Efferent = effect (motor) and afferent = sensory
How many segments does the vertebral column have?
33
Plueral linkage
The pleural membranes and fluid are integral to allow the expansion of the ribcage to translate to expansion of the lungs.
"Pleural linkage” acts to connect the lungs to chest wall
Resonance and phonation
Resonance - resonators (enhance voice)
Phonatation - vibration and vocal folds
Name the four lobes of the brain
Frontal, Parietal, Occipital and Temporal
Name CNVIII
Vestibulocochlear
Conduction and Sensorinueral deafness
Hampers sound conduction to the fluids of the inner ear
Damage to the neural structures at any point from the cochlear hair cells to the auditory cortical cells
Provide the name of three function cortexes of the cerebrum
Primary motor cortex
Primary auditory cortex
Primary somatosensory cortex
Wernicke's area
Broca’s area
Automatic breathing controlled by
Brainstem - medulla
What is amplitude? What is it measured by?
What is frequency? What is it measured by?
Amp = loudness / dBz
Frequency = pitch / hertz
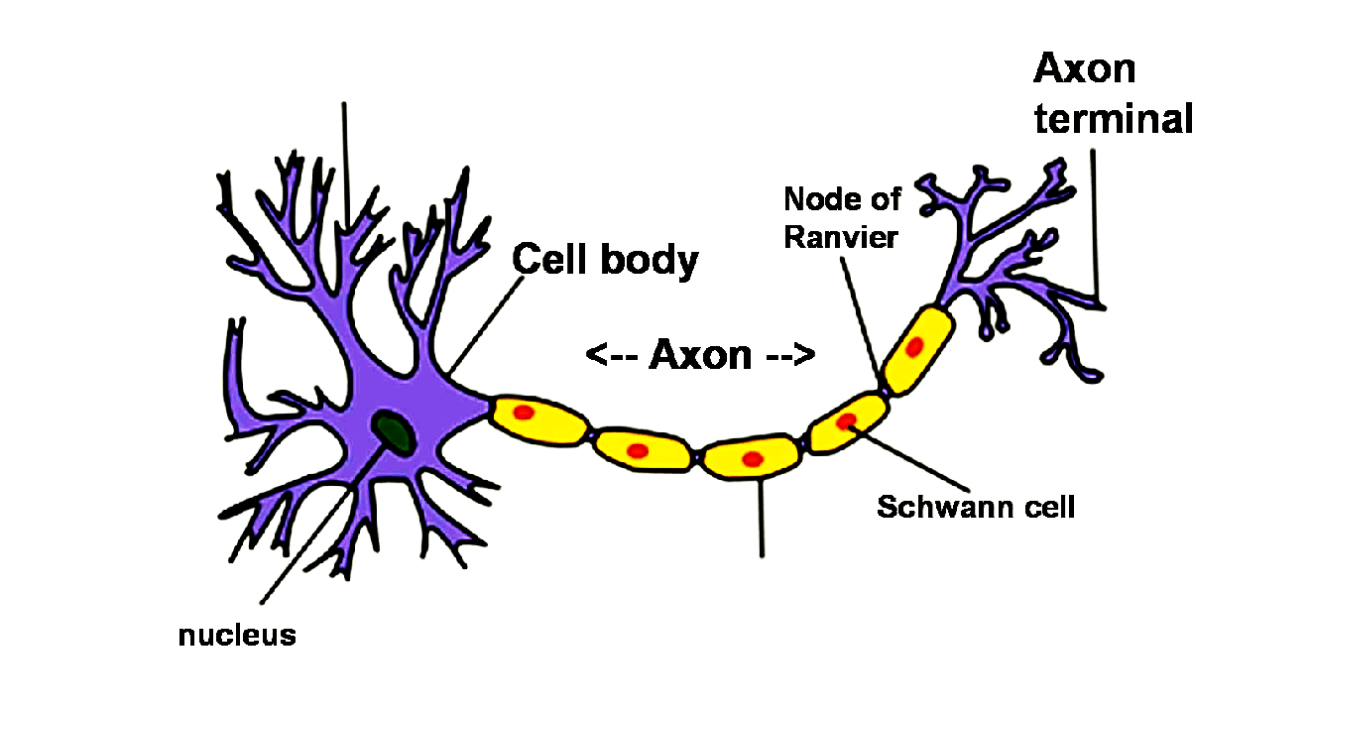
Myelin sheath and dendrite
What provides sensory innervation to the pharynx?
Glossopharyngeal
Costosternal joints vs costosternal joints (and their joint type)
Costosternal (cartilagenous) - Slightly mobile but allow twisting and bending
Elevation and Depression of the ribs occurs at the costovertebral joints (synovial)
Of the ossicles (and what they do!)
Malleus, incus and stapes.
Amplfy the sound enegery applied to T>M. to to the fluid in the cochlea
Boyles law -
Boyles Law.....“As volume increases, the pressure of the gas decreases in proportion. In contrast, as volume decreases, the pressure of the gas increases in proportion.”
(Air is driven by a pressure gradient) - breathing :)
What's the difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic?
P = rest and digest, S = fight or flight
Adductor muscles of larynx
Lateral cricoarytenoid, arytenoid muscles (Oblique and Transverse parts)
Provide 2 different examples of what CNVII innervates.
1. Facial expression
2. Special visceral afferent (anterior 2/3rd tongue taste)
3. General somatic afferent from posterior ear canal
4. General visceral efferent fibers to the glands (e.g. tears & saliva)
COPD
An umbrella term for a number of lung diseases that prevent proper breathing.Three of the most common COPD conditions are emphysema, chronic bronchitis and chronic asthma
Provide 3 common causes of voice disorders
• Vocal misuse/abuse,
• Nerve damage,
• Trauma, e.g. football injury
• Neurodegenerative disorders,
• Normal aging process (presbyphonia)
• Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
• Illnesses, such as colds or upper respiratory tract infections.
• Smoking – laryngeal cancer
The perilymph.
Movement of perilympth leads movement of the basilar membraine. Movement of basilar memberane means hair cells bend which cause the action potential to be sent along the cochlea nerve
Normal respiratory cycle vs on speech (percentage)
Normal: Inspiration takes up to 40% of the cycle
Expiration takes up to 60% of the cycle
Speech: 10/90
Abductor muscles of larynx
Posterior cricoarytenoid
Name the CNI, CNII and CNIII
Olfactory, Optic and Oculomotor
The three attack types for sound production
1. simultaneous attack: Air released as folds compress (most words)
2. Breathy attach: Air released BEFORE folds compress “Harry”
3. Glottal attack: Folds compress BEFORE air released “I” - all vowels
What is the carina?
Junction point of trachea (where splits)
Vocal Fold Length Change (how?)
Vocal folds lengthen with contraction of the
cricothyroid muscles and shorten with contraction of
the thyroarytenoid (vocalis and muscularis) muscles
FVF and TVF (structure/function) AND layers
FVF/ventricular folds: above the TVF - prevent food entering airway - formed by the draping of muscosa over the medial & borders of the vestibular ligament
TVF: vocal ligament - formed by superficial border of conus elasticus. Adduction & abduction. Cover (squamous epithelium, superficial lamina) transition (intermediate lamina, deep lamina) and (vocalis muscle) body.
State two branches of the nerve that innervates the larynx. Differentiate their sensory innervation
superior (above VF - mucosa) and recurrent (below VF -mucosa)
Name the nerve that is primarily responsible for innervating the larynx. Name the two branches of this nerve.
Vagus - Recurrent & Superior
Fundamental frequency - what happens across the lifespan
Puberty: During infancy and childhood the larynx enlarges (increases in mass) and descends within the neck. Fundamental frequency decreases across infancy and childhood in both boys and girls.
Aging:Cartilages ossify and calcify, muscles atrophy, connective and epithelial tissues change (slowing of movement)
What are the three segments of the sternum?
Manubrium
Body Of Sternum
Xiphoid Process /Xiphisternum
What passes through the superior thoracic apeture? Name 3.
Carotid arteries, Jugular veins, Phrenic nerve, Vagus nerve, Trachea, Esophagus
Cricoarytenoid joints and cricothyroid joint
Cricoarytenoid - Allows the vocal folds to open or close to varying degrees
• Adduction/ abduction
• Medial compression
Cricothyroid - pitch changes/rotation and gliding - stretching and relaxing VF
Bernoulli effect and why relevant:
“If volume flow is constant, velocity must increase at an area of constriction, but have a corresponding decrease of pressure at the constriction”
- Force of air pushes the folds apart and the negative pressure this creates pulls them together again....Vibration
Provide the name of the three branches of the trigeminal nerve (CNV) & state their function.
Ophthalmic (CN V1) - sensory
Maxillary (CN V2) - sensory
Mandibular (CN V3) - mixed