We classify matter in different ways. Name at least 3 of the classifications. The more you can name, the better!
Mass, Physical State, Solubility, Magnetism, Conductivity, and Relative Density
What is the acronym we use to remember the energy types and what does each letter stand for?
MELTS; Mechanical, Electrical, Light, Thermal, Sound
What are the steps in the water cycle?
Precipitation, collection, evaporation & transpiration, and condensation
What are the natural disasters which cause rapid changes to land?
Earthquakes, volcanoes, landslides & flash floods
Give an example of a living organism depending on a nonliving component of its environment.
Teacher chooses if your answer is correct
I have a bucket with sand, wood beads, and glass marbles. How could I separate these items?
Use a sieve to separate the wood beads and glass marbles from the sand. Put the beads and marbles into water. The wood beads will float and can be scooped off the top.
What are the three behaviors of light that we learned about? Draw a picture to represent each.
Reflection, refraction, and absorption
What is the difference between rotation and revolution?
The earth rotates on its axis, which takes 24 hours, but its revolves around the sun, which takes 1 year.
Name and describe the fossil fuels.
Oil - black, liquid, made from ancient plants and animals
Coal - black, rock like, made from ancient swamp plants
Natural Gas - invisible, gas, made from ancient plants and animals
Explain the difference between inherited traits and acquired traits. Explain the difference between inherited behaviors and learned behaviors.
Inherited traits come from your genetics and acquired traits are gotten throughout your life. Inherited behaviors are things we are born knowing how to do, and learned behaviors are things we have to learn throughout our lives.
How are solubility and relative density similar? How are they different?
They both require water to test. However, relative density describes whether an item will sink or float in water, while solubility describes an item's ability to dissolve in water.
A conductor, a power source, and a load
At what time/s of day are shadows the longest?
Early morning and late afternoon/evening
Describe the process of sedimentary rock formation.
Weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction, cementation
Weathering breaks rock down into sediment, erosion takes the sediment to a new location, sediment is dropped off in the new location through deposition. The weight of layers upon layers of sediment causes compaction, then water and nutrients seep through the layers, gluing them together in cementation.
Describe a life cycle we have learned about.
Frog - egg, tadpole, froglet, frog
Tomato plant - seed, young plant, mature plant, flowers, fruit
Lady Beetle - egg, larva, pupa, adult
Choose 3 classifications of matter. How do we test them?
Mass - triple beam balance or scale
Physical State - our senses; sight, touch
Relative Density - put items in water; items that float are less dense than water, items that sink are more dense than water
Solubility - stir items into water; items that dissolve are soluble, items that do not dissolve are insoluble
Magnetism - use a magnet near the item; items that are attracted to the magnet are magnetic, items that are not attracted to the magnet are nonmagnetic
Conductivity (electrical) - connect the item to a circuit; items that close the circuit or turn the load on are good electrical conductors, items that open the circuits or do not turn the load on are good electrical insulators
Series circuit - a circuit with multiple loads, but only one path of energy
Parallel circuits - a circuit with multiple loads and multiple paths of energy
Name the eight planets in order.
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
Through heat and pressure
What are the classifications we give to animals based on what they eat and what does each mean?
Herbivore - eats plants
Omnivore - eats plants and other animals
Carnivore - eats other animals
Describe the difference between mixtures and solutions.
In a mixture, each substance maintains in physical properties and can be easily separated. In a solution, the substances may have a change in physical properties and cannot be easily separated.
Why is it important to know what materials are good conductors or insulators when working with electricity or heat?
To protect ourselves; ex: charging wires have conductors on the inside to allow electricity to follow from the outlet to our device, but have an insulator on the outside so we do not get shocked when we touch it.
What causes the moon phases?
The moon revolves around the earth about every 28 days, causing us to see different sides of the moon. This makes the moon appear to us in different shapes.
Name the landforms we discussed this year.
Canyon, U-Shaped Valley, River Delta, Sand Dune
Identify a producer, a primary consumer, a secondary consumer, and an apex predator.
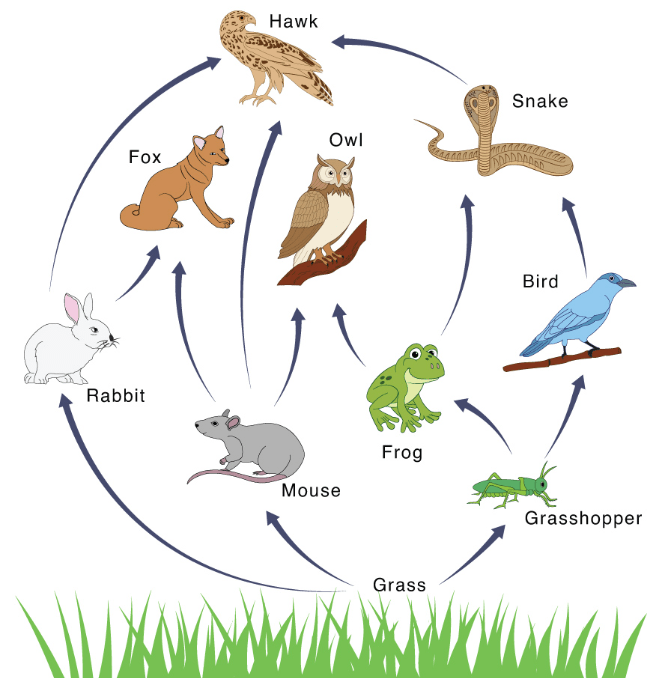
Producer: Grass
Primary: Grasshopper, mouse, or rabbit
Secondary: Bird, frog, owl, or fox
Apex Predator: Hawk or owl