An elevated level of this electrolyte can be related to kidney stone formation.
What is Ca++
The main electrolyte in the extracellular fluid which promotes retention of water.
What is sodium (Na+)?
Type of IV solution, such as 0.9% NaCl and Ringers Lactate (LR -- Lactated Ringers), which resembles the concentration of plasma and increases only extracellular fluid volume.
What is an isotonic solution. Watch for cardiac overload if fluid is overloaded beyond client's tolerance?
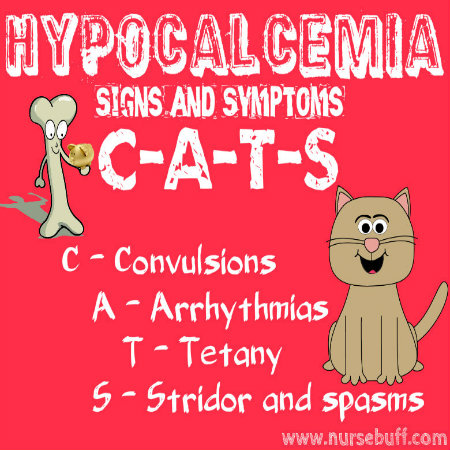
Too little of this electrolyte is characterized by Trousseau's/Chvostek's signs, convulsions, arrhythmias, tetany, spasm/stridor ("CATS")
What is hypocalcemia. Normal range: 8.5-10.5(serum)
Nursing interventions for hypo and hypermagnesemia
What is: Hypo: assure safety (monitor confusion, seizure precautions), VS,educate client about intake of foods rich in magnesium
Hyper: Assess VS, check DTRs frequently, patient teaching regarding magnesium containing OTC meds(antacids and laxatives)
Major cation of the intracellular fluid. A low level of this cation can cause paralytic ileus and heart rhythm changes. An elevated level can cause ECG changes... even cardiac arrest.
What is K+
Weak, rapid pulse and HR, Flattened neck veins, ↑ temperature, and cool clammy skin are clinical manifestations of this condition.
What is fluid volume deficit (FVD)
D5NS (0.9%) and D51/2NS (0.45%) are examples of what type of fluid?
What are hypertonic solutions. Hypertonic solutions increase osmotic pressure and draw fluids from cells. Watch for cellular dehydration if the amount infused is beyond the client's tolerance.
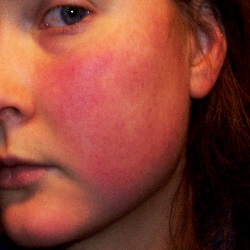
Too much of this electrolyte is characterized by flushing and warmth of the skin hypoactive reflexes
What is hypermagnesmia. Normal range: 1.6mEq/L- 2.6mEq/L
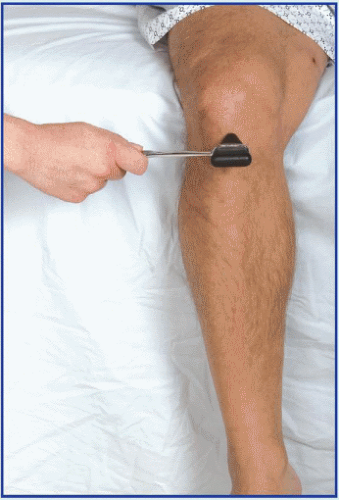
Name nursing interventions for hypo and hypercalcemia.
Hypo: seizure precautions if hypocalcemia severe, monitor airway, take safety precautions, educate those at risk for osteoporosis about need for dietary calcium intake. Hyper: safety precautions if confused, increase mobilization, encourage bulk in diet, encourage fluids to prevention of renal stones
These two electrolytes work together and move fluids and electrolytes through fluid compartments.
What is Na+ and Cl-
↓ Hematocrit, ↓ BUN, dilute urine AND ↓ Specific gravity are clinical manifestations of this condition.
What is fluid volume excess (FVE)
Too much of this electrolyte parallels symptoms of hypocalcemia.
What is hyperphosphatemia.
Normal range is 2.5-4.5mg/dL
Name nursing interventions for hypo and hyperphosphatemia?
Hypo: assessment, encourage foods high in phosphorus, gradually introduce calories for malnourished pts. receiving parenteral nutrition
Hyper: assessment, avoid high phosphorus foods/phosphate containing laxatives, signs of hypocalcemia
Depletion of this electrolyte is seen in alcohol withdrawal. Watch for paresthesia, joint stiffness, seizures, and impaired oxygenation
What is phosphate?
Fatigue, restlessness, altered level of consciousness, intense thirst, dry sticky mucus membranes,decreased urine output, low-grade fever, seizures -> coma
What is hypernatremia?
Drop in temperature around IV site, local swelling at the site. a slowed infusion, pale skin and a damp IV dressing can indicate which potential complication of IV therapy?
What is infiltration. Infiltration is when the IV fluid "infiltrates" into the surrounding tissues and does not stay in the vasculature. If the IV infiltrates, stop the infusion immediately. Clamp the tubing. Apply a sterile gauze pad over the site without putting pressure on the vein.
Too little of this electrolyte makes you feel nauseous, lethargic, and confused with muscle cramps/twitching, even seizures due to cerebral edema
What is hyponatremia. Normal range: 135-145mEq/L
Name nursing interventions for hypo and hypernatremia
Hypo: assessment of GI/CNS symptoms, monitor fluid losses and gains, encourage dietary sodium and fluid intake Hyper: assessment of CNS symptoms, assess for OTC sources of sodium, offer and encourage fluids to meet pts. needs, provide sufficient water w/ tube feedings
Loss of this cation may occur with prolonged nasogastric suction, chronic alcoholism which may lead to neuromuscular irritabilty, disorientation,mood changes and dysrhythmias.
What is Mg++?
Name 5 specific nursing interventions for clients with Hypernatremia and Hyponatremia
Hypernatremia: Monitor I&O, Monitor serum sodium level, VS and restrict sodium intake(IV solutions that do not contain sodium) Seizure precautions if severe
Hyponatremia: Monitor I&O, Monitor serum sodium level,Increase sodium intake,Administer IV saline infusion Seizure precautions
Type of IV catheter which places fluid or drug straight into the central circulation allowing for long term therapy.
What is a Central Venous Access Device(CVAD)

Too much of this electrolyte spells, "MURDER"
What is K+ (3.5-5.0mEq/L). Manifestations of hyperkalemia include: M (muscle weakness), Urine (oliguria/anuria), Respiratory Depression, ECG changes, Reflexes (diminished)
Name nursing interventions for hypo and hyperkalemia
Hypo: assessment of ECG changes, administer oral supplements as ordered, patient teaching to increase dietary potassium, nursing care related to IV potassium administration
Hyperkalemia: assessment of serum potassium levels, monitor meds affects, dietary potassium restriction