You press one of Snoopy's skin lesions against a glass slide, stain it with Wright-Giemsa, and see the cells in the following image.
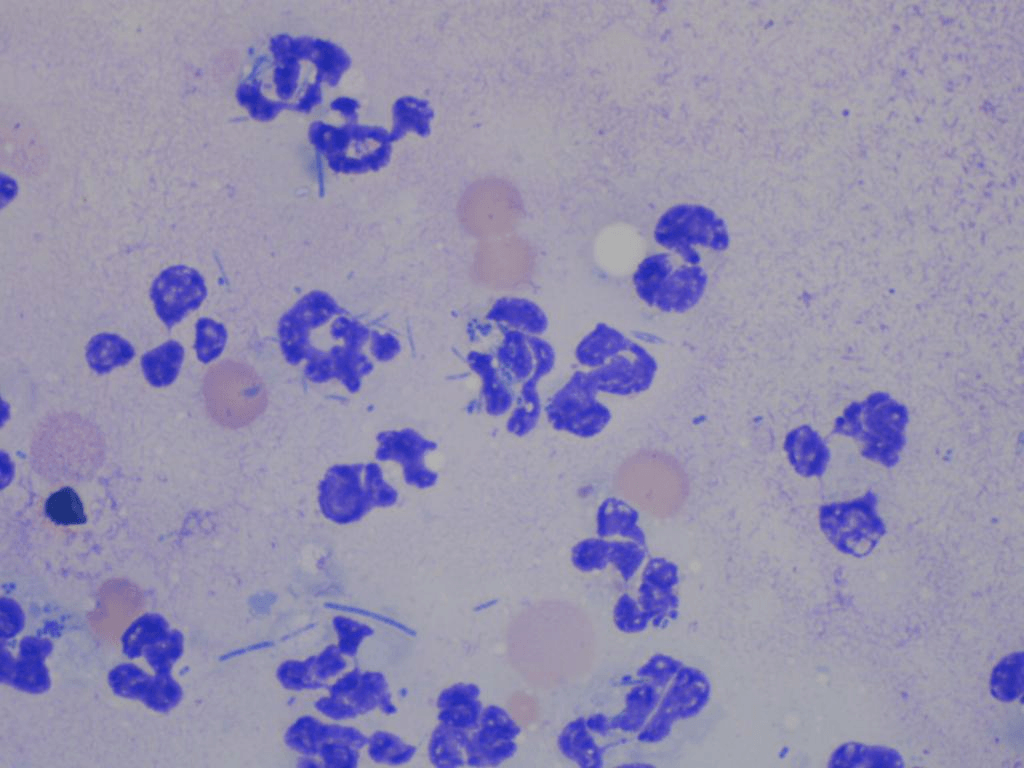
What are neutrophils?
Skin is primarily composed of this protein.
What is keratin?
When performing your physical exam on Snoopy, you lightly touched his lateral thorax and noticed that his skin twitched. The skin twitching was caused by contraction of this muscle.
What is the cutaneous trunci?
Axons are coated with this fatty substance, which helps to accelerate the speed of information transfer along the axon length.
What is myelin?
Snoopy's skin lesions arose abruptly with a short clinical course, indicating that it is likely a(n) _____ condition.
What is acute?
This is the main activated (cleaved) complement component, which has a potent chemotactic effect on neutrophils.
What is C5a?
This layer of the epidermis consists of several layers of flattened cells that contain keratohyalin granules.
What is the stratum granulosum?
You notice that many of Snoopy's skin lesions are distributed along the eyes, nose, and muzzle, which is best described as this directional term.
What is rostral?
In the diagram below, this structure is indicated by #2.
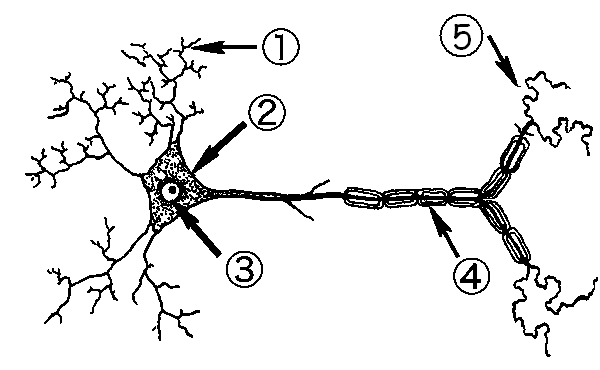
What is the cell body?
This is the most common cause of puppy pyoderma and is a normal skin inhabitant in dogs.
What is Staphylococcus pseudintermedius?
This structure is highlighted by the star in the following image of a macrophage, and binds to antigens.
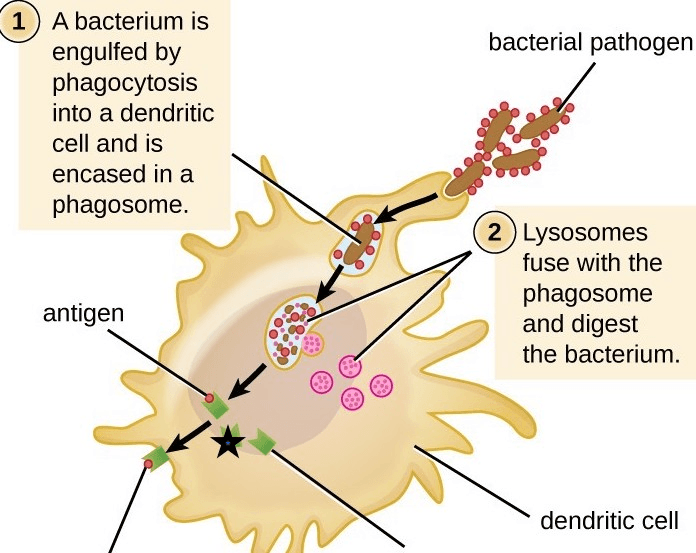
What is MHC II?
This structure is highlighted by the black arrow in this histology image of canine skin.
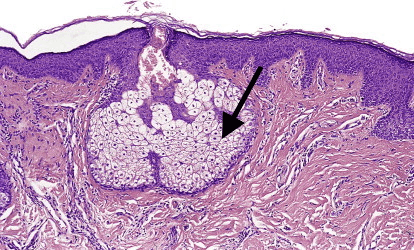
What is a sebaceous gland?
The axillary lesions on Snoopy extend along the proximal forelimb to the biceps brachii muscle, which is innervated by this nerve.
What is the musculocutaneous nerve?
In the diagram below, these structures are indicated by #1 and this is their function.

What are dendrites, and what is to transmit electrical impulses to the neuronal cell body?
The structure shown below is an important differential diagnosis for skin lesions in young puppies.
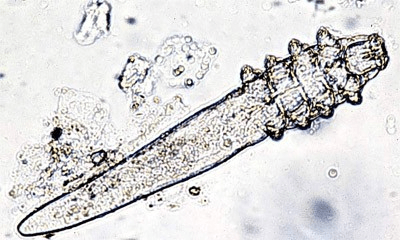
What is demodex (mite)?
Neutrophils function to primarily defend against this type of pathogen.
What are bacterial organisms?
You examine a biopsy sample of one of Snoopy's skin lesions and notice the cells highlighted by the arrows. These cells are responsible for producing pigment in the skin.
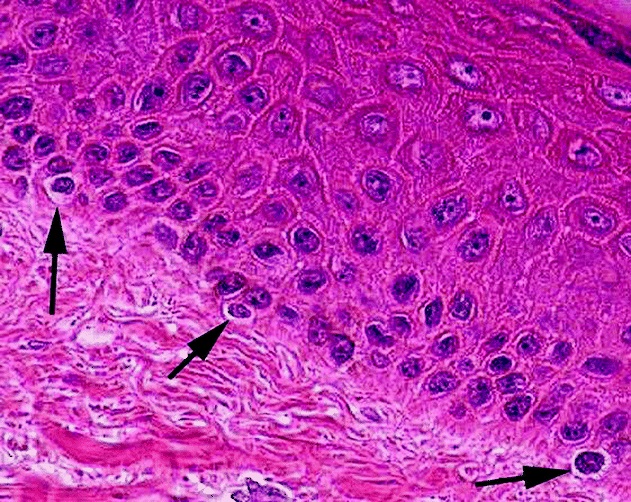
What are melanocytes?
You want to use your "doctor words" to describe the distribution of the skin lesions to Snoopy's parents, and many of these lesions are on the abdomen. What is the best directional term for the area indicated by the black arrow?

What is ventral?
This ion is necessary for neurotransmitter-containing synaptic vesicles to release their contents by exocytosis.
What is calcium?
After initial physical examination, this is an appropriate next diagnostic step for Snoopy.
What is skin lesion impression smear/fine-needle aspirate?
What is culture of the lesions?
What is skin biopsy?
These are the complement activation pathways that produce the lysis and death of bacteria without antibody participation.
What are the alternative and lectin pathways?
This is the name for specialized protein complexes that localize to intercellular junctions in the skin.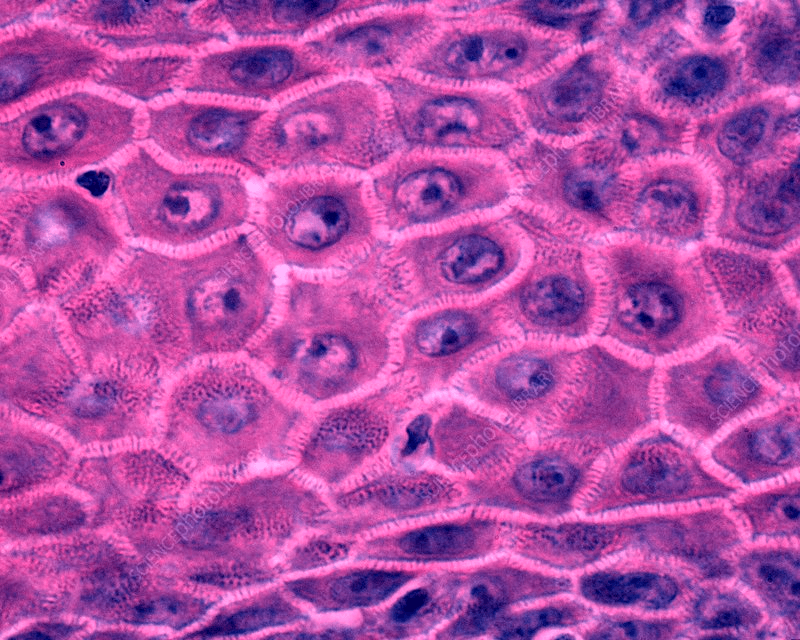
What are desmosomes?
This peripheral (palpable) lymph node would likely be enlarged in Snoopy, given his extensive facial and ventral skin lesions.
What is the prescapular lymph node?
This cell membrane pump helps to maintain resting membrane potential, and does so in this manner.
What is the Na+/K+ pump?
Pumps three Na+ out of the cell for every two K+ inside of the cell.
This is often a first line of treatment for puppy pyoderma.
Topical treatment, e.g. medicated shampoo.
All 3 complement pathways converge to activate this component, which generates the terminal complement complex.
What is C3?
The structure in the center which can be simple or compound in different animal species. 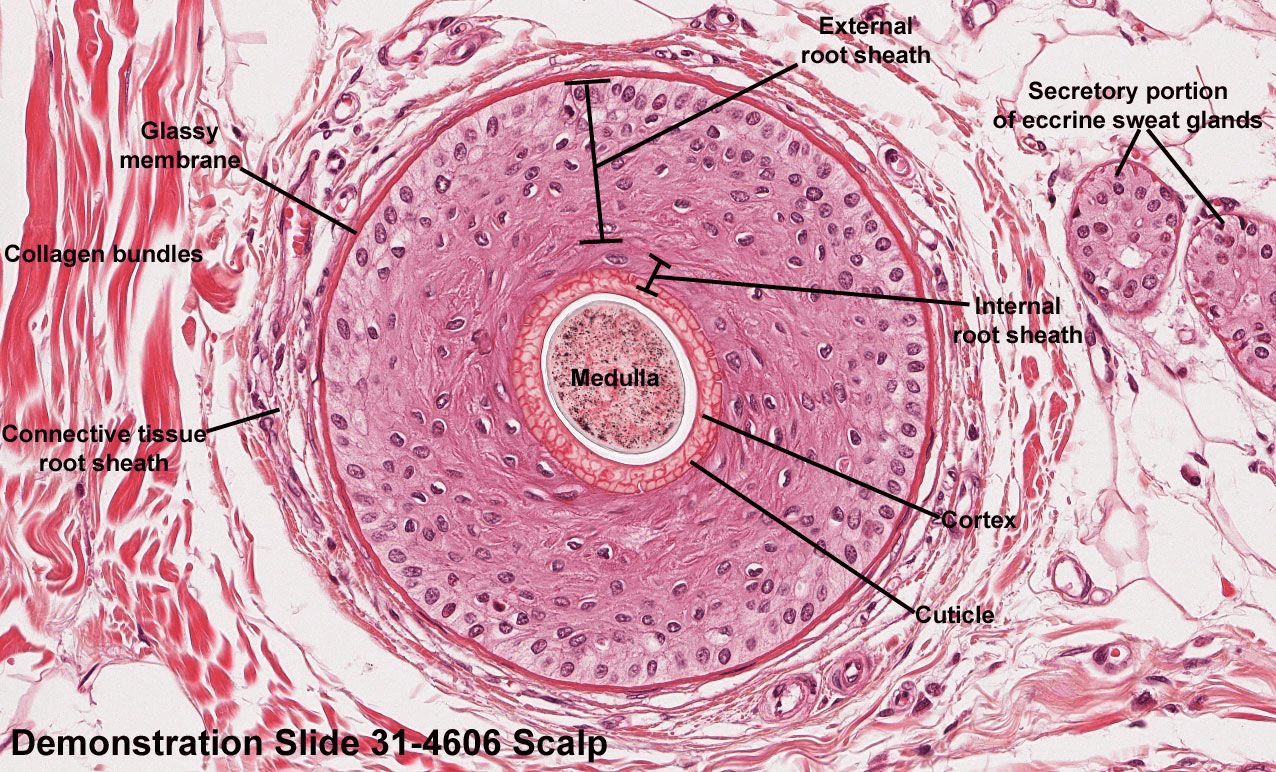
What is hair follicle?
These are the origins and insertions of the biceps brachii muscle.
What are the supraglenoid tubercle and the ulnar and radial tuberosities?
These are the two components of the diencephalon in the central nervous system (CNS).
What are the hypothalamus and thalamus?
This is the appropriate dermatologic/pathologic term for accumulation of pus in the epidermis?
What are pustules?
This component of bacterial cell walls stimulates the production of inflammatory cytokines from neutrophils, such as IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-a.
What is lipopolysaccharide?
This is the name for the sebaceous gland of the eyelid.
What is the Meibomian gland?
This is the action of the muscle indicated by the yellow star in the image below.
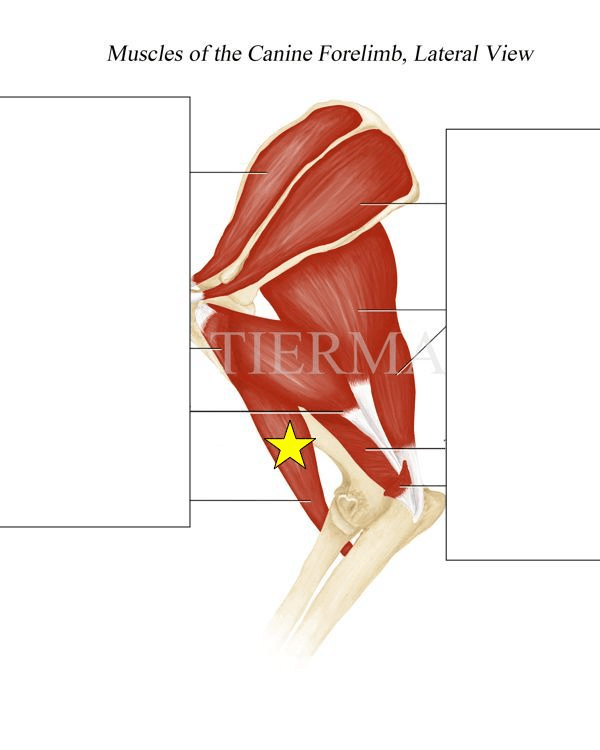
What is to flex the elbow joint?
In the neuron, generation of ATP results from the nearly exclusive metabolism of oxygen and this substance.
What is glucose?
This would be the best time to schedule the next appointment with Snoopy in order to reassess the skin lesions and administer the last DHLPP booster (he is 3 months old).
What is in 4 weeks?
These are the components of the complement membrane attack complex (MAC).
What are C5b, C6, C7, C8, and C9?
This is the name of the muscle found in the dermis whose contraction causes "goosebumps."
What is the arrector pili muscle?
These two muscles attach at the structure indicated by the star.
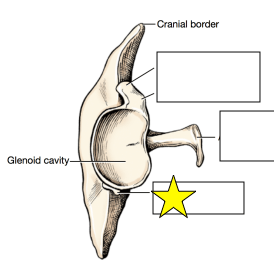
What are the teres minor and the long head of the triceps?
In terms of ions, this is what happens during the repolarization phase of an action potential.
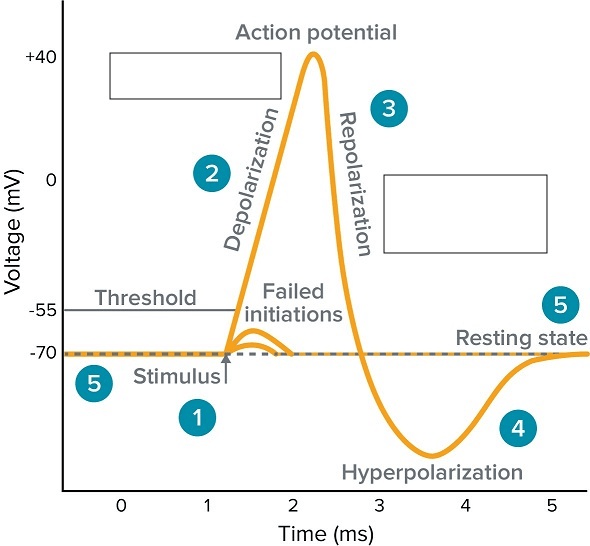
What is potassium efflux?
This substance is produced by the ventricles of the brain and can be analyzed microscopically to test for CNS infection, inflammation, or neoplasia.
What is cerebrospinal fluid?