A system of words, letters, or other symbols that stand for other words, letters, or symbols.
Code
A sound that bounces off a surface and travels back to someone's ears.
Echo
The way sounds travel in an up-and-down pattern.
Soundwaves
Part of your throat that vibrates when you talk or sing.
Vocal cords
The smallest possible unit of matter are
Atoms
to exchange information.
Communication
Vibrations that you can usually hear with your ears.
Sound
The distance between two points of a wave.
Wavelength
A form of energy, such as what usually powers light bulbs.
Electricity
The highest point on a wave. Also called the crest.
Wave Peak
A quick movement back and forth.
Vibration
How high or how low a sound is when you hear it.
Pitch
The height of a wave.
Amplitude
A part of the ear that vibrates to help us hear sounds.
Eardrum
A measure of how many waves go by you in a set amount of time.
Frequency
To take a code and change it to a different form that can be understood.
Decode
How loud a sound is, measured by the height of a sound wave.
Volume
When the disturbance moves parallel to the direction of the wave. Put simply: When a wave moves forward and back.
A person who uses science to come up with solutions to problems.
Engineers
Someone who comes up with something new, often an object or a way of doing something.
Inventor
An empty space without any air.
Vacuum
The invisible gas that surrounds the Earth.
Air
When the disturbance moves perpendicular to the direction of the wave. Put simply: When a wave moves up and down.
Transverse Wave
A device that can show what sound waves look like.
Oscilloscope
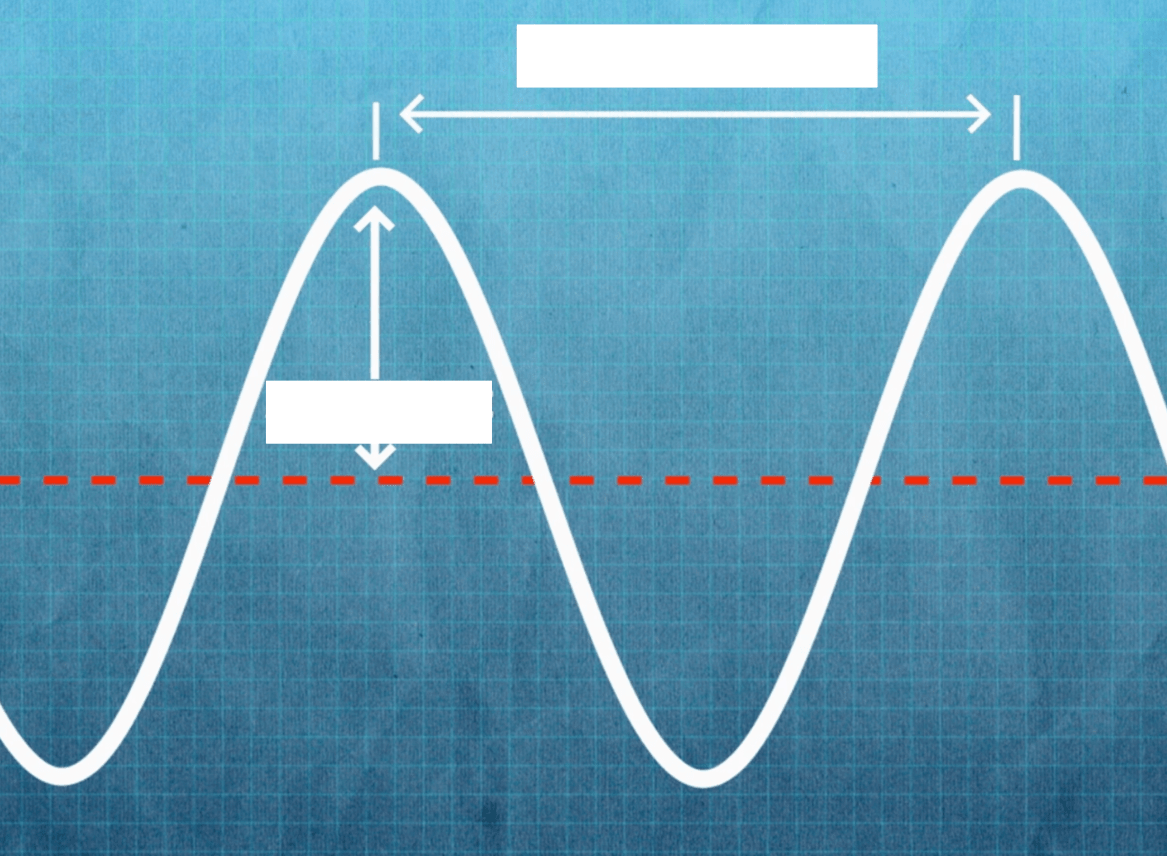
Wavelength <- ->
Amplitude ^v