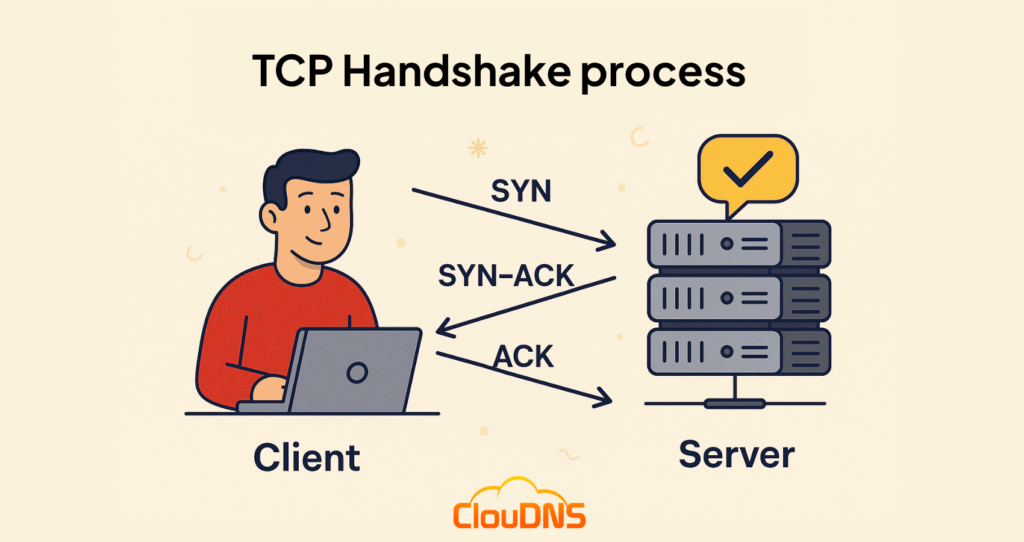
Decrypt and define the concept of TCP?
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is a transport protocol that provides reliable data delivery.
What is the MDA , give a transcript ?
Model Driven Architecture is an approach to software development in which models become the main artifact, and code is created automatically based on these models.
What does decomposition mean in a modular structure?
Decomposition is the process of dividing a complex system into smaller, independent modules that solve individual parts of a problem.
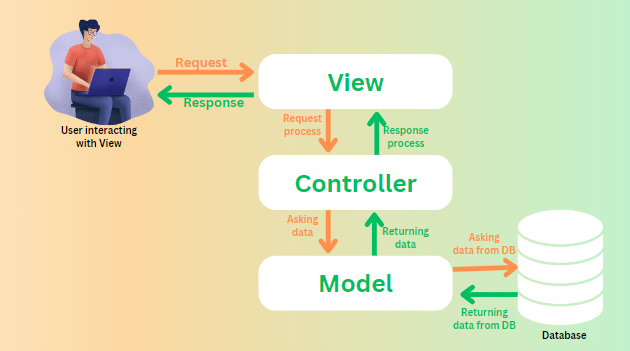
Decrypt and define the MVC ?
One of the most well-known structural template for a project is Model-View-Controller (MVC) is a template developed as part of the Smalltalk-80 programming environment.
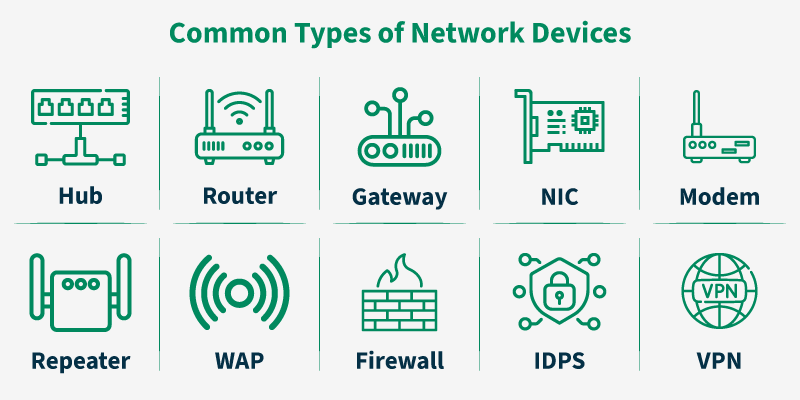
What network tools do you know?
•Router: Defines the packet transmission path between networks.
•Switch: Connects devices in a local network, transmitting data only to the addressee.
•Modem: Provides internet connection via telephone lines or fiber optic.
•Access Point: connects wireless devices (Wi-Fi).
•Network adapter: Provides a physical connection of the computer to the network.
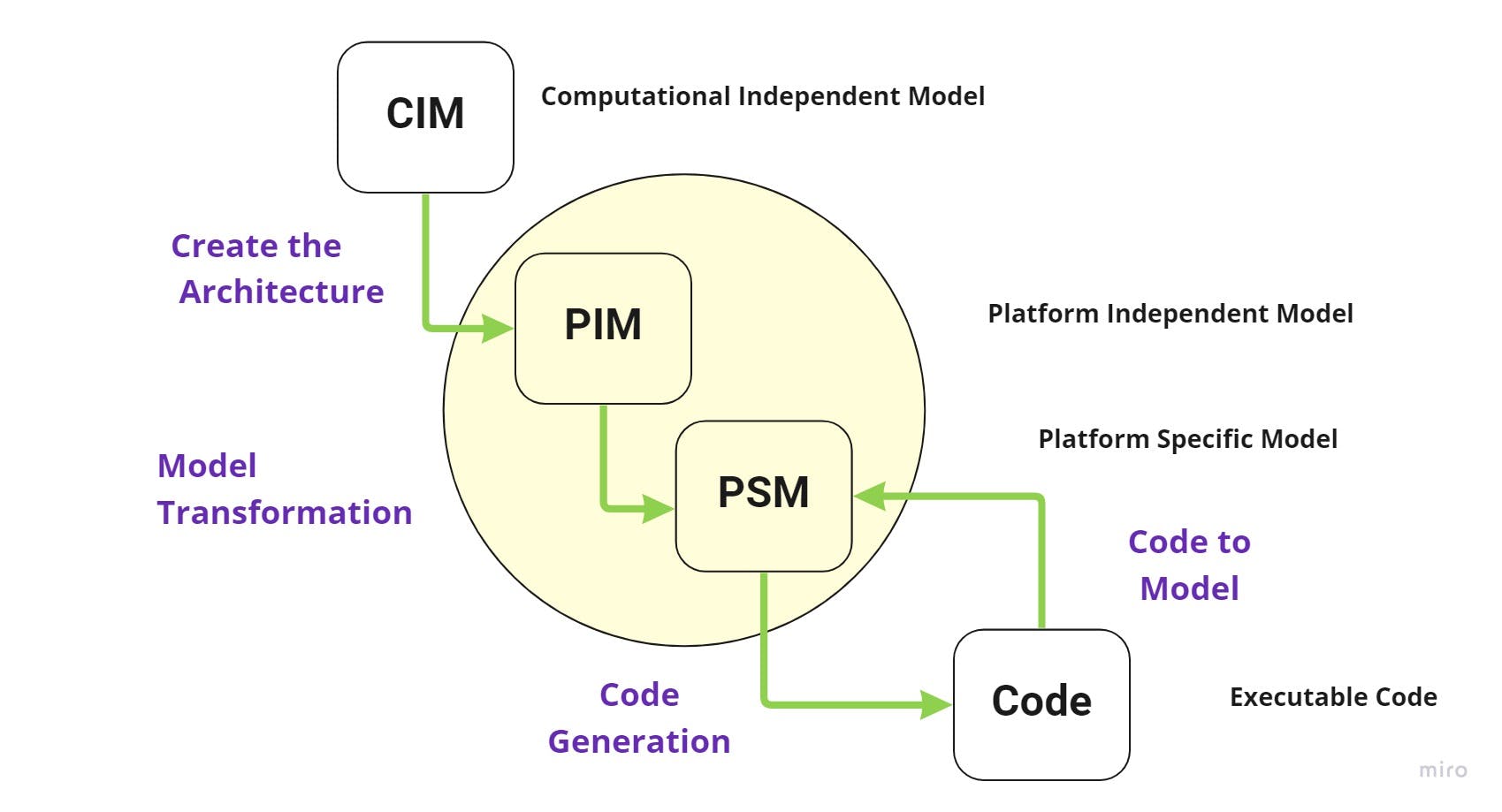
Describe the types of models in MDA
PIM (Platform Independent Model) is a logical model that does not depend on technology.
CIM (Computing Independent Model) is a business model that describes what is happening in an organization.
PSM (Platform Specific Model) is an implementation model that takes into account a specific platform.
Describe the form of abstraction - generalization and classification
Generalization - creating a more general concept from several particular ones. The cat + Dog → Animal
Classification - Dividing objects into groups based on attributes.Animals → Domestic / Wild
What are the 6 main attributes of Information System quality?
Main attributes:
Reliability
Security
Scalability
User-friendliness
Performance
Maintainability
Describe the protocol levels
7 levels:
•Physical: transmission of electrical/optical signals.
•Channel-based: organization of communication between neighboring nodes (Ethernet).
•Network: Packet routing (IP).
•Transport: delivery control (TCP, UDP).
•Session mode: supports dialogs between applications.
•Representations: data format conversion (encryption, encoding).
•Application: the work of programs (HTTP, FTP, SMTP).
The MDA Development Lifecycle
What is syntax and semantics?
Syntax determines how language constructions should be written correctly (How is it written correctly?), while semantics determines the meanings of language constructions (What does this mean?).
What is a framework? Frameworks used according to the black box principle
A framework is a pre-built software structure that defines how applications are built and run.
Black-box frameworks
•Developers use the framework’s interfaces and APIs without modifying the internal code.
Examples: React, Django, Angular,.NET.

Give a definition of sockets, How is a connection established using sockets?
A socket is a software interface that provides communication between two devices over a network. It combines an IP address and a port.
Stages of work:
•Creating a socket.
•Binding to a port (bind).
•Listening (listen) or connecting (connect).
•Data transmission (send/receive).
•Closing the connection (close).
Types: TCP sockets (reliable).UDP sockets (fast).
Describe the ways in which model transformations are applied
1) Manual conversion
Performed entirely by humans.
Used when the system is too complex or unique.
2)Semi-automatic conversion
The tool does some of the work, the specialist completes the rest.
3)Fully automatic conversion
The entire transformation is performed by the MDA tool.
It is possible to generate code for different platforms.
What does the distribution of functions in the software structure mean? Types of distribution ?
The distribution of functions is the division of responsibilities between the components of a system so that each module performs a strictly defined set of functions.
Types of distribution:
- Functional — modules are distributed by tasks
Authorization, order processing, reports
- Layered — the system is divided into levels
UI → Business Logic → Data Access
- Service (Microservice) — each function is in a separate service, Payment, mailing, shopping cart — separate services
Describe the Principles of PCMEF
The basic PCMEF principles are as follows:
•the principle of Downward Dependency (DDP);
•the Upward Notification Principle (UNP);
•the Neighbor Communication Principle —NCP);
•The Explicit Association Principle —EAP);
•the Cycle Elimination Principle —CEP);
•the Class Naming Principle (CNP);
•the principle of using the dating package (Acquisition Package Principle —APP).