What is soil?
what does soil contain?
Soil is the loose upper layer of the Earth's surface, where plants grow, and is a mixture of organic materials, rocks, minerals, water, and living organisms
What is this diagram called?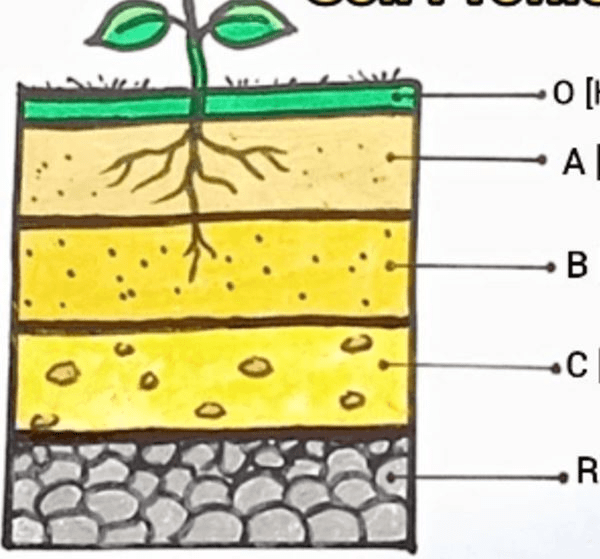
A soil profil
What are the 3 types of soil?
Clay, sand and loam
How is soil useful to our water sources?
Soil filters and cleans the water, preventing harmful substances from reaching groundwater.
Which 3 natural forces cause soil erosion?
wind, water and ice
This type of soil, which has loose particles, is more easily eroded by wind or water.
SANDY SOIL
This method involves planting trees or shrubs to hold soil in place and reduce erosion caused by wind and water.
Reforestation
This technique involves planting tall trees as wind barriers to reduce wind speed and prevent soil erosion.
Wind breaks
What is humus?
The decayed parts of plants and animals found in soil, which is dark in color and provides nutrients for plant growth.
This is the topmost layer of the soil profile, rich in organic matter and nutrients, where most plant roots are found.
Topsoil
This soil type has tiny particles that pack closely together, making it smooth and sticky when wet, and it holds water very well; becomes waterlogged.
CLAY
Give 2 reasons soil is important to plants.
- It provides water, minerals, and nutrients, which they need to grow.
- It anchors plant roots firmly in the ground.
This human activity involves clearing large areas of forest, often leading to increased soil erosion.
Deforestation
Soil that is moist and contains this decomposed organic material is harder to erode.
HUMUS
Creating step-like structures on a slope to slow down water runoff and prevent erosion is known as this.
Terracing
This farming method involves leaving plants in the soil and not disturbing it through tilling, which helps keep soil in place.
no-till farming
This type of soil is best for gardening because it contains a balanced mix of sand, silt, and clay, and is rich in humus.
Loam
This layer beneath the topsoil consists mostly of weathered minerals, and plant roots may penetrate it, but it contains fewer nutrients than the topsoil. 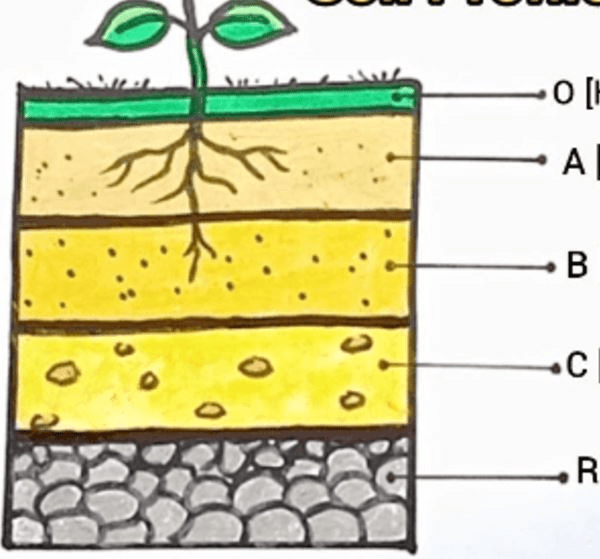
subsoil
Why is it harder for plants roots to grow in clay soil?
It doesn't allow air to pass through easily because it has small air spaces
List 2 micro-organisms that live in the soil.
Fungi
bacteria
algae
Overgrazing and this practice of planting the same crops season after season can deplete soil nutrients, leading to erosion.
Over-cropping
The steeper the slope or gradient of the land is, the higher the rate of soil erosion.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
This farming practice involves ploughing along the contours of the land, which helps slow water runoff and prevents soil from being carried downhill.
contour farming
Covering soil with organic materials like straw or leaves to protect it from rain and wind is known as this.
mulching
This soil type, often found in deserts, has large particles, drains water quickly, and does not hold nutrients well.
Sand
This layer, found above the topsoil, consists primarily of decomposed organic material such as leaves, twigs, and plant matter
organic layer
This soil type, found in areas like riverbeds and floodplains, is smooth, fertile, and holds moisture better than sand.
Silt
Whay are micro-organism like fungi and bacteria beneficial to the soil?
- they break down/decompose organic materials to make humus, which is needed for healthy soil that promotes the growth of vegetation.
This human activity, which involves the construction of roads and buildings, can increase soil erosion by disturbing the land's natural structure.
Urbanization
This force helps water and soil to flow downhill on slopes.
gravity
Planting crops, like grass or legumes, to protect the soil during bare periods is known as this.
cover cropping
This is a structure built on hillsides or riverbanks using rocks or mesh to prevent soil erosion. 
Gabion baskets
This type of soil tends to have a high amount of humus, which is great for plant growth and helps soil retain moisture without becoming waterlogged.
Loam
This layer is made up of bedrock, which is usually unweathered, and is the lowest layer of the soil profile.
parent material
Why is Soil an Important Resource?
- supports plants that humans and other animals need for food.
- needed to grow crops for food, clothing and wooden products and to feed animals.
- habitat for organisms
This gas, often released by soil, is important for regulating Earth's atmosphere and contributes to climate change.
Carbon dioxide
This layer of soil is removed by natural forces and human activity duirng erosion .
Topsoil
The faster the wind blows, the greater the rate of soil erosion it causes.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
This method of farming involves changing the type of crops grown in the same area each season, which helps to maintain soil health.
crop rotation
A rain barrel collects this resource from rooftops to reduce soil erosion and can be used later for watering plants.
rain water