This theorem states that P(A|B) = [P(B|A) × P(A)] / P(B
What is Bayes' Theorem?
H0:p=p0 is a null hypothesis for this type of test?
What is z-test for the Population Proportion
This type of experimental design helps control for confounding variables by assigning subjects to different treatment conditions in a randomized way
What is randomized controlled trial?
In hypothesis testing, this error occurs when we fail to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false
What is Type II error?
This measure of central tendency is determined by the value that minimizes the sum of absolute deviations
What is the median?
This sampling technique divides the population into non-overlapping groups and then selects entire groups at random
What is cluster sampling?
H0:μ=μ0 is the null hypothesis for this type of test.
z-test for the Population Mean
This type of sampling bias occurs when individuals with certain characteristics are more likely to select themselves into a study.
What is selection bias (or self-selection bias)?
This value represents the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is false and is equal to 1 minus the probability of Type II error.
What is statistical power?
This formula is to find_____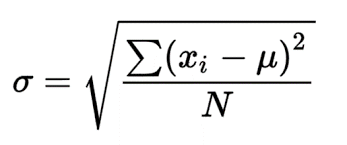
What is the population standard deviation
This concept describes the situation where the probability of an event doesn't match its long-run frequency due to limited data
What is the law of small numbers (or sampling variability)?
The test statistic is a measure of the evidence in the data against this.
What is the null hypothesis
This type of sampling involves dividing a population into subgroups based on shared characteristics and then randomly selecting individuals from each stratum to create a sample. This ensures each subgroup is represented proportionally in the sample.
What is a stratified sampling ?
You have been told the human eye blinks an average of 4,200,000 times a year. If you want to create a 95% confidence interval for this, what value of z would you use?
What is 2
The formula is: μ = np describes the center of this type of distribution.
What is a binomial distribution?
A mathematical function that assigns probabilities to different possible outcomes of a random variable
What is a probability distribution?
For given data, the p-value of the two-sided test is always how much bigger than it is for a one sided test.
What is twice as big?
This type of sampling involves dividing a population into groups and then randomly selecting some of those groups for study
What is cluster sampling?
The value we use to describe the correlations below. 
What is the correlation coefficient?
σ = √(npq) describes the ______ of a binomial distribution.
The birthday paradox is a probabilistic phenomenon where, surprisingly, in a group of just 23 people, there's a greater than (FILL IN THE BLANK) chance that two individuals share the same birthday.
What is 50%
Results that are based on a _______ sample carry more weight, and therefore results that are not significant (do not provide evidence to reject H0) may become significant if based on a ____ sample size
What is larger ?
This type of sampling is a non-probability sampling method where participants are selected based on their accessibility to the researcher rather than random selection
What is convenience sampling?
This principle is often used in science where, when confronted with two hypotheses that explain the data equally well, the simpler one is preferred.
What is Occam's razor?
The name of this drawing below.
What is the BIG PICTURE