Explain the difference between the neurocranium and viscerocranium
Neurocranium (cranium)
• Houses and protects the brain
• Provides attachment for head and neck
muscles
• Houses the special sense organ for
hearing
Viscerocranium (facial skeleton)
• Framework for the face
• Houses the special sense organs for
vision, smell and taste
• Contains the openings for the respiratory
and digestive tracts
• Contains the teeth (in oral cavity)
• Anchors the muscles of facial expression
What movements does the zygomatics minor and major do?
Smiling, laughing!
What do the sinuses do? What are they made of?
Airpockets in skull lined with mucous:
Functions:
• Lighten the skull
• Warm and humidify inspired
air
• Create resonance of the voice
Describe where the oseophagus sits and what is is connected to
Oseophagus is posterior to larynx, laryrgopharynx sits above, stomach receives food below
Name the three/four stages of swallow
Oral preparatory phase
Oral Transit phase
Pharyngeal phase
Oesophageal phase
Point to the: Maxilla, Zygomatic, Mandible, and Nasal Bones

Name 2 muscles involved in frowning
Procerus
Located vertically between
the eyebrows
• Action: depresses medial
aspect of eyebrows, producing
transverse wrinkles in the skin
between them
• Involved in frowning
Corrugator Supercilli
Located deep to the skin of
the eyebrows
• Action: draws eyebrows
inferomedially, producing
vertical wrinkles in the skin
between them
• “Frowning muscle”
Depressor labii inferioris
Located inferior to the lower
lip
• Action: depresses lower lip
Extends inferiorly from the
angle of the mouth
• Action: depresses angle of
mouth
Depressor anguli oris
* Depress mouth muscle
Name the three branches of CNV and what they do
Ophthalmic nerve (V1)
• Maxillary nerve (V2)
• Mandibular nerve (V3)
Name the three segments of the small intestine
Duodenum
• Receives chyme and digestive secretions
• Neutralises stomach acids
Jejunum
• Chemical digestion
• Nutrient absorption
The Ileum
• Ends at ileocecal valve (sphincter)
What part of the swallow is voluntary vs involuntary?
Oral phase: voluntary
Pharyngeal/below: reflexive/involuntary
What is the purpose of the velum?
Important for closing off the upper
airway (nasopharynx) during
swallowing
Elevates, depresses and tenses. Important for speech and swallowing.
Name the five branches of the nerve responsible for innervating the muscles of the face
CNVII
Temporal
• Zygomatic
• Buccal
• Mandibular (marginal mandibular)
• Cervical
Name the main artery and vein of the face.
External carotid artery, External and internal jugular artery
Name two functions of large intestine
Absorption of vitamins produced by bacteria
• Reabsorption of remaining water
• Compaction and storage of feces prior to defecation
• Produces mucous for lubrication
• Motility
• Mass movements
1-3 times/day, lasting 15 mins
Explain what happens during the oral prep and transit phase
Prep:lip seal, masticate, move food, form bolus
Transit: tongue lifts to palate, push food to pharynx...
What connected the skull bones together - what are the fibrous joints called? Name 2, and explain the difference between adults and children skulls
Sutures:
1. Coronal: between frontal and
parietal bones
2. Sagittal: between parietal
bones
3. Lambdoid: between parietal
and occipital bones
4. Pterion - between
frontal, parietal, temporal and
sphenoid bones
Children - Fontanelles (squishy bits)
- smaller facial skeleton, sinuses (if any) and developing infant teeth
What innervates the extrinsic muscles of the tongue?
Hypoglossal CNXII (all intrinsic and extrinsic - genioglossus, styloglossus, hyoglossus), palatoglossus innervated by CNX
What are: palatine rugae, gingavae and buccae? What is the difference between oral cavity proper and vestibule?
Buccae: cheecks, palatine rugae: bumps on palate, gingavae: gums,
Proper: internal to the teeth &
gingivae
• Oral vestibule:
between teeth &
gingivae and the lips
& cheeks
Explain the differences between the three segments of pharynx
Nasopharynx
Function(s):
Respiratory function
Pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids)
Lymphatic tissue
Resonance variation
Auditory tube
Connects to middle ear cavity
Pharyngeal recess
Behind auditory tube
Oropharynx
• Digestive & speech function
• Palatine tonsils
• Accessory Airway
Laryngopharynx
- connects with larynx and oesophagus
Name three protective mechanisms during swallow
TVF/FVF closure
Velum move upwards
Epiglottus folds over
Reflexive cough/gag is also acceptable
Name the 2 of the four muscles of mastication, explain their movements and what nerve they are innervated by. What kind of joint is the TMJ?
There are four muscles of
mastication (paired):
• Temporalis - elevate and retract mandible
• Masseter - elevate mandible
• Medial pterygoid - elevate/protrude mandible/deviates to contralateral side
• Lateral pterygoid - protrude/assist with depressing/deviates to contralateral side
Mandibular devision of CNV
Synovial-hinge joint
Name the four intrinsic tongue muscles and their function
Superior longitudinal
• Shortens tongue
• Curls tip and sides superiorly
Inferior longitudinal
• Shortens tongue
• Curls tip inferiorly
Transverse
• Elongates and narrows tongue
Vertical
• Widens and flattens tongue
Salivary Glands - name the three and types of saliva they produce:
Are they activated during parasympathetic or sympathetic?
Salivary glands
Parotid gland – mostly serous
• Submandibular gland – mixed
• Sublingual gland – mostly
mucous
Parasympathetic
Name the two types of pharynx muscles and their role
Constrictors: peristalsis
Longtitudinal muscles: raise pharynx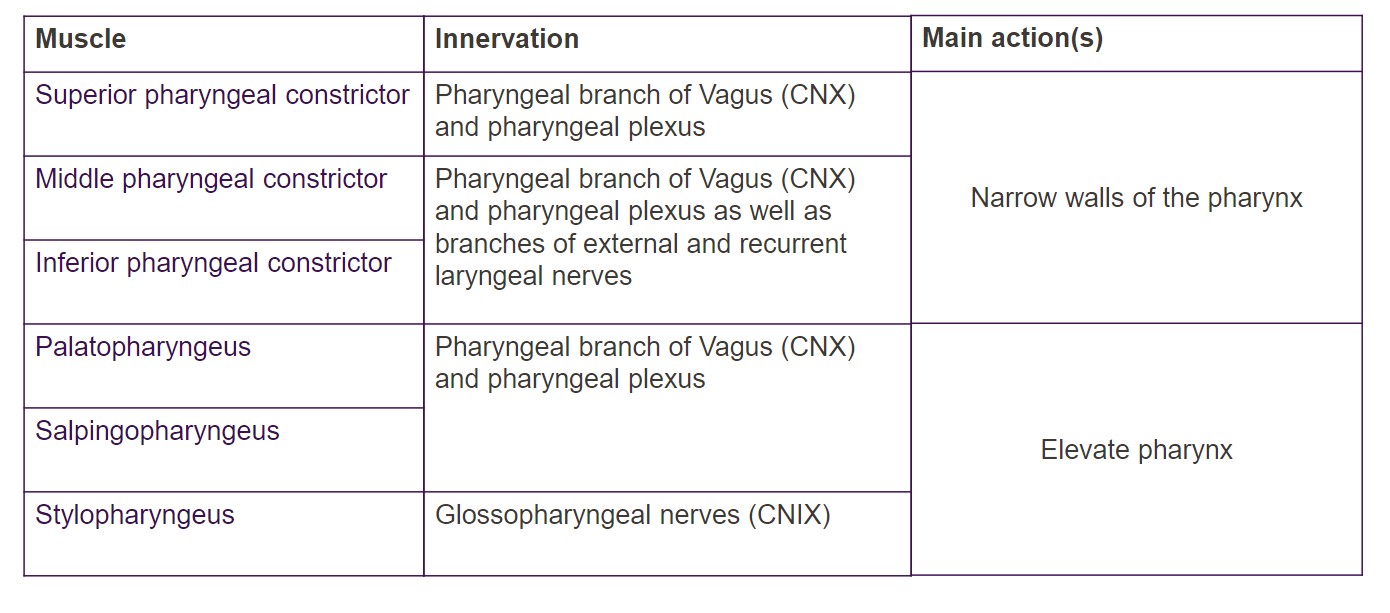
What is a disorded swallow called? Explain what might go wrong and what this could mean for the patient
Dysphagia.... oral prep/transit or pharyngeal... stages
ASPIRATION/PENETRATION into airways is main risk.