Describe the overall relationship between the strength of the five forces and the profit potential of the industry
Inverse (strong forces, low profit potential
explain increasing return to adoption and list the two sources of it?
The more a technology is used, the more it is improved
Sources of increasing returns to adoption:
Learning Curve
Network Effects
Suppose that several senior managers recently left Target Corporation and went to work at rival Walmart. What part of the ““stocks and flows”“ of resources does this represent for Target Corporation?
Leakages
How is differentiation parity different from cost parity?
Differentiation parity deals with value not cost.
An industry with high exit barriers, high fixed costs, low marginal costs and slow growth should experience ___________ rivalry. However, _________ can serve to limit rivalry and increase industry profitability. Fill the blank spaces
high / switching costs
List at least three conditions/scenarios under which the power of suppliers is high
✓Supplier’s industry is more concentrated than the industry it sells to. – concentration is a market scenario where a few large companies have a very high market share in the business in the industry.
✓Suppliers do not depend heavily on the industry for their revenues.
✓Incumbent firms face significant switching costs when changing suppliers.
✓Suppliers offer products that are differentiated.
✓There are no readily available substitutes for the products or services that the suppliers offer.
✓Suppliers can credibly threaten to forward-integrate into the industry.
List the three dimensions of the technology stack
Value is based on the stack:
Technology utility (good itself)
Installed base
Complementary goods
How are the critical assumptions of the resource-based model of a firm fundamentally different from the way in which a firm is viewed in the perfectly competitive industry structure?
In perfect competition, all firms have access to the same capabilities, whereas in the resource-based model, resource differences exist between firms in the same industry.
When companies position themselves as differentiators, they aim to provide unique features that increase value, so that consumers pay a higher price. What are three drivers that increase perceived value of consumers?
product features, customer service, and complementary products
How does Shein keep costs low and remain competitive? give two reasons and explain
extensive supply network
management systems
range of products
low cost of labor and other inputs
Give at least three reasons why Walmart is a powerful buyer
The retail giant Walmart provides perhaps the most potent example of tremendous buyer power. Walmart is not only the largest retailer worldwide (with over 12,000 stores and 2 million employees), but it is also one of the largest companies in the world (with $530 billion in revenues in 2019). Walmart is one of the few large big-box global retail chains and frequently purchases large quantities from its suppliers. Walmart leverages its buyer power by exerting tremendous pressure on its suppliers to lower prices and to increase quality or risk losing access to shelf space at the largest retailer in the world. Walmart’s buyer power is so strong that many suppliers co-locate offices directly next to Walmart’s headquarters in Bentonville, Arkansas, because such proximity enables Walmart’s managers to test the supplier’s latest products and negotiate prices.
What are complementary goods?
A product, service, or competency that adds value when used with the original product.
We Build & Build’s’ core competency is building multi-family housing in urban areas. This competency is based primarily on the decisions made by the company’s top management over several years to focus on building in densely populated cities. In current days, the corporation benefits from the process of
path dependence
Give two examples of firms successfully using blue ocean strategy discussed in class and explain what drives their success
Cirque de Soleil & Trader Joes
How did Stitch Fix disrupt the fashion retail industry?
By offering an easier way to shop; reducing burden of choice; stylist; etc.
Suppliers in the carbonated drink industry have ________ power because ___________
Low; they are weakly differentiated
For tech-based companies, it can be very difficult to catch up with the learning curve because it is based on
Cumulative outputs
List and define the two main assumptions of the resource based view.
Resource Heterogeneity.
•A firm is a unique bundle of resources, capabilities and competencies.
•These bundles differ across firms.
Resource Immobility.
•Resources are “sticky,” and don’t move easily from firm to firm.
•Resources are difficult to replicate.
•Resources can last for a long time.
List the four factors/drivers that keep costs low (e.g. that firms need to focus on if they are pursuing cost leadership)
Cost of input factors:
•Raw materials, capital, labor, and IT services.
•Why does location matter?
Economies of scale:
•Decreases in cost per unit as output increases.
Learning-curve effects:
•Less time to produce output with experience.
Experience-curve effects:
•Improvements to technology and production processes.
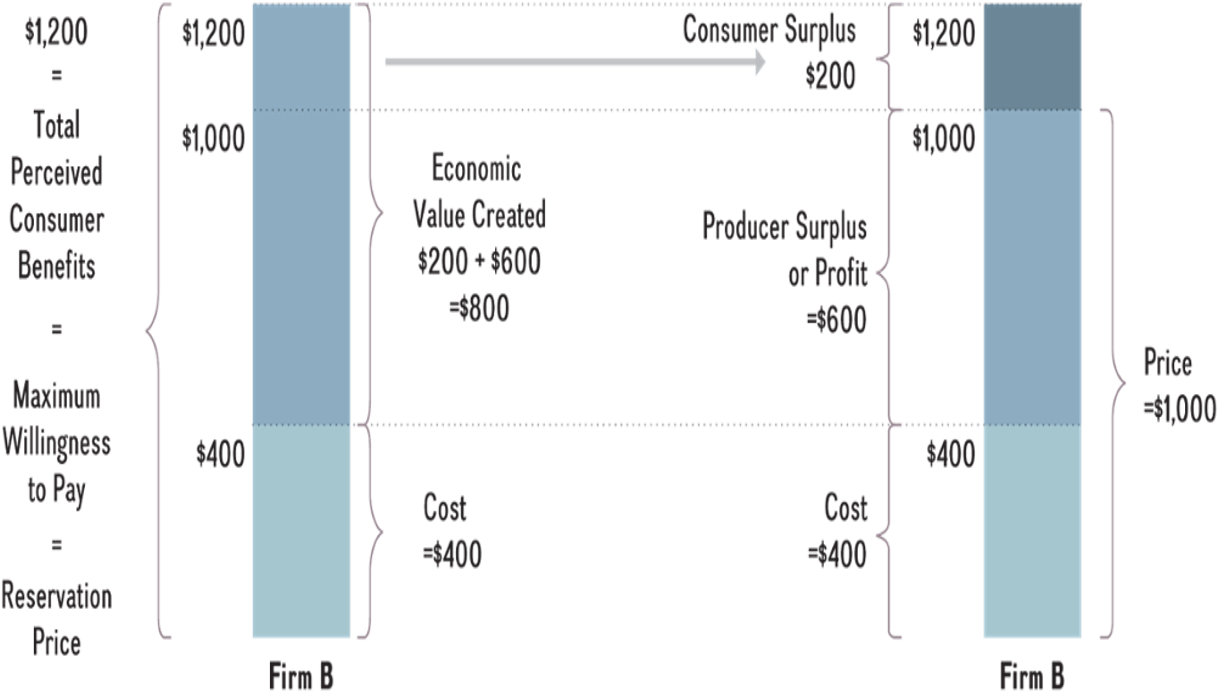
Explain consumer and producer surplus and give an example of how a firm can increase the consumer surplus
In the fast food industry, buyers are very powerful because they can choose which brand to buy from. Why is this sentence wrong?
Individual buyers have no power. Customer loyalty play a huge role in determining power.
Low buyer power.
How can new entrants challenge dominant players in tech industries?
•Challenges frequently come from firms in adjacent markets -> build its own stack and move it to another industry
•Amazon: e-commerce retailer and has built its stack in e-commerce and now it’s entered into Netflix territory, Cloud, digital advertise with Search.
List five (yep all five) isolating mechanisms
•Better expectations of future resource value.
•Real estate agent identifying a parcel of land in up and coming rural area
•Path dependence: past decisions limit current options.
•Carpet industry in Dalton and GM with Electric Cars
•Causal ambiguity: cause and effect are vague.
•Can you pinpoint why Apple is successful?
•Social complexity: social and business systems interact.
•More systems ( e.g. org culture, human interaction with processes, etc.) make it more complex to replicate). E.g. Zappos success with a Chief Happiness Officer won’t be replicated by Lockheed Martin in defense
•Intellectual property (IP) protection.
•Patents, designs, copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets all make it illegal and/or difficult to imitate). For example Pfizer’s Lipitor cost roughly 2.5 billion$ but accumulated over 125 billion$ in sales. Once patent expired generics enter and 45 out of 55 million of Pfizer’s prescriptions went generic
How does product differentiation affect market competition in the luxury fashion industry?
By creating barriers to entry for new competitors. Product differentiation can create unique market niches and customer loyalty, which in turn can act as barriers to entry for potential new competitors by increasing the costs and challenges associated with entering the market
Important topics when discussing Cost Leadership Strategies are the drivers that help firms keep costs under control. However, firms can experience challenges associated with such pursuit. Please comment (define with your own words) on the concept of diseconomies of scale, using an industry of your choice to exemplify TWO sources of diseconomies of scale (the examples do not need to be real).
Just as economies of scale can generate cost advantages for larger firms, important diseconomies of scale can actually increase costs if firms grow too large. If other firms in an industry have grown beyond the optimal firm size, a smaller firm (with a level of production closer to the optimal) may obtain a cost advantage even when all firms in the industry are producing very similar products. Sources are
1. Physical limits to efficient size
2. Managerial diseconomies
3. Worker motivation
4. Distance to markets and suppliers