What is the dominating school of thought today?
Neoclassical
An increase in the price causes a decrease in quantity demanded. Law of ___?
Demand
Consumers want to buy cheaper goods/ services from abroad
Import
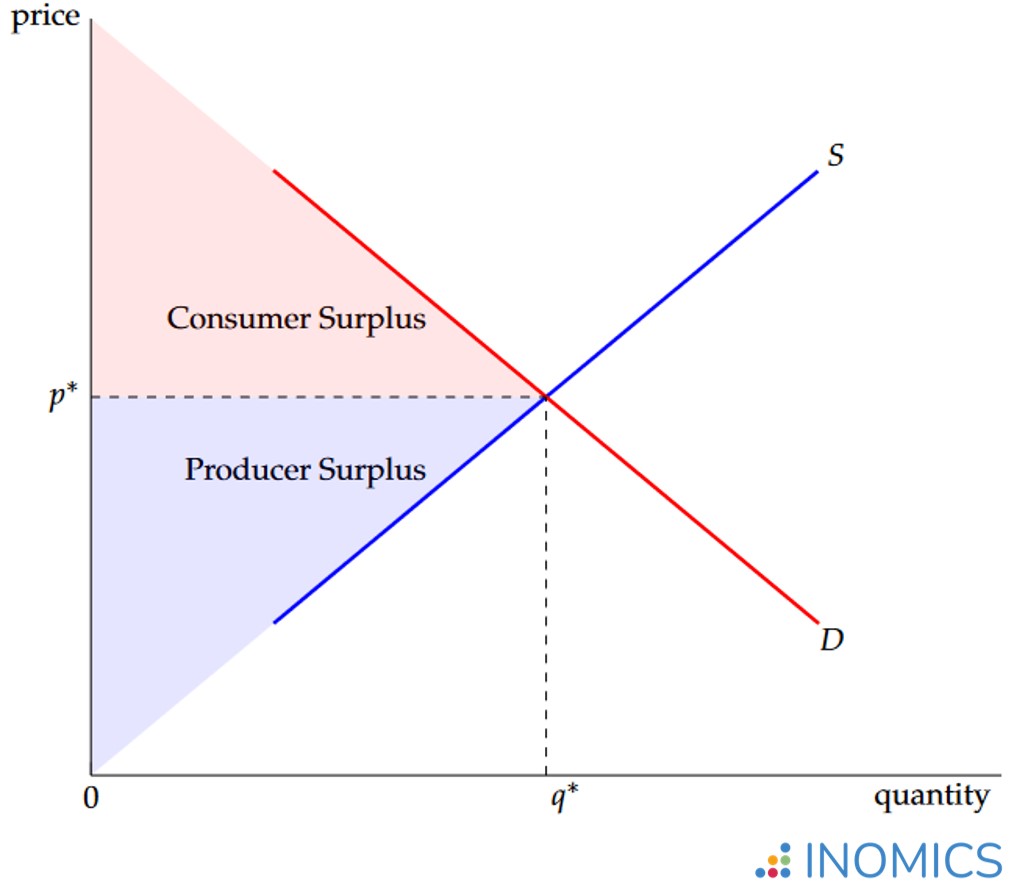
Total surplus = ?
consumer surplus + producer surplus
What is Katie's Dogs name?
Emma!
“alternative” - catch-all for any school that differs from neoclassical
hetrodox
That price where the amount firms want to sell is equal to the amount people want to buy
equilibrium
Sellers can make more money selling abroad
Export
Consumer surplus =
Demand Curve - P*
A line/graph showing all the combinations of output possible given resources and technology
Production Possibilities Frontier
Neoclassical economic systems are defined by answering 3 questions, what are they?
What and how much to produce?
How to make goods and services?
Who gets these goods and services?
Double points if you explain how you determine the change in price and quantity equilibrium when both curves shift.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/IntroductiontoSupplyandDemand3_3-389a7c4537b045ba8cf2dc28ffc57720.png)
This is what a good/service sells for in the world market
Producer Surplus
P* - Supply Curve
All the employees own the business together
Workers "buy in" with money to the business when they start
Each are paid a share of the profits after expenses are taken care of
Worker co ops
Consumers decide what is made via demand
Firms decide how to make goods and services by focusing on profit-maximizing methods
Consumers get the goods and services if they can afford it
Ultimately, it's the individuals (consumers and firms) that make decisions
Capitalism – neoclassical
Name the determinants of supply
Change in number of producers
change in imput costs
change in producer expectations of the future
change in technology or productivity
Why do nations trade?
To enjoy a higher standard of living without purchasing more scarce economic resources
what happens when P* moves to the right
Producing with less opportunity cost than another firm. What do you have?
The comparative advantage
Typically, what most people think of as "communism" I.e. ussr
Government controls inputs
Workers made products
Government controlled profit
State capitalism – heterodox
Name the determinants of demand (five or six)
Change in number of consumers
change in consumer expectations of the future
change in price of a related good/substuite
chance in consumer income
change in consumer taste and preferences
exchange rate fluctuation
What are government tools to restrict trade?
Tariffs
Quotas
Embargos
Draw a producer and consumer surplus graph on the board.
What is Katelyn's major
Marketing and econ!