Flying mammals that use echolocation and are associated with vampires.
What are bats?
The most common external parasite on dogs and cats.
What are fleas?
Neutralizes snake venom.
What is antivenom?
The biggest animals are primary consumers.
What are herbivores
Large eyes, big ears, and camouflage
What is nocturnal adaptations/characteristics?
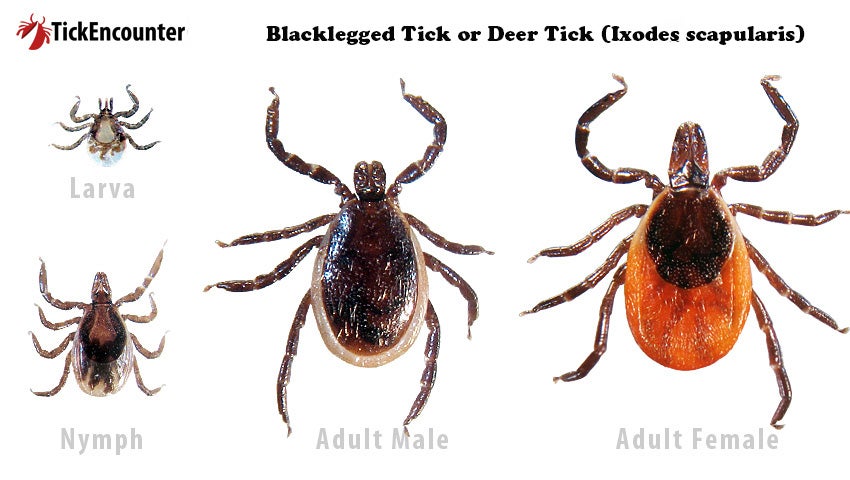
Causes Lyme disease.
What are Blacklegged Ticks?

The evaluation of toxicoses, identification and characterization of toxic substances, determination of their fate in the body, and treatment of toxicoses.
What is toxicology?
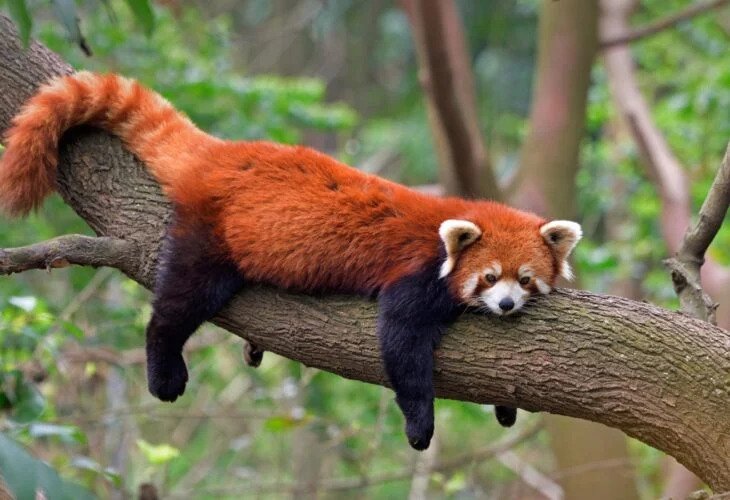
Red, feed mainly on bamboo using their opposable thumb
What are Red Pandas?

These arachnids are nocturnal hunters that wait for prey in their burrows.
What is Curly hair tarantula (Brachypelma albopilosum)?
A hard external skeleton that protects the outer surface made of chitin.
What is an exoskeleton?
It has the fastest-acting venom.
What is Australian box jellyfish?

This mammal has a heart about the same as a Volkswagen Beetle.
What is a blue whale?

~70%
These winged insects prefer to nibble on horses but also dogs with pointed ears.
What are Biting Horse Flies?

What is Blue-Ringed Octopus?
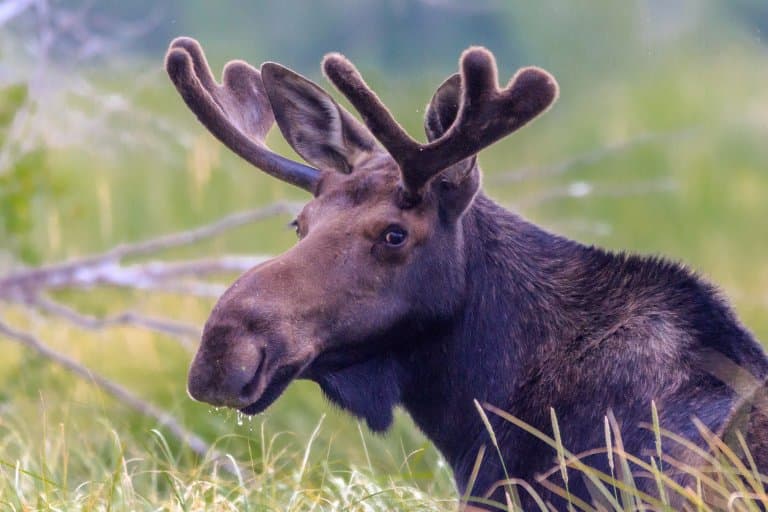
The largest members of the deer family, standing six feet (1.8 meters) tall from hoof to shoulder, and weighing in at more than 1,000 pounds. You will be K.O'd if they attack you.
What is a Moose?

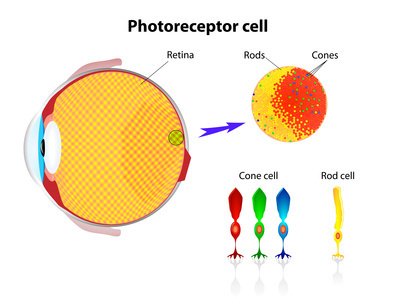
These are special eye cells, nocturnal animals, such as bats and aye-ayes, that allow vision in dim light to signal shape and motion in shades of gray.
Rods
Tiny, non-segmented worms that prey on flea larvae used in yards for flea prevention.
What are Nematodes?
The only venomous mammal in the world.

What is Pygmy slow lorises?
- Modified sweat glands near their elbows allow pygmy slow lorises to secrete a toxin. They can lick these glands when alarmed, spreading the toxin to their teeth. Their venom can incapacitate predators as large as humans.

Who wins? 2 million chickens vs. Godzilla
Chickens? (debatable)
