3 yo with 30 PD ET, CRx +4.50 sp OU
What is AccET?
This particular type of exotropia is associated with neurologic impairments or craniofacial disorders.
What is infantile constant exotropia?
XT 45
XT 35
XT 20
What is a V pattern?
This Special type of Strabismus causes poor abduction, esotropia in primary gaze, a left head turn, globe retraction on adduction and upshoot.
What is a left Duane type I syndrome?
This type of vertical deviation causes one or both eyes to slowly drift upwards and outwards with simultaneous extorsion when occluded or during periods of visual inattention.
What is Dissociated Vertical Deviation?
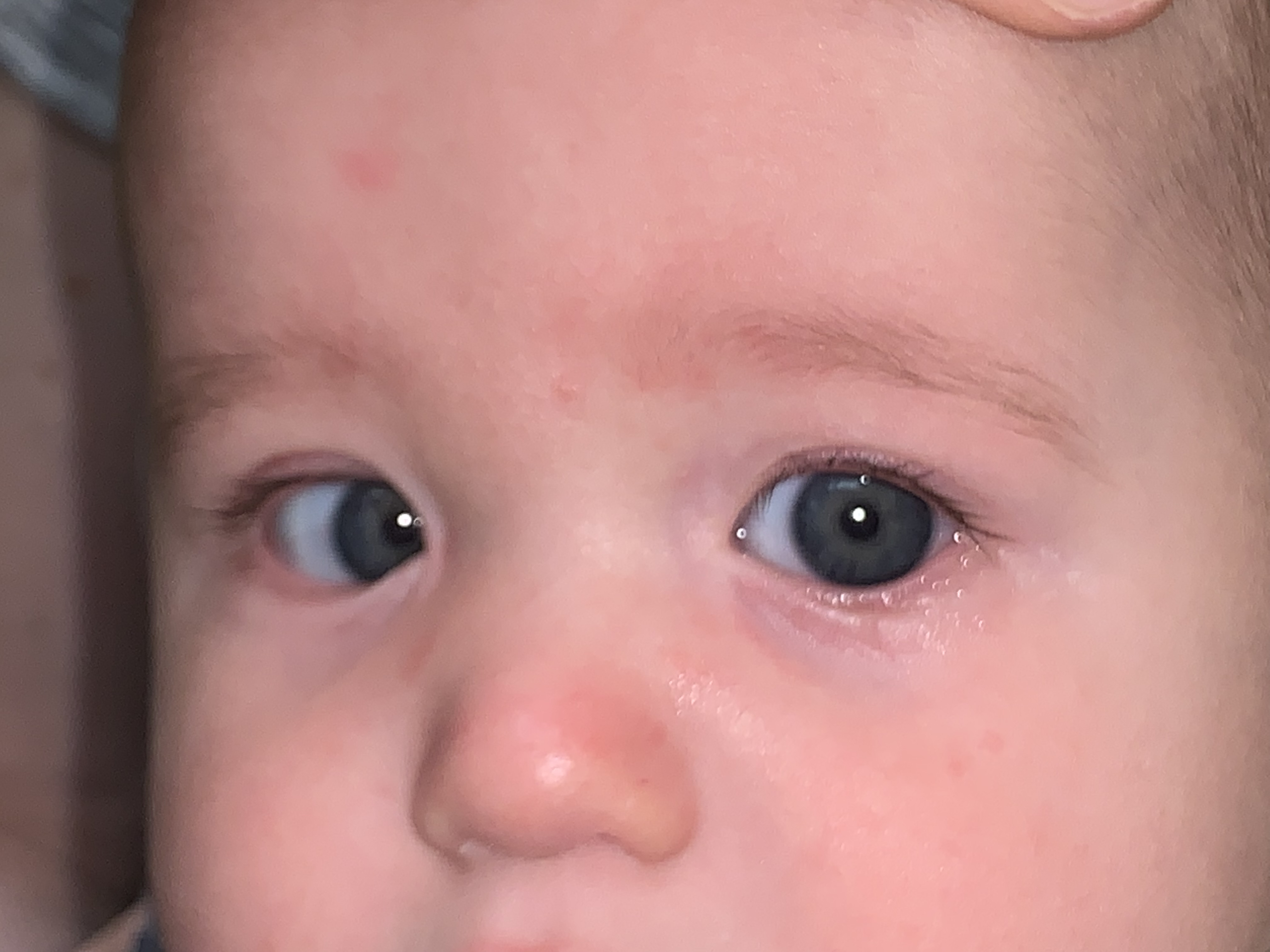
What is Pseudoesotropia?
Correction of refractive error, patching, prism glasses, orthoptic exercises
What are nonsurgical treatments to exotropia (strabismus)?
ET 20
ET 30
ET 45
What is an A pattern?
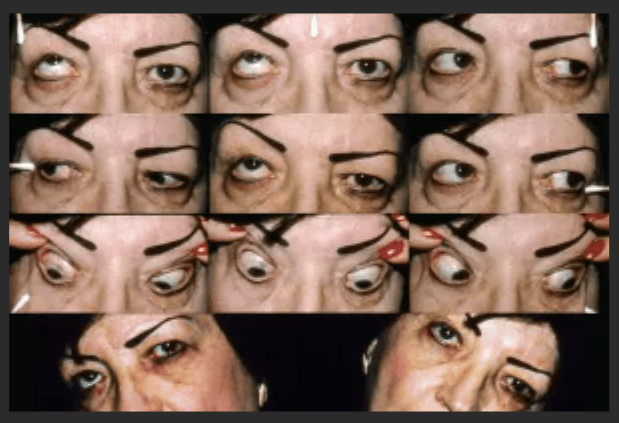
What is an inferior oblique palsy?
This procedure can temporarily weaken a muscle without incisions. Can be used in lieu of surgery or in addition to surgery.
What is botulinum toxin injection?
This test distinguishes between true divergence excess and pseudodivergence excess.
What is the patch test?
This type of pattern is thought to be due to a pseudo-overaction of the inferior oblique muscle.
What is a Y pattern?
Preexiting head tilt, large vertical fusional amplitude, facial asymmetry suggest this specific type of muscle palsy.
What is congenital superior oblique palsy?
Primary gaze ET 25 PD
Right gaze ET 12 PD
Left gaze ET 55 PD
What is a Left abducens nerve/CNVI palsy?
This particular type of exotropia can be commonly associtated with Parkinson's Disease.
A V pattern is usually due to overaction of this muscle.
What is the inferior oblique?
This phenomenon occurs when a patient with RSO palsy of the right eye looking left results in the appearance of a left superior rectus palsy.
What is inhibitional palsy of the contralateral antagonist?
Thyroid Eye disease, orbital myositis, medial wall fracture with entrapment
What are forms of Incomitant Esotropia?
This diagnostic test can distinguish between true convergence paralysis and malingering.
Pupillary constriction on attempted convergence
Two methods to correct pattern strabismus.
What is recession of the oblique muscle?
What is transposition of the horizontal rectus muscles?
This type of deviation results in a different measurement when in supine position.
What is skew deviation?