This variable represents heat added or removed
Q
This is the formula that includes heat, specific heat, mass, and temperature change
Q = m c deltaT
Julian puts 1 kg of water and 1 kg of oil on the stove. The initial temperatures of both are 20 °C. The water takes more time to reach 40 °C than the oil. Which substance has a higher specific heat - water or oil?
Water
Thermal energy is added to a sample of 15°C water. Which of the following quantities must increase?
| A. | the water’s mass | |
| B. | the water’s salinity | |
| C. | the water’s specific heat | |
| D. | the water’s temperature |
D
This variable represents mass
m
What is the change in temperature of an object whose initial temperature is 40 °C and reaches a final temperature of 65 °C?
15 °C
Material A and Material B each absorb 500J of heat. The temperature of Material A rises more than the temperature of Material B. Which material has a greater specific heat capacity?
Material B
The specific heat of water is 4.2 J/g⋅°C. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 100 g of water by 5°C?
| A. | 84 J | |
| B. | 119 J | |
| C. | 500 J | |
| D. | 2100 J |
D
This variable represents specific heat capacity
How much heat must be absorbed by 375 grams of water to raise its temperature by 25°C? (The specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g°C.)
39187.5 J
We use metal for our pots and pans. This is because metal has a high/low specific heat capacity, so its temperature changes slowly/quickly.
We use metal for our pots and pans. This is because metal has a low specific heat capacity, so its temperature changes quickly.
A student heats 200 g of water from 20°C to 70°C. How much heat did the student add to the water if the specific heat for water is 4.2 J/g • °C?
| A. | 10,000 J | |
| B. | 14,000 J | |
| C. | 42,000 J | |
| D. | 76,000 J |
C
This symbol represents change
delta
What mass of water can be heated from 25.0 °C to 50.0 °C by absorbing 2825 J of thermal energy? (The specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g°C.)
27g
Which material has a greater specific heat capacity?
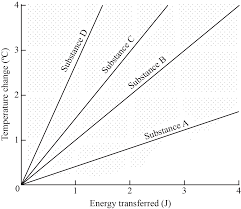
Substance A
A student mixes 70 g of water at 80°C and 140 g of water at 20°C in an insulated cup, as shown in the diagram below.
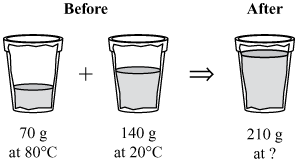
What is the expected temperature of the water in the cup after 1 min?
| A. | 20°C | |
| B. | 40°C | |
| C. | 70°C | |
| D. | 80°C |
B
delta T
1840 J of heat is needed to warm 50 g of iron from 20 °C to 100 °C. What is the specific heat of iron?
0.46 J/g°C
Material A and Material B are put into a freezer. The temperature of Material A decreases faster than the temperature of Material B. Which material has a greater specific heat capacity?
Two U.S. quarters, initially at the same temperature, are heated with a flame. One of the quarters was made before 1965 and is composed of silver. The other quarter was made after 1965 and is composed mostly of copper. What information is needed to determine which quarter will heat up faster?
| A. | the specific heats of the metals and the mass of each coin | |
| B. | the initial temperature of the coins and the mass of each coin | |
| C. | the temperature of the flame and the specific heats of the metals | |
| D. | the initial temperature of the coins and the temperature of the flame |
A