Name the 5 systems involved in the communication process
Nervous, Respiratory, Auditory, Phonatory, Articulatory/Resonatory
Anatomy is..
Physiology is..
Anatomy is the study of the structure of an organism
Physiology is the study of the function of the living organism and its parts, as well as the chemical process
The position with the body erect with the arms at the sides and the palms forward is referred to as the ______________ position
Anatomical position: Upright, palms forward, eyes directly ahead, feet together 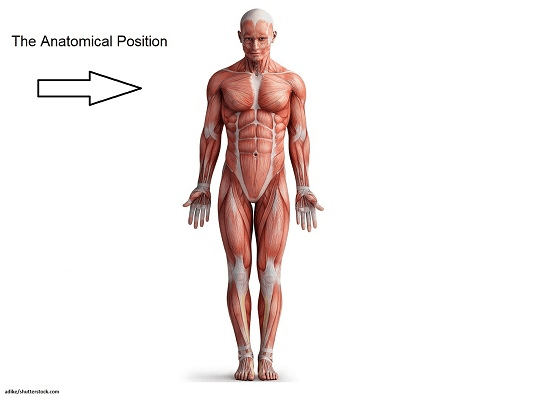
11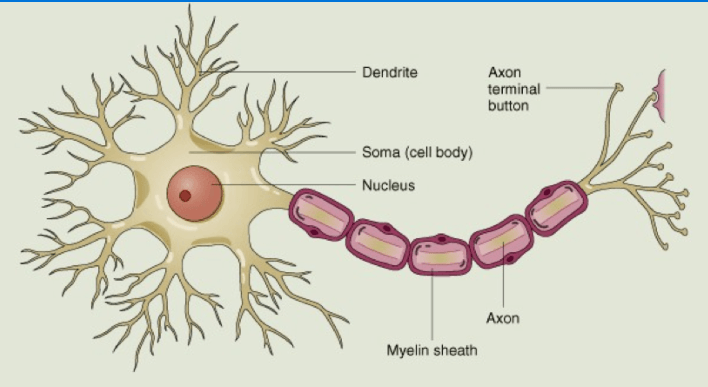
Nerve Cell
List the four primary types of tissue.
epithelial
connective
muscle
neural
Abduction is..
Adduction is..
Abduction - Movement away from midline
Adduction - Movement toward midline
How is Respiratory involved in the communication process?
The respiratory system (involving the lungs) provides the “energy source” for speech
Applied anatomy is..
Applied anatomy (clinical anatomy) –the application of anatomical study to diagnosis and treatment of disease, particularly as it relates to surgical procedures.
What is the difference between midsagittal and sagittal planes?
Sagittal Section- Left and right portion but not equal
Midsagittal plane – divides the body into equal halves (right and left halves) at the medial plane
Sagittal plane – divides the body into right and left parts that are unequal.
13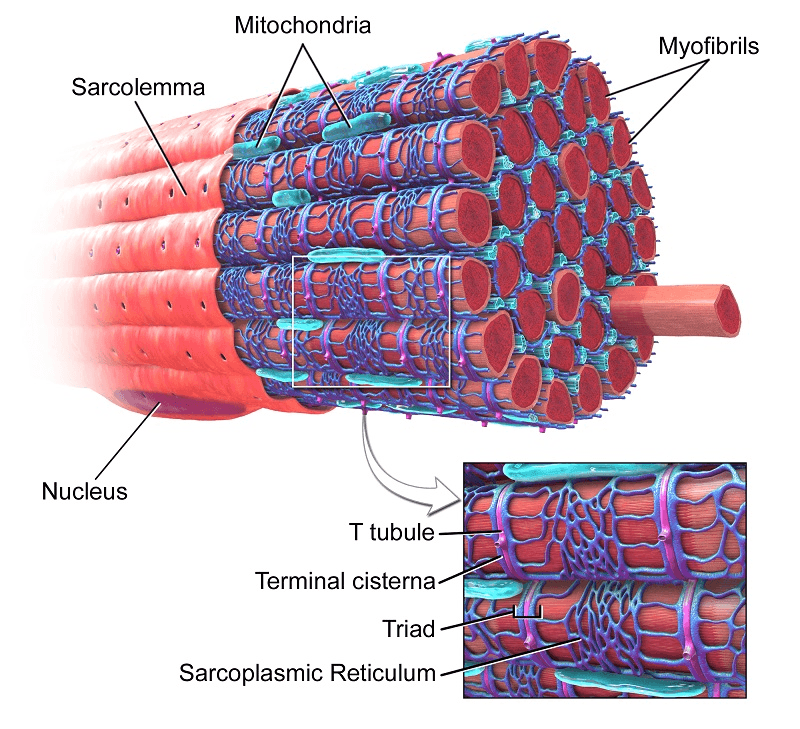
Muscle Cell
Describe the purpose of connective tissue.
Connective tissues bind structures together, form a framework and support for organs and the body as a whole, store fat, transport substances, protect against disease, and help repair tissue damage. They occur throughout the body. Connective tissues are characterized by an abundance of intercellular matrix with relatively few cells.
Connective tissue cells are able to reproduce but not as rapidly as epithelial cells. Most
connective tissues have a good blood supply but some do not.
List the types of joints
diarthrodial - which are high mobility joints.
amphiarthrodial - are joints with limited mobility.
synarthrodial - are immobile joints.
How is the articulatory/resonatory system involved in the communication process?
The articulatory/resonatory system modifies the acoustic source provided by voicing (or other gestures) to produce the sounds we acknowledge as speech
Responsible for the movement of structures to produce speech sounds Add nasal (air flowing into nasal cavity) – oral (airflow through the mouth (differenate between phonemes)
Descriptive Anatomy is..
Descriptive anatomy (systemic anatomy) – the part of anatomy involved in the description of individual parts of the body and the relations to functional systems, but not of their disease conditions. For example, the study of the anatomical parts of the larynx and their relation to phonation.
5. ______ near the tail or hind parts; posterior
6. ______ relating to the skull or cranium
5. Caudal is near the tail or hind parts; posterior
6. Cranial is relating to the skull or cranium
12.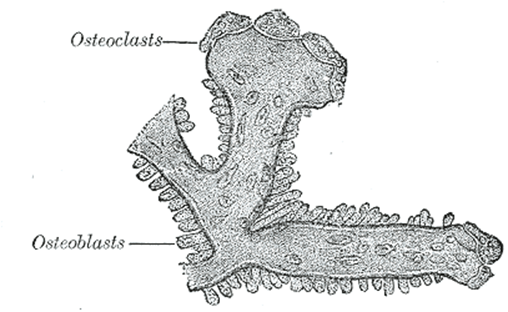
Bone Cell
Smooth muscle is voluntary or involuntary?
Smooth muscle is found in the digestive tract and blood vessels it is involuntary in nature.

Define origin and insertion
origin - the point of attachment with the least mobility.
insertion - the point of attachment with the most mobility, which moves due to muscle contraction.
How is the nervous system involved in the communication process?
innervate muscles for communication
Gross Anatomy is..
Gross (macroscopic anatomy) - The study of the organs, parts, and structures of a body that are visible to the naked eye.
7. ______of, at, toward, or from the side or sides. A side part of something
8. ______furthest away from the center of the body or from the point of attachment
7. Lateral: toward the side of the body
8. Distal: Further from the trunk or thorax; further from the attached end
Describe Nerve Cells
Nerve cells also known as neurons are found in the nervous system. Nerve cells transmit impulses by electrochemical signaling. Neurons are the smallest unit of the nervous system and comprise the core components of the brain, spinal cord, cranial nerves and peripheral nerves.
Cardiac muscle is voluntary or involuntary?
Cardiac muscle is involuntary. Cardiac muscles help with the function of the heart and are controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
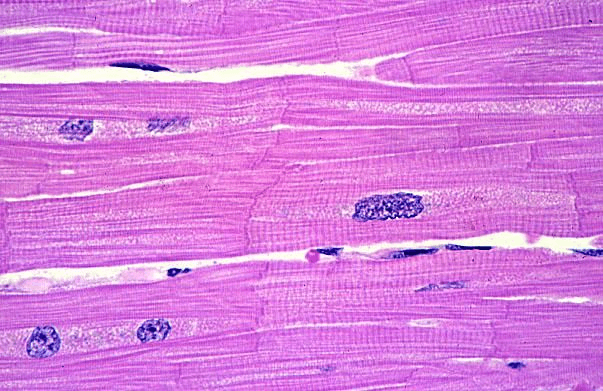
List four levels of organization of the body.
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Systems
How is the auditory system involved in the communication process?
The auditory mechanism processes speech and nonspeech acoustic signals received by the listener who is trying to make sense of her or his world.
Auditory System – hearing speech sounds – respond – communication partners – transit waves forms to ear and brain – perceive and comprehend speech production
Microscopic anatomy is..
Microscopic anatomy – the study of body structures through the use of microscopy.
9. ______ (frontal plane) is any vertical plane that divides the body into ventral and dorsal (belly and back) sections
10. ______ nearer to the center of the body or the point of attachment
9: Coronal plane: Any vertical plane that divides the body into ventral and dorsal sections.
10. Proximal: Closer to the trunk or thorax; nearer to the attached end
Describe Muscle Cells
Muscle cells - A myocyte (also known as a muscle cell) is the type of cell found in muscles.
Each myocyte contains myofibrils, which are long chains of sacromeres, the contractile units of the cell.
Skeletal muscle is voluntary or involuntary?
Skeletal muscle is the only voluntary type of muscle tissue. It moves skeletal structures (i.e. bones).
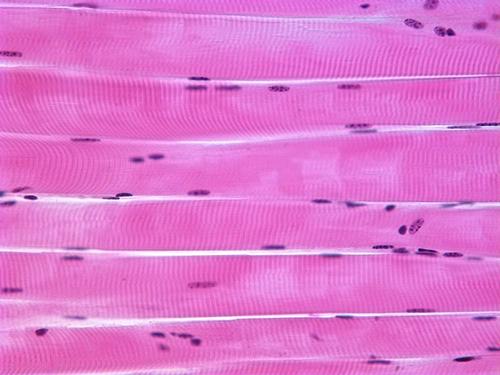
What is the difference between sensory neurons and motor neurons?
Sensory neurons - respond to touch, sound, light and numerous other stimuli effecting sensory organs and send signals to the spinal cord and brain.
Motor neurons - receive signals from the brain and spinal cord and cause muscle contractions and effect glands.
Inter-neurons connect neurons to other neurons within the brain and spinal cord.
How is the phonatory System involved in the communication process?
The phonatory system allows us to generate a laryngeal tone. In order for us to produce voiced phonemes we need the vocal folds.
The phonatory system involves the larynx and provides voicing.
Surface Anatomy is..
The study of internal structures as they relate to the overlying skin surface e.g. the clavicle and ribs can be viewed in part by observing the skin surface.
Another term for posterior is ____________________________ and anterior is
__________________.
Posterior- AKA -Dorsal: Pertaining to the back of the body or the posterior surface
Anterior AKA -Ventral: Pertaining to the belly or anterior surface
Name and describe the two major type of bone cells
Osteoblasts - a type of cell that is responsible for bone formation. Bone is a dynamic tissue that is constantly being reshaped by osteoblasts, which build bone. Osteoblast cells decrease as individuals become elderly, thus decreasing the natural rebuilding of the bone tissue.
Osteoclasts - a type of bone cell which removes or resorbs bone tissue.
Name and describe these tissues
A. 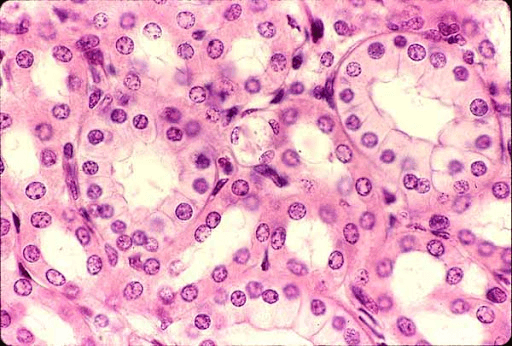 B.
B. 
A. Simple Cuboidal Epithelial tissue is cube shaped in nature and have a secretory function (e.g. thyroid). Found in glandular tissue, ducts, and in the kidney tubules.
B. Simple Squamous Epithelial tissue - a single layer of flat cells. A surface view gives the appearance of a "tiled floor“, thus also named "pavement epithelium”. It’s found in the lining of body cavities, blood vessels, pulmonary alveoli, heart, etc…)
Describe the four levels of organization of the body.
Cells – The smallest structural unit of an organism that is capable of independent functioning, consisting of one or more nuclei, cytoplasm, and various organelles, all surrounded by a semipermeable cell membrane.
Tissues –An aggregation of morphologically similar cells and associated intercellular matter acting together to perform one or more specific functions in the body. There are four basic types of tissue: muscle, nerve, epidermal, and connective.
Organs - A differentiated part of an organism, such as an eye, a wing, or a leaf, that performs a specific function.
Systems - A group of physiologically or anatomically complementary organs or parts: For example, the respiratory system, the phonatory system, the articulatory system, the nervous system.