What is the purpose of ankle ligaments?
Helps to limit motion
Sprain vs strain vs fracture
- Ankle sprain: tear in an ankle ligament
- Strain: pulling of muscle
- A broken ankle is a fracture or multiple fractures of one or more bones in the ankle
What are the Ottawa ankle Rules
Ottawa ankle rules are a set of guidelines for clinicians to help decide if a patient with foot or ankle pain should be offered X-rays to diagnose a possible bone fracture.
Ankle X-ray is only required if:
- There is any pain in the malleolar zone; and,
- Any one of the following:
- Bone tenderness along the distal 6 cm of the posterior edge of the tibia or tip of the medial malleolus, OR
- Bone tenderness along the distal 6 cm of the posterior edge of the fibula or tip of the lateral malleolus, OR
- An inability to bear weight both immediately and in the emergency department for four steps.
Is this injury acute or chronic?
What are the TART presentations for acute vs chronic?
Acute
T= Texture: Hot, moist, boggy
A= asymmetry is present. Probably more obvious compared to chronic
R= Restriction pain with motion
T= Tenderness: intense and sharp
Chronic
T= cool, dry, ropy
A= asymmetry present
R= Decreased to no pain with movement
T= Achy and dull
Name as many tarsal bone of the foot as you can.
How many metatarsals on each foot?
How many phalanges on each foot?
Tarsal bones:
- Talus—articulates with the tibia and bears most weight
- Calcaneus—largest tarsal bone—this is where gastrocnemius and solus attach making the Achilles tendon
- Navicular--- in front of talus
- Cuboid—in front of calcaneus
- Medial cuneiform
- Intermediate cuneiform
- Lateral cuneiform
5 metatarsals
14 phalanges
Great toe: proximal and distal phalanges with interphalangeal joint in between.
Lesser toes: proximal, middle, and distal phalanges. With PIP and DIP joints
What bones make up the ankle joint?
Tibia, fibula, and talus 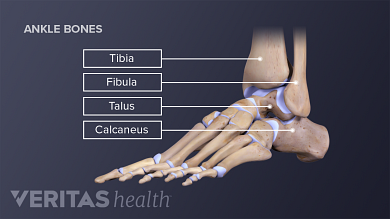
The greater trochanter is on what bone?
Where is the lateral femoral condyle?
Femur
Methods for treatment of ankle sprains
- Rest. Avoid activities that cause pain, swelling or discomfort.
- Ice. Use an ice pack or ice slush bath immediately for 15 to 20 minutes and repeat every two to three hours while you're awake.
- Compression. To help stop swelling, compress the ankle with an elastic bandage until the swelling stops.
- Elevation. To reduce swelling, elevate your ankle above the level of your heart, especially at night.
Ligaments are formed from connective tissue. How does that relate to the importance of range of motion exercises during the healing process
Ligaments are the connective tissue that's located between the bones. Over time, ligaments can become less elastic and result in reduced flexibility. In the case of our pt-- the healing process may diminish flexibility if not moved properly
Aside from tenderness of the right anterior talofibular ligament, Ms. Arcoleo also has mild tenderness over her right deltoid ligament. What is the purpose of the deltoid ligament?
To provide medial stability to the tibiotalar joint by providing a firm fixation between the tibia and talus
Between which two bones is the anterior talofibular ligament?
What is the purpose of this ligament?
What is the significance of this ligament?
Anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL): attaches to talus and fibula. Limits anterior movement of the foot. Also limits inversion during plantar flexion. **most commonly sprained ligament **
See pic
What is RICE?
Hint: if the question before this one was chosen then you already know the answer (hopefully).
Hint: if the question before this one was not chosen then you know the answer.
Rest, ice, compression, elevation
Why not heat? When do you apply heat?
Ice: for acute injuries. Use on joints, bones, and to reduce swelling
Heat: for muscle and soft tissue pain and tightness
This patient did not break skin but if she did outline regeneration vs scar tissue formation.
Regeneration:
Some tissues are able to replace the damaged components and essentially return to a normal state; this process is called regeneration.
Regeneration may occur by proliferation of differentiated cells that survive the injury and retain the capacity to proliferate.
Labile, stable, permanent cells
Inflammation:
Breakdown products of complement activation, chemokines released from activated platelets, and other mediators produced at the site of injury function as chemotactic agents to recruit neutrophils and then monocytes over the next 6 to 48 hours. Ex: TNF-alpha and IL8
M1 macrophages for "clean-up" -- phagocytes
Cell proliferation:
Epithelial cells respond to locally produced growth factors and migrate over the wound to cover it up.
Endothelial cells and pericytes proliferate to form new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis
Fibroblasts proliferate and migrate into the site of injury and lay down collagen fibers that form the scar.
Formation of granulation tissue: Migration and proliferation of fibroblasts and deposition of loose connective tissue, together with the vessels and interspersed mononuclear leukocytes, form granulation tissue. M2 is prone to promote angiogenesis and neovascularization.
Deposition of connective tissue. Granulation tissue is progressively replaced by deposition of collagen.
Ankle joints!
There are two major ones.
Hint: the first helps with dorsi and plantarflexion. The other helps with inversion and eversion of the foot
- tibiotalar joint: articulation of tibia with talus forms a mortis joint with medial and lateral malleolus with the talus in between allows for dorsiflexion or plantarflexion
- subtalar joint (aka talocalcaneal joint): between talus and calcaneus allows for inversion and eversion of the foot
Bones between the posterior talofibular ligament?
purpose of this ligament?
Posterior talofibular ligament: attaches to the fibula and talus on posterior surface. Prevents posterior translation of foot on tibia and prevents rotatory subluxation of the talus.
Two idiots are painting the roof of the barn when it catches on fire. The only way down is to jump into the manure pile.
The first idiot says, I'll jump first and tell you how deep it is. He jumps, and a few seconds later the second idiot hears, it's only ankle deep!
The second idiot jumps and says, What on earth? I'm up to my neck!
What did the first idiot respond?
And the first idiot says, Well you jumped feet first
What is the importance of ankle range of motion exercises after injury?
Strength: Strengthening the muscles that support your lower leg, foot, and ankle will help keep your ankle joint stable. Keeping these muscles strong can relieve foot and ankle pain and prevent further injury.
Flexibility: Stretching the muscles that you strengthen is important for restoring range of motion and preventing injury. Gently stretching after strengthening exercises can help reduce muscle soreness and keep your muscles long and flexible.
Target Muscles: The muscle groups of the lower leg are targeted in this conditioning program, as well as the tendons and ligaments that control movement in your feet
The foot is supplies by which arteries from the leg?
Supplied by anterior and posterior tibial arteries
Anterior tibial artery: becomes dorsalis pedis artery
After a year long struggle, my diabetic uncle just had both legs amputated below the ankle.
I guess you could say he was...
de-feeted
What are the two arches of the foot and what is their purpose?
Arches of foot: help with absorption of shock
- Medial longitudinal arch: higher
- Lateral longitudinal arch: more lateral
*both course from back of foot to metatarsals
Inversion vs supination
Eversion vs pronation
Inversion vs supination
- Inversion is the movement of foot toward midline that acts on subtalar joint
- Supination: inversion + plantarflexion (at tibiotalar joint) and adduction (of forefoot)
Eversion vs pronation
- Eversion: at subtalar joint where plantar surface of foot faces wall.
- Pronation: Eversion + dorsiflexion (at tibiotalar joint) and abduction (of forefoot)
I don't regularly roll a joint, but when I do...
it's usually my ankle.
What else should a physician worry about when a patient presents with a serious injury dealing with fracture/sprain?
Hypoxia and nerve damage. Just from the dorsals pedis artery the dorsal portion of the foot is supplied by a lot of arteries that could potentially be damaged at sites of injury.
The plantar aponeurosis starts from calcaneus and courses forward and knits itself into 5 digits. So it is a flat structure on the bottom of the foot. What is the importance of this structure?
Hint: flat footed people feel pain in this structure when running or walking quickly or for long periods of time.
- Purpose to maintain longitudinal arches during pressure. ALSO big toe flexion tightens the plantar aponeurosis while arch gets bigger (windlass mechanism)-->pulls calcaneus toward head of metatarsals.
- **Important because at heal strike the great toe extends to provide stability for weight bearing