The variable that is changed and the variable that is measured in a scientific experiment, respectively.
What is the independent and dependent variable?
This organelle, known as "the brain of the cell", directs cell processes by providing DNA instructions. It is surrounded by its own membrane and is covered with pores.
What is the nucleus?
The main unit of energy that cells use.
What is ATP?
The hormone responsible for lowering blood sugar levels.
What is insulin?
The body system responsible for gas exchange.
What is the respiratory system?
The group in which a variable is not being tested as a baseline comparison in a scientific experiment.
What is the control?
The organelle responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells.
What are chloroplasts?
The internal stability that all organisms maintain.
What is homeostasis?
Specially shaped proteins that digest or synthesize large molecules. They are needed for most metabolic activities.
What are enzymes?
The nervous system is a complex communication network, coordinating actions and sensory information through signals transmitted between various parts of the body. It is made up of these organs...
What is the brain, spinal cord, nerves.
List the independent and dependent variables in the following hypothesis. If soil temperatures rise, then plant growth will increase.
What is...
Independent variable - soil temperatures
Dependent variable - plant growth.
This selectively permeable organelle, consisting of a phospholipid bilayer, controls what goes in and out of the cell.
What is the cell membrane?
Diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion are forms of this type of transport
What is passive transport (does not use energy)?
The pores & cells that plants use to bring in CO2 and regulate water loss.
What are stomates / guard cells?
Fill in the blanks. The immune system protects the body from ____-producing ____
What are antigen-producing pathogens?
These are the general steps in the scientific inquiry process.
What is:
1. Have a question/problem you want to be answered
2. Create a hypothesis
3. Set up experiment with variables
4. Analyze/compare results
5. Share results and repeat experiment
These organelles follow DNA instructions to make proteins. They are free-floating or may be found attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
What is a ribosome?
The mitochondria, "the powerhouse of the cell", is the organelle responsible for this key cellular function.
What is cellular respiration (generation of ATP/energy).
These proteins are made by white blood cells, and have a special shape to fit into and recognize pathogens/antigens to destroy them or label them for destruction (immune response).
What are antibodies?
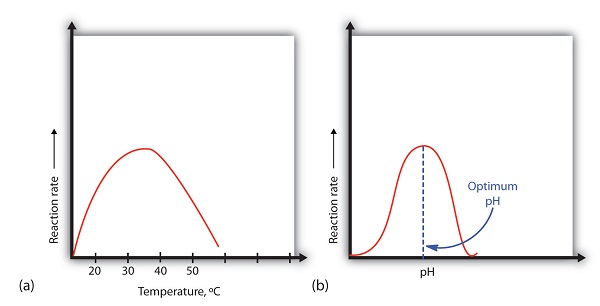
Enzyme activity is impacted by the following factors...
What is temperature & pH
Thinking about the hypothesis: If soil temperatures rise, then plant growth will increase. What might a control in this experiment be?
What is: using the same potting soil, making sure both plants have an equal amount of light etc.
The two main differences between plant and animal cells are:
1. Plant cells have cell walls.
2. Plant cells have chloroplasts
Name at least 4 major life functions essential to all life
What are...
1. Transport... of nutrients, waste products, etc.
2. Regulation/coordination of cellular processes
3. Cellular respiration/metabolism - converting food to energy
4. Excretion - gets rid of waste products from cellular reactions
5. Nutrient acquisition - need food!!!
Name two body systems (e.g. cardiovascular) and explain how they interact to maintain homeostasis.
....
This type of feedback mechanism helps maintain stable internal conditions in the body?
What is a negative feedback mechanism?