: People who stutter tend to stutter on the same words each time they read a passage.
Adaptation: People who stutter less each time they read a passage up to about six readings.
Discuss the following as they relate to stuttering: behavioral patterns, affective changes, cognitive influences.
What is:
Affective: Stutterers tend to be more anxious; Temperament: More sensitive or inhibited
Cognitive: Brain Structure and Function; Overactivation of right brain areas; Deactivation of left auditory cortex; Less dense white matter; Dysfunction of neural loop that sends signals from planning through to the motor cortex. This impacts the timing – initiation, continuation, or termination of motor functions.
Behavioral: General: Competition in neural development may lead to delayed speech-motor control; Physical: Physical and speech motor skill development may be delayed; Speech & Language: Sometimes language is underdeveloped – not always; Cognitive: Not a disorder of intellect, but those with cognitive limitations may be at a greater risk; Socio-Emotional: A variety of phases of social development -phases impact stuttering behaviors.
What is malingering?
What is:
Malingering is false stuttering. It may occur someone who would gain by being diagnosed with true stuttering. For example, to claim an insurance payout. Sometimes a malingerer is a person accused of crime, where they were fluent during crime, but claim innocence because they actually stutter and wouldn’t have been fluent.
Differentiate SSI and OASES.
What is:
The most commonly used measure of severity is the Stuttering Severity Instrument (SSI-4) which captures the severity of overt stuttering behaviors as a composite of three important dimensions: frequency, duration, and physical concomitants.
The Overall Assessment of the Speaker's Experiences (OASES) is a questionnaire designed to assess the impact of stuttering on a person’s life.
Discuss why it is important to make evaluation a continuous part of the intervention process.
What is:
Ongoing evaluation is important during the intervention process to hone your judgment, to be able to change decisions and redirect therapy as additional information and understanding become available, and because stuttering is highly variable, and no individual can be completely evaluated in just an hour or two.