What is the correct order of segments of the small intestine?
"DJ Ileum" - Duodenum, Jejunum, & Ileum
Quality of pain in the abdomen?
Cramping

What is the basic/simple test to find SBO?
X-ray of the abdomen
What is the purpose of the nasogastric tube?
To alleviate nausea, vomiting, and bloating
.png)
How does the Ondansetron work?
By blocking serotonin receptors centrally in the chemoreceptor trigger zone, and vagal nerve terminal in intestines. The prevention of Serotonin release in the small intestine reduces vomiting.
What are the common causes of SBO?
Scar tissues (adhesions), hernias, and cancer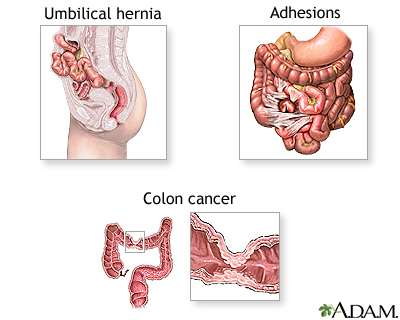
What causes abdominal distention?
Accumulation of fluid and gas

What test is the most accurate test to diagnose SBO?
CT scan of the abdomen
What are some good sources of potassium?
Bananas, oranges, potatoes, and brown rice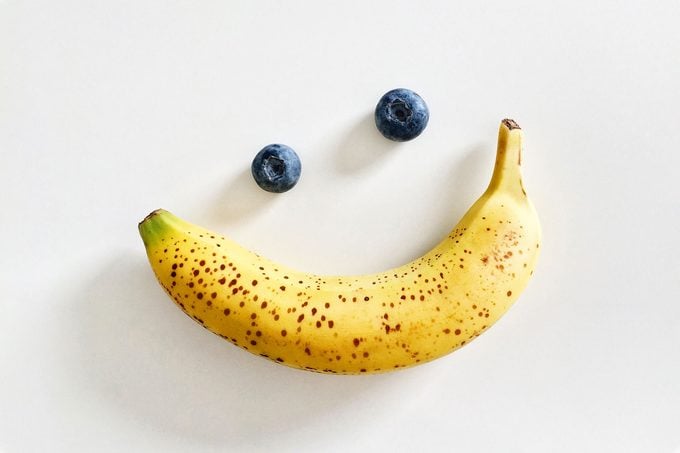
Why 0.9% NaCl is the standard fluid given in both boluses and fluid maintenance?
0.9% NaCl is isotonic solution, when given through IV no net movement of fluid or electrolyte into or out of the cells, thereby, no necessary swelling or shrinking of the cell when infuse:
Can be given in most situations such as dehydration, hyponatremia, fluid maintenance, hypotension with shock
What are the potential complications of SBO?
Electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, renal impairment, bowel ischemia/necrosis, perforation, and sepsis/septic shock.
What color is the patient's vomit? What is it?
Dark green, bile

What analysis will be done to diagnose SBO?
A complete blood count and electrolyte analysis

The CDC currently recommends how much sodium per day?
No more than 2,300mg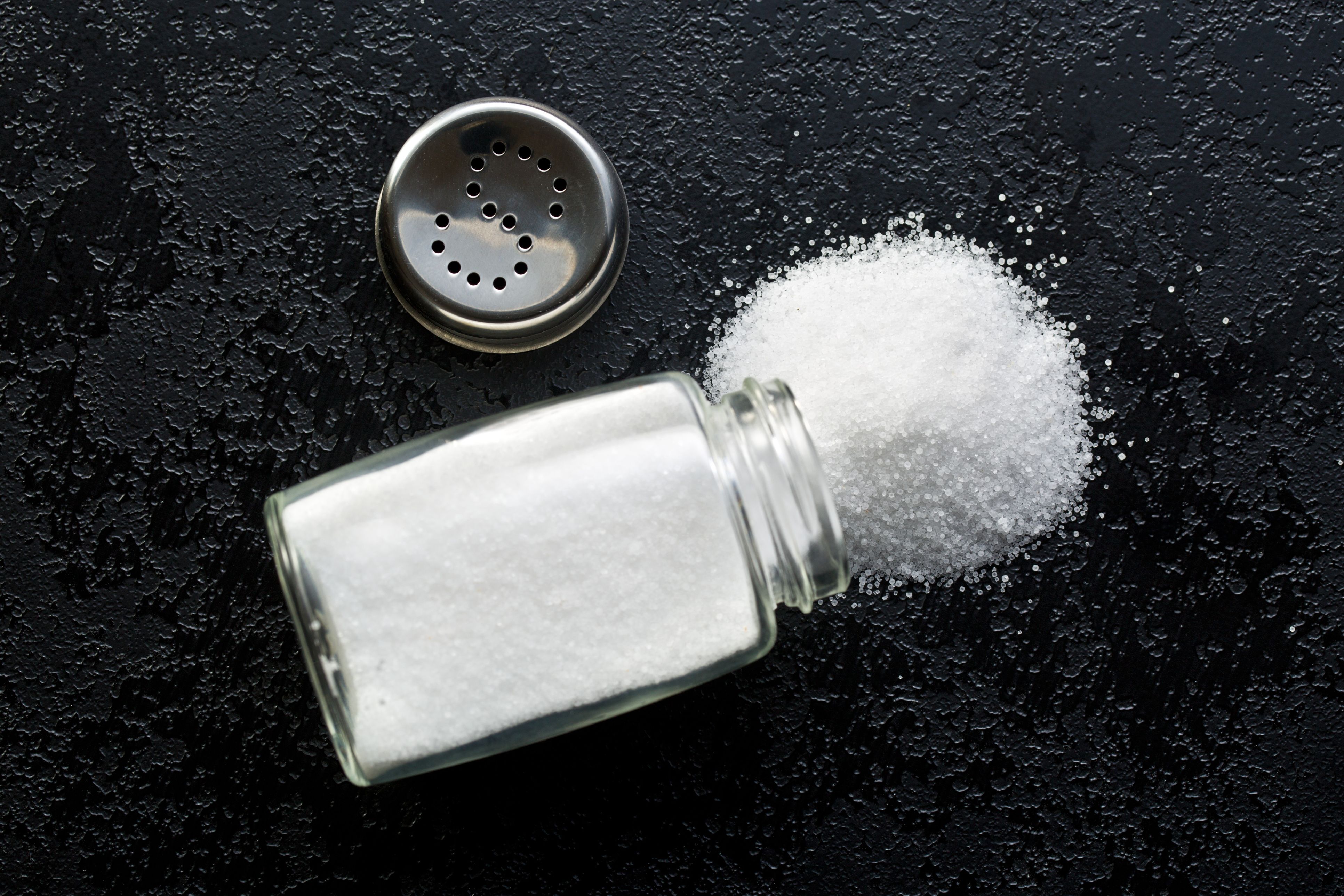
What is the onset of Morphine on IV route, its peak and duration?
Onset is rapid, peak is 20 minutes, and duration is 4-5 hours