Match
1. First line therapy for mild to moderate symptoms
2. First line for moderate to severe symptoms
3. Second line
1. First line therapy for mild to moderate symptoms: ibuprofen
2. First line for moderate to severe symptoms: triptan
3. Second line gepants, ditans, ergot alkaloids, anti emetic
How are candidates for buprenorphine treatment screened? Who should be screened?
All adult patients should be screened for substance use with a validated questionnaire. Patients who are on long-term opioid therapy should be assessed periodically. Those who meet the DSM5 criteria should be offered treatment
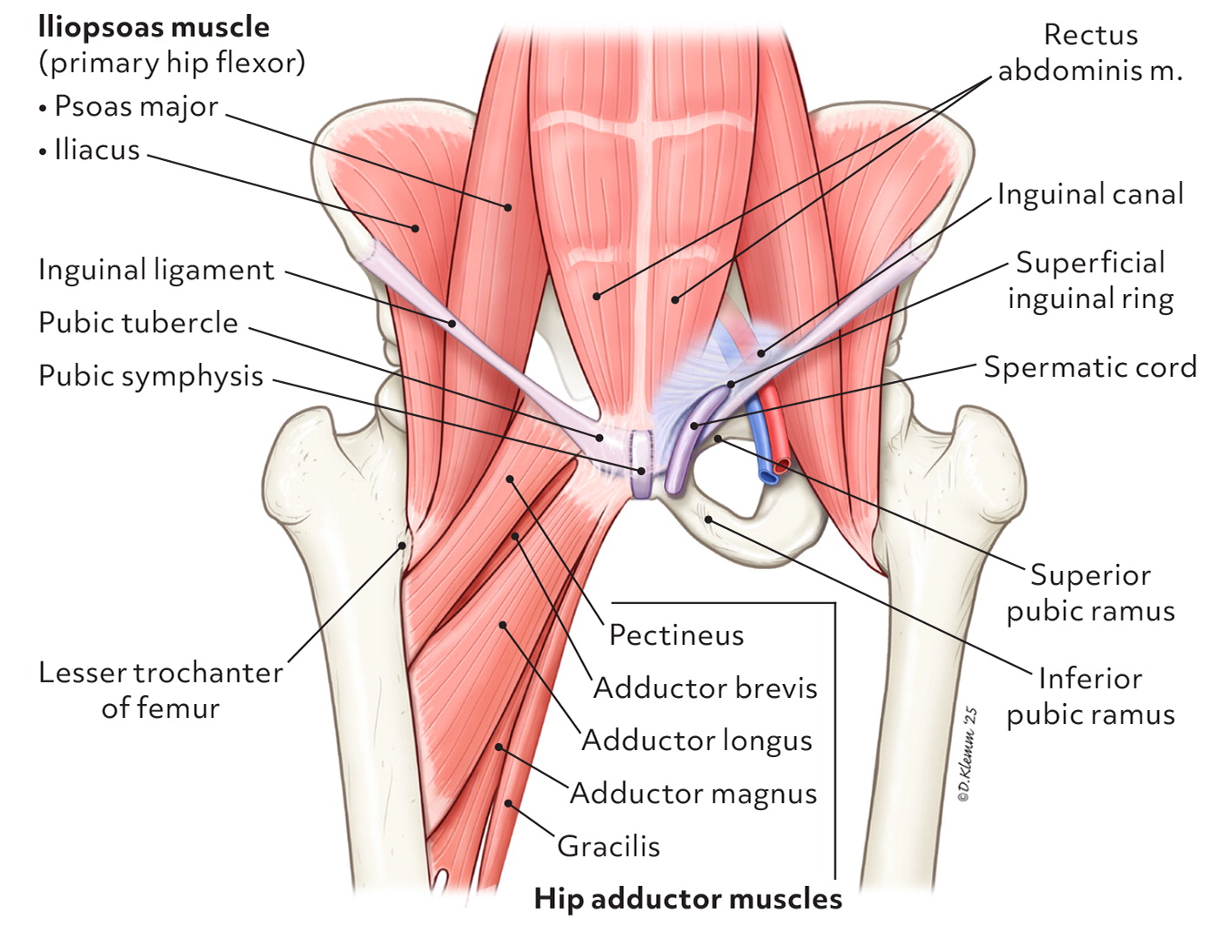
Name the four clinical entities for groin pain in athletes category?
1. Adductor
2. pubic
3. inguinal
4. iliopsoas
USPTF screening for depression in the pediatric population?
Answer: The USPSTF recommends screening for major depressive disorder (MDD) in adolescents aged 12 to 18 years.
True or false question:
Continued beta blocker use after acute MI reduces hospitlization in addition to cardiovascular deaht, acute MI, or stroke
False:
What is the POUND mnemonic? List what each word stands for.
* What is SNNOOP10 mneumonic
POUND criteria that can quickly and reliably point to a migraine diagnosis
Pulsatile quality of headache
One- say duration of headache (4-72 hours if untreated or unsuccesfully treated)
Unilateral Headahce
Nausea or vomiting
Disabling intensity of headache
SNNOOP10 Mneumonic is a crtieria for secondary headhache: is a tool used in clinical practice to identify potential red flags for secondary headaches, which are headaches caused by an underlying medical condition
Which of the following statements most accurately reflects current evidence and prescribing guidelines regarding buprenorphine for opioid use disorder?
A) Buprenorphine is less effective than methadone and should only be used in a specialized addiction clinic
B) Methadone is preferred over buprenorphine in primary care due to its longer history of use
C) Physicians with schedule III authority can prescribe buprenorphine for moderate to severe OUD, which has a safer profile than methadone and can be managed in primary care
D) Buprenorphine requires daily in-person dosing similar to methadone, but it carries a higher risk of cardiac arrhythmia
C) Physicians with schedule III authority can prescribe buprenorphine for moderate to severe OUD, which has a safer profile than methadone and can be managed in primary care
As of 2023, Physicians with Schedule III authority can prescribe buprenorphine for OUD, It is as effective as methadone, but safer with a lower risk of misuse, cardiac issues, and overdose. Unlike methadone, it can be prescribed in primary care settings with fewer regulatory restrictions. It is only approved for moderate or severe MOUD, therefore, diagnosis should be confirmed using DSM5 criteria
Which of the following statements about a patient with adductor-related groin pain is correct?
A. Ultrasonography is the initial imaging modality of choice
B. Surgical release of the adductor longus has been show to reduce symptoms
C. Active physical therapy is unlikely to improve outcomes
D. Bony findings on magnetic resonance imaging are rare
B. Surgical release of the adductor longus has been show to reduce symptoms
MRI of the pelvis is the preferred imaging modality in patient with adductor- related groin pain. The most common MRI findings in symptomatic patients are moderate to marked pubic bone subchondral boen marrow edema, co. PT is the initial choice of treatment. Patient who remain symptomatci after conservative treatment should be referred for srigcla adductor long tendon release wich has been show to reduce sympotms.
A 66-year-old woman with a 20-pack-year smoking history quit smoking 10 years ago. Should she receive lung cancer screening?
YES
The USPSTF recommends annual screening for lung cancer with low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) in adults aged 50 to 80 years who have a 20 pack-year smoking history and currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years. Screening should be discontinued once a person has not smoked for 15 years or develops a health problem that substantially limits life expectancy or the ability or willingness to have curative lung surgery.
What was the primary outcome measured in the network meta-analysis of 137 randomized controlled trials on acute migraine treatment, and which medication demonstrated superior pain relief compared to others?
The primary outcome measured in the network meta-analysis was pain relief at 2 hours and the use of rescue drugs within the first 2 to 24 hours. Eletriptan was found to produce greater pain relief compared to other treatments and decreased the need for rescue drugs in the first 2 to 24 hours, when compared to sumatriptan, which was used as the standard.
Which of the following medications would be most appropriate for a patient with MIDAS score of III and a history of ongoing coronary artery disease
A) Rizatriptan
B) Ubrofepant
C) Naproxen
D) Lasmiditan
B) Ubrogepant
Explanation: Gepants like ubrogeptant have no vascular contraindication and are suitable for patients who cannot use triptans due to cardiovascular conditions.
MIDAS (Migraine Disability Assessment) is a validated questionnaire that can be used to assess migraine severity for stratified treatment. Use it during the stratified care technique to guide medication choice.
MIDAS grades I and II: simple analgesics are recommended
Midas III and IV: targeted migraine medication
True/ false Questions for key recommendation:
1. Buprenorphine treatment should be offered to patients with moderate to severe opioid use disorder
2. A patient must receive behavioral therapy while receiving opioid use disorder medication
3. Concurrent Benzodiazepine or stimulant use is a reason to withhold buprenorphine treatment
4. Buprenorphine should be continued for at least one year but not indefinitely
1. True - evidence rating A
2. False - evidence rating B: Do not require behavioral therapy as a condition for receiving treatment. Should be offered on a patient's need and preference
3. False-evidence rating B: Limit quality evidence from large population cohort studies. Concurrent use of a benzo with Buprenorphine or stimulant may be associated with a slightly increased risk of OD, but the small risk is outweighed by the significant risk of relapse if MOUD is withdrawn or held.
4. False- Buprenorphine should be continued for at least one year and possibly indefinitely if it remains beneficial. Evidence rating B
Which of the following is the most appropriate initial management strategy for an athlete presenting with pubic-related groin pain?
A) Immediate surgical referral for pubic symphysis curettage
B) Corticosteroid injection into the pubic symphysis
C) Physical therapy focusing on core and pelvic stability
D) Complete rest without rehabilitation for 12 weeks
C. Physical therapy focusing on core and pelvic stability
The recommended first-line treatment for pubic-related groin pain—managed similarly to adductor-related groin pain—is physical therapy, especially targeting core and pelvic stability. This approach leads to faster return-to-play compared to surgical interventions. Surgery, including curettage or arthrodesis, is considered only after 12 weeks of failed conservative management.
Who should be screened for osteoporosis, and what is the recommended screening tool?
Women greater than or equal to 65: Screen with DEXA
or Younger post menopausal women with increased fracture risk based on clinical risk assessment
What were the key differences in the treatment outcomes between hyaluronic acid and triamcinolone hexacetonide injections for patients with Morton neuroma, as reported in the study?
Both treatments led to clinically meaningful pain improvement, but the degree of improvement was greater in those treated with triamcinolone hexacetonide (1.7–3.4 points on the visual analog scale, which were clinically meaningful pain differences).
A Patient with moderate migraines fails to respond to sumatriptan and rizatriptan. According to the American Headache Society, which treatment option is preferred before initiating a gepant?
A) Try Dihydroergotamine
B) Trial of another triptan in a different route
C) Switch to acetaminophen- asprin- caffeine combination
D) Begin daily prophylaxis with beta blockers
B) Trial of another triptan in a different route
Explanation: Guidelines suggest trying two different oral triptans or a different route of administration before escalating to geptant, which are more expensive and second line
Rationale:
• A is incorrect: There was no reduction in adverse events in the 6–9 month cohort.
• B is incorrect: Risk declines only after 12 months and continues to improve through at least 18 months. • C is correct: Evidence shows only the 12–15 and 15–18 month cohorts had significant reductions in ED visits and prescriptions.
• D is incorrect: Overdose rates remained similar (5–6%) across all time-in-treatment cohorts.
A 30-year-old male recreational soccer player presents with 3 months of localized groin pain that worsens with activity. On examination, he reports pain in the inguinal canal region, and you note tenderness with palpation, especially during Valsalva maneuver, but no palpable hernia is detected. Dynamic ultrasonography is nondiagnostic. After 10 weeks of core-focused physical therapy, his symptoms persist.
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management, and what is the rationale?
A) Continue conservative treatment for an additional 4–6 weeks before considering surgical options, as imaging was nondiagnostic.
B) Refer for MRI of the pelvis to assess for posterior abdominal wall weakness and other occult pathology.
C) Order a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis to reassess for occult hernia or other intra-abdominal pathology.
D) Refer directly to general surgery for consideration of laparoscopic mesh repair, as physical therapy has failed.
B) Refer for MRI of the pelvis to assess for posterior abdominal wall weakness and other occult pathology.
Explanation:
While this patient has clinical findings suggestive of inguinal-related groin pain, he lacks a definitive hernia, and dynamic ultrasonography was nondiagnostic. According to current guidelines, in patients with persistent symptoms and inconclusive ultrasound findings, MRI of the pelvis is the recommended next diagnostic step to evaluate for posterior wall weakness and other structural abnormalities. Surgery may be considered after confirming pathology or if MRI supports the diagnosis and conservative therapy has failed.
A is incorrect: There is a need for further imaging before simply extending conservative management.
C is incorrect: CT is less sensitive than MRI for soft tissue and pelvic wall abnormalities.
D is premature: Without a confirmed diagnosis via imaging, direct surgical referral is not the best next step.
A 4-year-old child presents for a well-child visit. The parents have no concerns. The child has normal growth parameters and is developmentally appropriate. The family history is unremarkable. According to the USPSTF, which of the following screenings is recommended at this age?
A) Vision screening
B) Lipid screening
C) Autism screening
D) Depression screening
E) Blood pressure screening
Explanation:
• Vision screening: Grade B — USPSTF recommends vision screening at least once in all children aged 3 to 5 years to detect amblyopia or its risk factors.
• Lipid screening: I statement — Insufficient evidence to recommend for or against in asymptomatic children/adolescents.
• Autism screening: I statement — Evidence is insufficient to assess benefits/harms in asymptomatic children under 3.
• Depression screening: Recommended starting at age 12, Grade B.
• Blood pressure screening: I statement — Not enough evidence to support screening in asymptomatic children/adolescents.
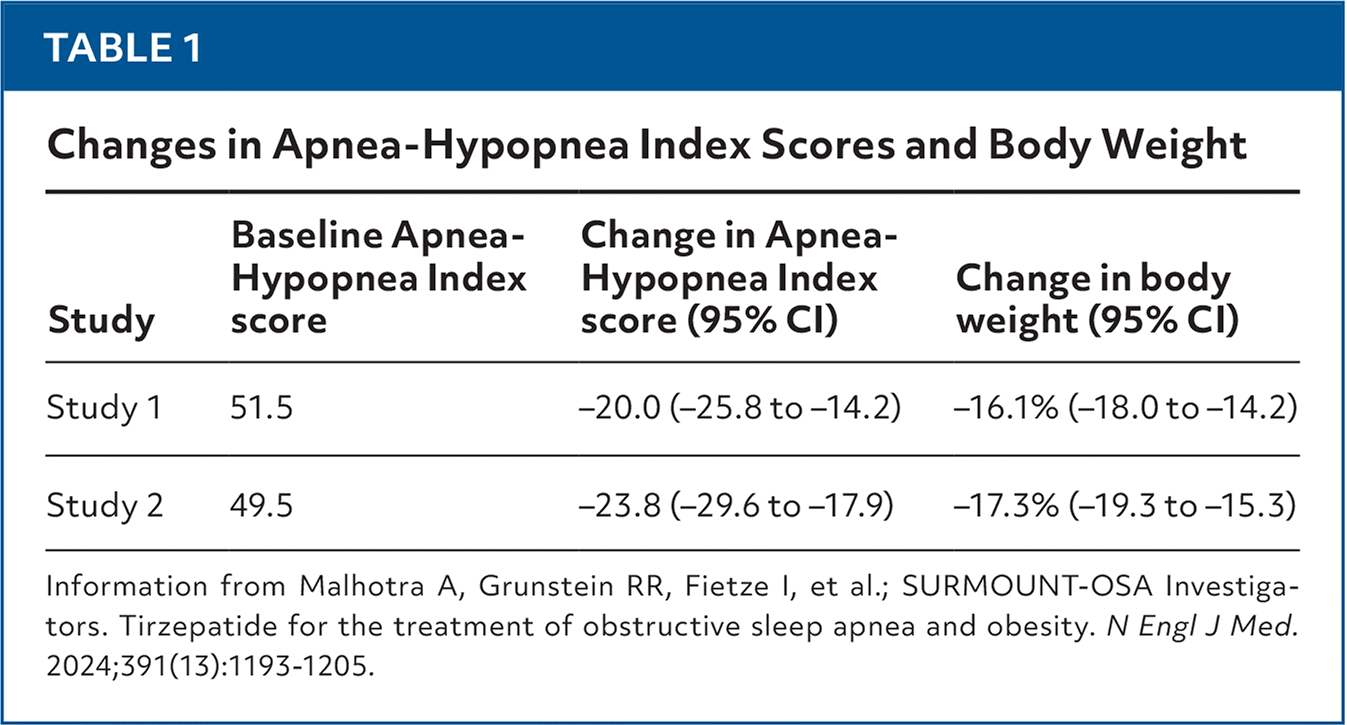
In the study examining tirzepatide's effects on adults with obesity and obstructive sleep apnea, what was the primary outcome measured, and how did tirzepatide compare to the placebo in terms of Apnea-Hypopnea Index scores?
The primary outcome measured in the study was the change in the Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI) score, which measures events per hour. Tirzepatide significantly reduced the Apnea-Hypopnea Index scores compared to the placebo. Additionally, tirzepatide was associated with significant weight loss in adults with obesity, but this effect was not observed in those with diabetes.
Which of the following statement is TRUE regarding greater occipital nerve blocks in acute migraine management?
A) They are only recommended for chornic migraine prevention
B) They are ineffective compared to sham procedure
C) They carry significant risk of serious adverse effects
D) They are supporsed by good evidence for acute pain relief and have minimal adverse effects
D) they are supported by good evidence for acute pain relief and have minimal adverse effects
Explanation:
Which of the following statements most accurately reflects advanced principles of buprenorphine initiation and dosing for opioid use disorder (OUD)?
A) Buprenorphine should always be started at a maintenance dose of 32 mg/day to ensure rapid symptom control regardless of withdrawal status.
B) Initiation of buprenorphine must occur after the patient is in moderate to severe withdrawal to prevent tolerance buildup.
C) The standard initiation strategy involves starting with low doses (2–8 mg/day) in mild withdrawal, with titration to a maintenance dose of 16–32 mg/day.
D) High-dose induction (≥16 mg/day) is contraindicated due to increased risk of respiratory depression and should never be used in outpatient settings.
Correct Answer: C Rationale: The standard initiation strategy involves starting with low doses (2–8 mg/day) in mild withdrawal, with titration to a maintenance dose of 16–32 mg/day.
• A is incorrect because 32 mg/day is the upper limit of maintenance, not the starting dose for all patients.
• B is incorrect; initiation should begin in mild withdrawal (COWS ≥8), not moderate to severe.
• C is correct based on the standard approach to minimize precipitated withdrawal.
• D is incorrect because high-dose induction is an accepted alternative, especially when close follow-up is not feasible.
A 26-year-old female long-distance runner presents with chronic anterior groin pain that worsens during uphill running and stair climbing. Examination reveals tenderness on palpation of the iliopsoas, pain with resisted hip flexion, and discomfort during passive hip extension. Dynamic ultrasonography reveals iliopsoas bursitis without snapping, and MRI shows no labral tear but mild femoroacetabular impingement (FAI). She has completed 8 weeks of iliopsoas-focused physical therapy with minimal improvement. She is considering more aggressive treatment to return to competition.
Which of the following represents the most evidence-aligned recommendation for her management at this point?
A) Proceed with arthroscopic iliopsoas tendon release to resolve persistent pain and address underlying muscle tension
B) Recommend a fluoroscopy-guided corticosteroid injection into the iliopsoas bursa, followed by continued physical therapy
C) Advise discontinuation of running and begin NSAIDs and watchful waiting, given limited evidence for other interventions
D) Refer to orthopedic surgery for FAI correction, as this is the likely primary contributor to her symptoms
This patient meets clinical criteria for iliopsoas-related groin pain, with confirmation of bursitis on ultrasonography and symptoms consistent with iliopsoas dysfunction.
Option B is correct because corticosteroid injection into the iliopsoas bursa is supported as an effective treatment in the presence of bursitis, particularly when conservative measures have failed.
Option A is incorrect because arthroscopic iliopsoas release is associated with potential harms, including iliopsoas atrophy and reduced hip flexion strength, and is not routinely recommended, especially in a high-level athlete who relies on hip flexion strength.
Option C ignores the imaging-confirmed pathology and the failure of conservative therapy—watchful waiting alone is not adequate.
Option D is premature; while FAI may contribute, the clinical and imaging findings point more directly to iliopsoas bursitis as the primary pain generator, and FAI treatment would typically be considered only after exhausting more targeted management strategies.
A 55-year-old woman with no significant medical history visits her primary care physician for a routine check-up. She is up-to-date with her vaccinations and has no current complaints. Based on the USPSTF guidelines, which of the following screening recommendations is most appropriate for her at this time?
A) Mammography screening for breast cancer every year
B) Screening for colorectal cancer with a colonoscopy every 10 years
C) Screening for osteoporosis with a bone density scan
D) Annual screening for depression using a validated screening tool
A) Mammography: The USPSTF recommends mammography every two years for women aged 40–74, not annually. Women aged 40–49 should discuss the benefits and risks with their healthcare provider.
B) Colonoscopy: The USPSTF recommends screening for colorectal cancer for average-risk adults aged 45–75, typically with a colonoscopy every 10 years. Since this patient is 55 years old and at average risk, this is the correct recommendation.
C) Osteoporosis: Screening for osteoporosis is generally recommended for women aged 65 and older or those at increased risk, not for women under 65 without risk factors.
D) Depression: Screening for depression is recommended for adults, but annually is not a specific USPSTF guideline; the USPSTF recommends screening for depression only in settings where there are systems in place to ensure proper follow-up, and the specific frequency is not annual by default.
Considering the results of the study on Morton neuroma, analyze the potential risks and benefits of using triamcinolone hexacetonide over hyaluronic acid. How might the occurrence of skin discoloration in some patients influence clinical decision-making for the treatment of Morton neuroma?
Using triamcinolone hexacetonide over hyaluronic acid presents both risks and benefits. The potential benefits of triamcinolone hexacetonide include greater pain relief (as measured by the visual analog scale and American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society score) and a potentially more significant improvement in patient symptoms. However, one notable risk is the occurrence of skin discoloration in 25% of patients, which may cause cosmetic concerns and reduce patient satisfaction with the treatment.
The presence of skin discoloration in some patients could influence clinical decision-making by encouraging clinicians to consider hyaluronic acid as a preferable option for patients who might be more sensitive to cosmetic side effects or who are concerned about skin changes. The choice of treatment may also depend on the severity of pain and the patient's preference for potential side effects versus a potentially greater degree of pain relief.