A patient has a muscle grade of <3/5 in more than half of their key muscles below the neurologic level. What is their ASIA score?
ASIA C

Scapular winging may result as a clinical finding of radiculopathy at what level?
C4
What fracture pattern in a Type II odontoid fracture is amenable to an anterior odontoid screw fixation?
Anterior superior to posterior inferior

A 75M presents with worsening low back pain which improves with sitting and worsens with ambulation and walking down stairs. What is the first line treatment for this patient's condition?
NSAIDS, physical therapy, weight loss and bracing. (all first line modalities for spinal stenosis)
DISH may be associated with what HLA type?
HLA-B8
A 28 yo male is involved in an MVA. On exam, he cannot move bilateral lower extremities and lacks sensation below the umbilicus. He has no deficits to bilateral upper extremities. There is no rectal tone when the foley catheter is tensioned. How would you classify his injury based on the ASIA classification?
Cannot determine at this time
A patient presents with RUE pain radiating from the neck with associated weakness of the biceps muscle group and ipsilateral loss of the brachioradialis reflex. At what level is he most likely to have a right-sided cervical disk protrusion on MRI?
C5-6
A 25 year old male presents to the ED after an MVA with a GCS of 15 with the below imaging. After CT scan, patient's GCS is 8. What is the next best step of management of this pathology?
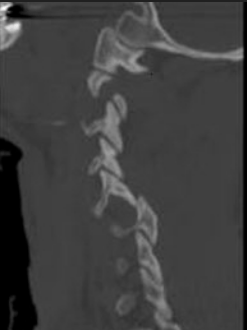
MRI
Patient with altered mental status, MRI must be performed emergently followed by open reduction and stabilization
At which phase of lumbar spine degeneration would a spondylolisthesis develop?
Instability
Phases of spine degeneration
1. Dysfunction
2. Instability
3. Stabilization
High mortality rates in patients with ankylosing spondylitis who sustain a fracture are secondary to what cause?
epidural hemorrhage or hematoma
A patient sustains a spinal cord injury leading to ipsilateral loss of proprioception, vibration, and touch sensation below the level of injury. What is their pathology?
posterior cord syndrome
Posterior cord syndrome results from trauma to the posterior column, posterior horn, and posterolateral region of the lateral column.
What is the most appropriate treatment for a 63F who presents with loss of finger dexterity, exaggerated DTR's in the LE's and this MRI finding?
Multilevel ACDF (or C6 corpectomy)
What radiographic measure and value is used to determine if there is a transverse ligament rupture?
Sum of Lateral Mass Displacement
>6.9 mm (rule of Spence) or >8.1 mm with radiographic magnification (rule of Heller)

Patient presents with 5 days of LBP and left leg pain and weakness after weightlifting. MRI images are below. What is the best initial treatment?
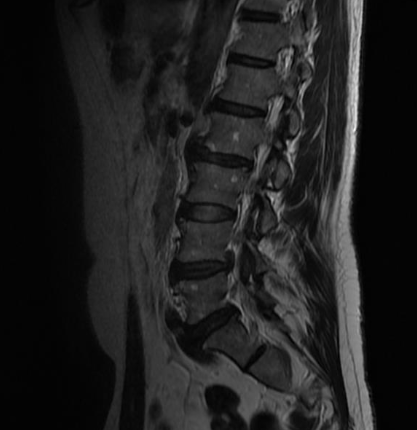
Conservative management/PT
What is the diagnosis?

Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament
The CT scan demonstrates thickening and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. This diagnosis is most common in individuals of Japanese descent and has a genetic linkage. The anterior osteophytes are smaller than those seen in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis and are not syndesmotic. Patients with ankylosing spondylitis typically have non-marginal syndesmophytes.
A 23 yo male presents to the ED s/p a stabbing incident on the right side of his neck. He is diagnosed with Brown-Sequard syndrome. What is his suspected motor exam and temperature exam consistent with this diagnosis?
Motor Exam: right sided loss of motor
Temperature Exam: left sided loss of temp

A patient presents with a cervical disk herniation at C7-T1 level with associated foraminal stenosis. There is no significant central stenosis. What is the associated motor AND sensory exam finding?
Numbness of the small finger and flexion weakness in all fingers. (C8 innervates FDS, FDP and FPL)
There are 6 risk factors for type II odontoid fractures. Name at least 3.
- posterior displacement >2mm (strongest predictor of nonunion
- age >40 years old
- ≥ 5mm displacement (>50% nonunion rate)
- delay in treatment >4 days
- angulations >10 degrees
- smoker
Here is the patient's MRI. What is the likely distribution of the patient's paresthesia?
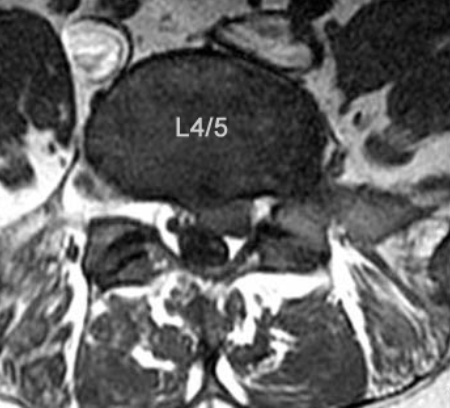
Dorsal aspect of the foot.
This patient has a left paracentral L4/5 disc protrusion which leads to compression of the traversing (descending) left L5 nerve root. Numbness over the dorsal aspect of the foot and weakness to gluteus Medius is consistent with a L5 radiculopathy.
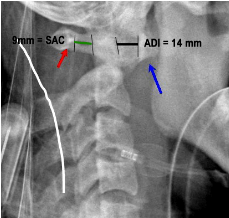
In patients with rheumatoid arthritis, an anterior atlanto-dens interval of 1.____ and posterior atlanto-dens interval or space available for cord of 2._____ is indicative of instability, necessitating the need for posterior C1-C2 fusion.
1. AADI >10mm
2. PADI/SAC <14mm
PADI >14mm predicts full neurologic recovery with surgical stabilization
A patient suffered a spinal cord injury but is able to operate a manual wheelchair with a sliding board transfers and can drive a car with manual controls. At what level is their spinal cord injury?
C6
At what level would radicular symptoms originate which could include ipsilateral Horner's syndrome?
T1 radiculopathy
- intrinsic hand muscle weakness
- axillary numbness
- ipsilateral Horner's syndrome
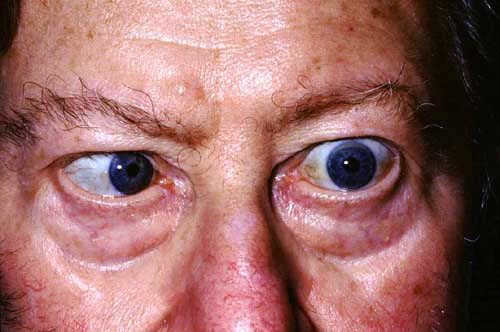
What is the most commonly injured cranial nerve with a halo orthosis immobilization device?
Abducens Nerve (CN 6)
Traction injury to CN6 that innervates lateral rectus muscles
Loss of lateral gaze on the affected side, diplopia
Observation as treatment, most resolve spontaneously
A patient is noted to have lumbar radiculopathy with hamstring weakness. What are the peripheral nerves which innervate the short head and the long heads of the biceps femoris respectively?
Common peroneal nerve (short head) and tibial nerve (long head) both L5-S2 nerve roots.
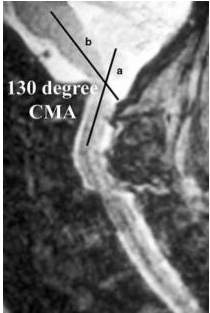
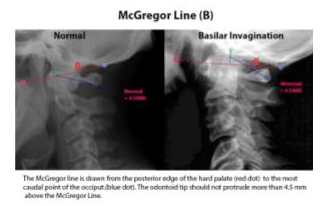
In patients with rheumatoid arthritis, basilar invagination can be measured by a cervicomedullary angle of ____ on MRI.
<135 degrees
Basilar invagination is characterized as the superior migration of the dens into the foramen magnum leading to compression of the medulla oblongata. This can be signified radiographically by the tip of the dens appearing >4.5 mm superior to McGregor's line (line drawn from posterior edge of the hard palate to the inferior edge of the occiput) or a cervicomedullary angle <135°. A cervicomedullary angle <135° is suggestive of impending neurologic impairment and should be addressed with surgical decompression and stabilization.