Behavioral changes of individuals of a species that allow for better survival. (Acquired traits)
When every organism of a species has died
What is extinction?
Which organism is the most distantly related to the others on the following trees?
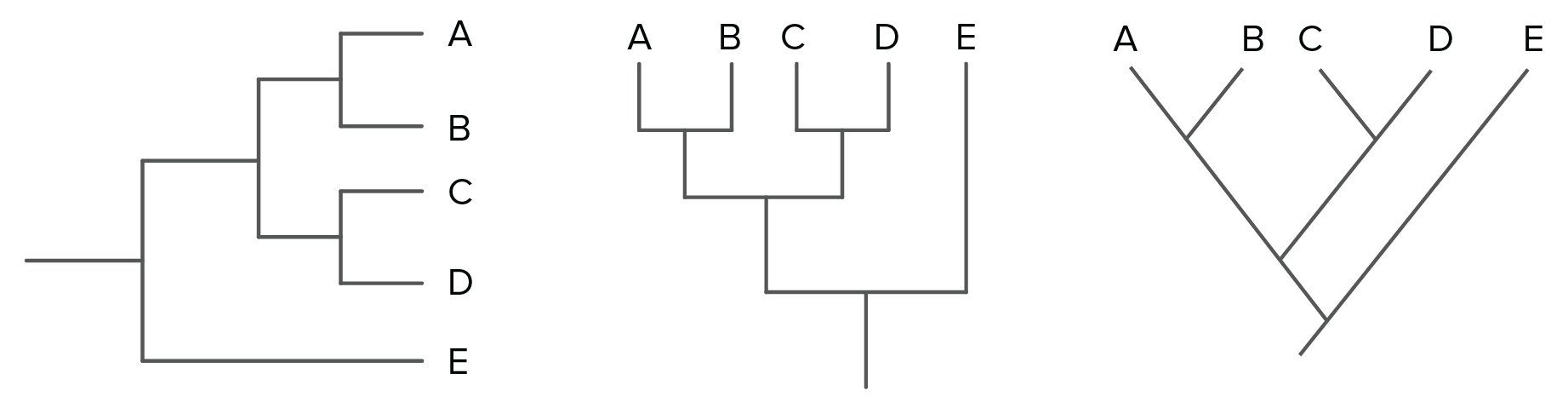
Organism E
The division of the cell nucleus
What is mitosis?
These biomolecules are responsible for the formation of cell membranes and long-term energy storage.
What are lipids?
Vestigial structures
ex: appendix, wisdom teeth, snake hindlimb bones
Which of the following is evidence to support the idea that two different species might have a common ancestor?
- They both live in the rainforest
- They have similar forearm bones
- Their fossils were found on the same continent
- They both can fly
They have similar forearm bones
consider: human forearm, bat wing, and whale flippers all have similar structure
The microscopic infectious particle that causes the highly contagious hoof-mouth disease in livestock requires a host to reproduce. Which of the following pathogens is most likely responsible for causing hoof-and-mouth disease in livestock? Justify your answer
A fungus
A protist
A virus
A bacterium
A virus, because it requires a host to reproduce
Which part of meiosis is responsible for genetic diversity in offspring?
Prophase, when crossing over takes place
Which of the following components bond with ADENINE in a section of double-stranded DNA
Phosphate Deoxyribose sugar
Ribose Sugar Uracil
Thymine Adenine
Guanine Cytosine
Thymine and Deoxyribose sugar
The long term survival of a species is only possible if an organism can
What is reproduce successfully?
Which of the following is the best example of natural selection?
- Giraffes with longer necks live to reproduce because they can reach more food
- A horse developing more muscle as it pulls equipment
- A dog being bred for greater speed and shorter fur
Giraffes with longer necks live to reproduce because they can reach more food
Give three examples of biotic factors specific to a desert ecosystem
Answers may vary
Examples: lizards, cacti, ants, camel, desert bush, scorpions
The function of chromatids
What is the even distribution of genetic material to daughter cells?
Which of these components are found in the cells of all living organisms?
i. Estrogen and testosterone
ii. Hemoglobin and lymphocytes
iii. Cytosine and guanine
iv. Cellulose and chlorophyll
iii. cytosine and guanine
Genetic diversity's function
What makes it possible for species to adapt when the environment changes?
Homologous structures
What are anatomical structures in different animals that come from a common ancestor but have different purposes?
example: human forearms vs whale flippers
3 cell organelles unique to plant cells
What are the cell wall, chloroplast, and large central vacuole?
A cell spends most of its life in
What is interphase?
What is the correct complementary DNA strand for the segment shown?
3’ AGGTCAGGT 5’
5’ TCCAGTCCA 3’
Some variety of white clover produces cyanide (CN), which is a powerful poison. What adaptive benefit does this give the plant?
The predators that eat it will die, which leads to greater amounts of surviving clover
Body parts in different species that serve similar functions but have evolved independently
What are analogous structures?
example: penguin flippers vs fish fins
Animalia, Plantae, and Fungi classifications are examples of ________
Kingdoms
*Remember: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus Species
This holds the two sister chromatids together
What is a centromere?
Students are modeling mRNA during the process of protein synthesis. How will the model of the mRNA strand being transcribed differ from the DNA template strand (2 part answer)
the mRNA strand is complementary to the DNA template strand
Uracil will pair with adenine instead of thymine