When a patient does not cough after material has passed into the trachea because of a lack of sensation, this is called:
What is silent aspiration?
Remember: 40-60% of bedside evaluations miss silent aspiration
You are rounding on the weekend and you walk in to the patient's room, introduce yourself, and ask how they're feeling today. The patient peers at you confused and utters a grunting noise but is unable to produce any further speech. They aren't able to read or write rendering them effectively uncommunicative. You deduce their lesion involves this vessel.
What is middle cerebral artery?
Global aphasia describes the most severe form of language deficits in which both written and spoken language are impaired. It involves both Wernicke's and Broca's areas and the MCA lesion spans over both anterior and posterior regions of the brain.
Recovery of hand function by this time point indicates up to a 70% chance of full or nearly full recovery.
What is 4 weeks?
Poorer prognosis for hand recovery if there was complete paralysis at onset and if there is no measurable grasp strength by 4 weeks.
It's 05:30 and you're paged about a patient having a neurologic change. You arrive at bedside and notice the patient is stiff with her lower and upper extremities extended, arms internally rotated, and ankles plantarflexed. You are concerned for imminent herniation and immediately call neurosurgery to arrange for transfer to NCCU. On your transfer note, you describe these physical exam findings as this type of posturing.
What is decerebrate posturing?

In decerebrate posturing, the lesion is involving the brainstem. Posturing is notable for stiff limbs in extension. Worse prognosis than decorticate posturing.
Decorticate posturing is marked by legs in extension but with elbows in flexion. The lesion is above the brainstem which portends a slightly better prognosis.
This Missouri native does not have a middle name. His parents gave hi the middle initial "S" as a tribute to his relatives whose names started with the letter S.
Who is Harry S. Truman?

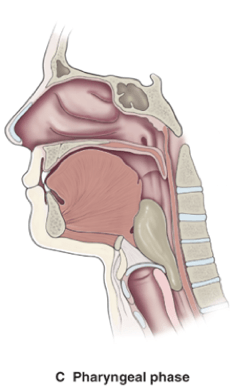
The phase of swallowing where aspiration is most likely to occur:
What is pharyngeal phase?
Phase where the bolus is propelled toward esophagus.
As the bolus leaves the oral cavity, it must pass the faucial pillars (where tonsils are located) where sensory receptors detect and set in motion the chain of events to move the bolus through the pharynx.
Transit time: 0.6 seconds (fastest phase of swallow)
This language disorder results in good comprehension, good articulation but poor repetition and word finding difficulties.
What is conduction aphasia?

A lesion involving the arcuate fasciculus in the parietal or temporal lobe disconnects Wernicke's and Broca's areas. Therefore, they are fluent and understand what you are saying but can't repeat things.
What is walking speed?
Spatial neglect is more commonly seen in lesions to this part of the brain.
What is the nondominant hemisphere?
Right hemisphere is often the nondominant hemisphere, responsible for gestalt analysis, awareness, and emotional prosody of speech. Causes left hemispatial neglect.
Can be associated with anosognosia (not knowing something is wrong, or denying that there’s a problem).
This 42nd US president is a two-time Grammy winner.
Who is Bill Clinton?

These two cranial nerves control the pharyngeal and esophageal phases of swallow:
What are CN IX and X?
These two phases are the two reflexive phases of swallowing (both oral phases are voluntary).
Pharyngeal phase: Palatal elevation -> laryngeal elevation -> folding of the epiglottis over the vocal folds -> adduction of the ventricular and true vocal folds -> elevation and anterior displacement of the larynx.
Esophageal phase: all muscles in the inferior pharynx relax except for cricopharyngeus which is an inferior pharyngeal constrictor (prevents esophageal reflux)
63 y/o right handed female with hypertension suddenly had difficulty getting words out. Her speech was sparse, halting, and labored. She was able to follow three-step commands and repeat words and sentences with 100% accuracy. You share with the speech therapist that the patient seems to have this type of aphasia.
What is transcortical motor aphasia?
Distinguish from Broca's, remember that transcortical lesions are extrasylvian therefore, the arcuate fasciculus and thereby repetition is intact.
This allows them to be more social due to overlearned social phrases.
The greatest amount of improvement in patients with aphasia occurs within this time frame:
A) 3 weeks
B) 3 months
C) 6 months
D) 1 year
What is 3 months?
By 6 months, there is a significant drop in rate of recovery. The majority of cases of patients with aphasia do not recover spontaneously after 1 year.
This cortical lobe contains the somatosensory cortex.
What is the parietal lobe?
Specifically, the postcentral gyrus contains the primary somatosensory cortex (Broadmann's areas 3, 1, and 2). Damage to this area results in decreased sensory thresholds and an inability to discriminate the properties of tactile stimuli or to identify objects by touch.
To test tactile extinction: “Put your hands on your knees (or on the table/bed cover). Now, close your eyes. I will touch your hand, either your left hand, your right hand or both your hands simultaneously. Please tell me or show me which hand I touched. Always keep your eyes closed”.
This Kansas native liked to play golf so much he had a putting green built on the White House lawn during his time as the 34th US president.
Who is Dwight D. Eisenhower?

You are consulted for a 65 year-old woman 6 weeks after a new onset stroke. She is still having difficulty swallowing and requires evaluation for a feeding tube. Her infarct most likely involves this structure.
A) Brainstem
B) Pons
C) Anterior cerebral artery
D) Middle cerebral artery
What is the brainstem?
A patient with continued feeding difficulty or swallowing more than 4 weeks after stroke is likely to have had damage to the brainstem. This is due to lesions of the interneuronal network between the central pattern generator (CPG) in the medulla and the cranial nerves for coordination.

Your patient demonstrates paraphasic speech with semantic substitutions. Most striking is the patient's echolalia, or repetition of phrases that are heard. Comprehension is poor but verbal repetition is intact. Reading and writing skills are poor. When you are staffing this patient with your attending, you determine that they are demonstrating this type of aphasia.
What is transcortical sensory aphasia?
Lesions often in temporal lobe.
Echolalia and paraphasias are technically fluent!
Your patient suffered a stroke 2.5 weeks ago that has resulted in deficits of contralateral numbness, ipsilateral Horner's syndrome, hoarseness, and dysphagia. You educate the family that a feeding tube may need to be placed if the patient's swallowing function has not improved by this time point (hint: weeks).
What is 4 weeks?
Patients with dysphagia from a unilateral stroke usually improve rapidly within the first few weeks after symptom onset. Only ~2% of patients still have difficulty at 1 month post-stroke; these patients are likely to have lesions involving the brainstem (ex: lateral medullary or "Wallenberg" syndrome).

You are taking care of a patient on blue service that communicates with vertical eye movements and blinking only. You astutely recognize that pain pathways remain in tact in this condition so you ask the patient to look upward if he is in pain. Outside the room, the medical student asks you which blood vessel is involved in this stroke syndrome.
What is basilar artery?

Locked-in syndrome is characterized by extensive damage to the pons, possibly medullary involvement and/or corticospinal and bulbar tracts but SPARES the reticular activating system. Sparing of the midbrain tectum allows retained upper eyelid control, vertical eye movements.
Walt Whitman's poem "Oh Captain, My Captain" was written about this 16th US president.
Who is Abraham Lincoln?

"O Captain! My Captain!" was written in 1865 in response to the death of Abraham Lincoln. It was the only one of Whitman's poem to appear in anthologies during his lifetime.
You are admitting a patient to the red team with a R MCA stroke. You see their family member feeding them applesauce and the patient begins coughing. You discuss with family that they should not feed their loved one until further notice from the rehabilitation team. You educate them that their loved one has an issue with the pharyngeal phase of swallowing. You elaborate to describe that these two structures must be in precise coordination for a successful and safe swallow to occur.
What is constriction of pharynx and cricopharyngeal (upper esophageal sphincter) relaxation?

The cricopharyngeus muscle is an inferior pharyngeal constrictor. It is unique in that is constricts as other muscles of the inferior pharynx relax. This is the only muscle that serves as a closing mechanism to prevent esophageal reflux into the pharynx. On the right, this shows the inferior pharynx muscles constricting and the cricopharyngeus relaxing which allows the bolus to pass through into the esophagus.
A patient was brought to the emergency department after a sudden onset of difficulty speaking. A neurological exam indicated that the patient was experiencing subcortical aphasia without findings to suggest brainstem involvement. Before looking at the brain MRI, you anticipate the patient possibly experienced a lesion in this structure.
What is the thalamus? Also accept basal ganglia.
Aphasia can result as a lesion involving the thalamus if the dominant hemisphere is affected due to damage to thalamotemporal projections. This produces dysfunction at the prelinguistic level, such as impairments in concept generation and dysfunction in the control of preformed speech patterns. Data seems to suggest that these deficits are transient with a quick recovery.
Your patient is approaching discharge. She unfortunately did not get much functional recovery of her affected right upper extremity. Her right shoulder subluxation has been managed with a sublux cuff and has been non-painful throughout her course. She is having mild pain that responds well to NSAIDs, tylenol, ice, and heat. She asks you what she can expect for her shoulder pain when she discharges. You discuss that you will see her in clinic to address the issue but educate her that she is at risk for impingement, bursitis, adhesive capsulitis due to malrotation of this bony structure.
What is scapular malrotation?

A lesion of the bilateral occipital lobes causes this syndrome.
What is Anton's syndrome?
Patient's have cortical blindness with denial of their vision loss and confabulate.

This 27th US president is the only president to also serve as Chief Justice of the Supreme Court.
Who is William Howard Taft?

William Howard Taft never really wanted to be President. He preferred law to politics and always aspired to serve on the Supreme Court. But his wife -- who wanted to be first lady -- had other ambitions for him. After four uncomfortable years as President, Taft left the White House and became a Professor of Law at Yale. In 1920, Taft finally realized his true dream when President Harding made him Chief Justice of the Supreme Court, a position which he held until just before his death in 1930.