Patient's mRS score if they now require assistance with preparing meals, but able to walk by themselves with a cane.
What is mRS 3?

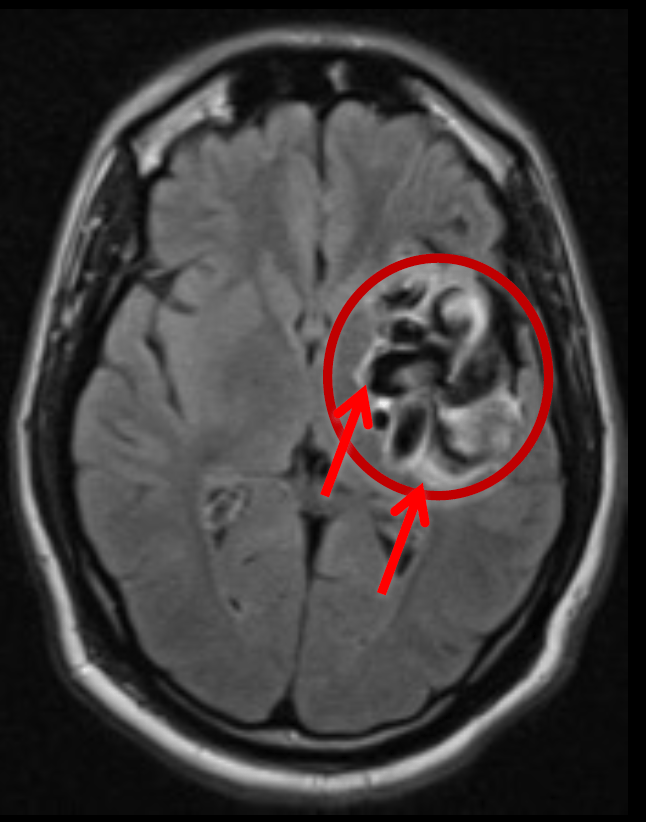
Cavernoma
- CT: hyperdensity sometimes
- MRI: prominent blooming SWI+, popcorn appearance, T2 hypointense hemosiderin ring
- CTA & DSA: occult
Should you start statin in a patient who is 46 years old and has diabetes?
What about if patient is 39 and has diabetes?
Age > 40 + Diabetes (YES)
Long term blood pressure goal after stroke for secondary prevention
< 130/80
Headaches
Anterior temporal lobe
External capsule
What is CADASIL
NOTCH 3 - Chr 19
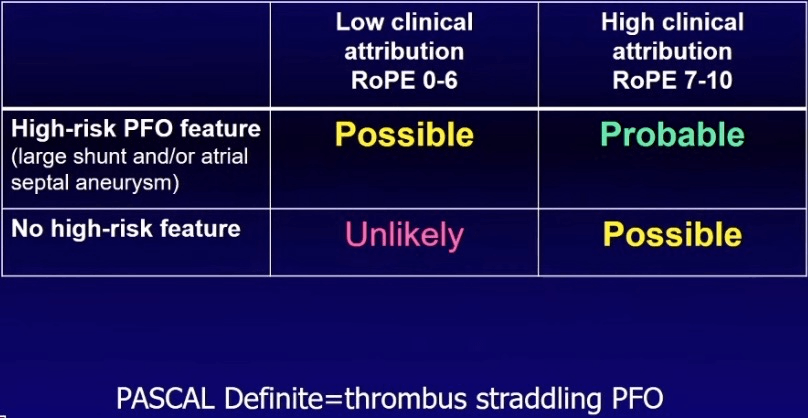
PASCAL score for 40M w/ hx HTN and cortical stroke and found to have a large shunt PFO.
ROPE score = 7, PASCAL = Probabale
Arteriovenous malformation AVM
CT: nidus hyperdensity of intermediary capillaries
MRI: T2 + tightly packed flow voids, minimal mass effect, SWI+
CTA: feeders, drainers
DSA: gold standard (ICA, verts, ECA injections)
Should you start a statin for a 55 year old with no other risk factors but has LDL 195.
LDL > 190, start high intensity statin for primary prevention of ASCVD.
LDL goal for secondary prevention if patient has ischemic stroke without CAD or atherosclerotic disease
LDL goal < 100

Weber syndrome - III nerve palsy with contralateral hemiplegia
PCA perforators or Basilar perforators
NIHSS score for ataxia where patient appears to have ataxia on the L arm but also significantly weak in the arm.
0, not scored if ataxia is NOT out of proportion to weakness.
Most common cerebral vascular malformation?
DVA - developmental venous anomaly
Don't bleed, associated cavernoma may bleed.
CT: if large, can see draining vein; linear/curvilinear feature on contrast CT
MRI: SWI+, post-contrast T1+
DSA: caput medusa sign of drainage; venous phase; possible arterial blush
32 year old resident presents to clinic asking whether he should be screened for cerebral aneurysm because his sister was found to have an unruptured aneurysm. Your response?
Screening for UIAs in patients with ≥2 first-degree relatives with SAH or intracranial aneurysms might be reasonable (Class IIb; Level of Evidence C).
In patients with no more than 1 relative with SAH or intracranial aneurysms screening is not recommended (Class III; Level of Evidence C).
LDL goal if evidence of atherosclerotic disease (intracranial, carotid, aortic, coronary)
LDL < 70
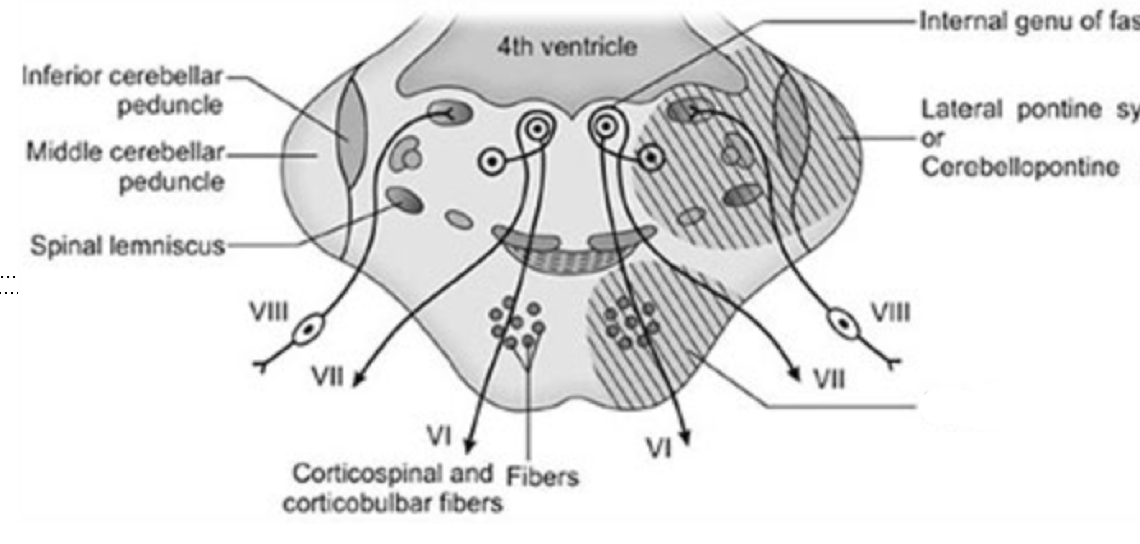
Millard-Gubler Syndrome (alternating facial hemiplegia, medial-ventral pons)
Involvement of VI, VII, pyramidal tracts
What score can you use to help in determining anticoagulation bleeding risk?

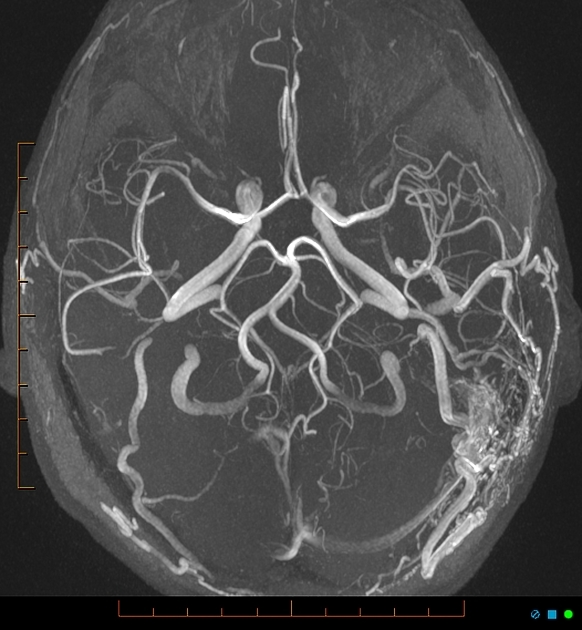
CT - hyperdensity if associated hemorrhage
CTA - dilated cortical veins, abnml dural venous sinus (arterialization in contrast phase due to early drainage)
MRA - venous structures light up on arterial study
In ICAD, this has been shown to have the greatest benefit in reducing ischemic stroke risk.
HTN vs weight loss vs physical activity vs DAPT
Physical activity
DOAC is indicated for stroke prevention in this specific type of AFIB. Define it.
Non-valvular AFIB
Valvular = moderate or severe MS, mechanical mitral valve
Vertebral Artery perforators, then PICA.
Is aspirin safe if patient has unruptured untreated aneurysm? Anyway to quantify risk?
Yes; PHASES/ISUIA scores
This lesion but otherwise well appearing, what is etiology?
Cavernoma
65 year old woman with hx of HTN presents to clinic stating she wants to take aspirin for primary prevention of stroke. What is your response?
Tough question.
USPSTF recommends aspirin for women age 55-79 for ischemic stroke risk reduction if a NET benefit is present (weigh risks of bleeding to possible benefit with colon cancer, cardiovascular events/MI, and stroke)
Patient with embolic appearing stroke and evidence of mitral stenosis but with normal sinus rhythm. What, if any, anti-thrombotic regimen should you start?
Anticoagulation is indicated in patients with mitral stenosis and a prior embolic event, even in sinus rhythm (Class I; Level of Evidence B).
So if SEVERE mitral stenosis or a rheumatic valve, consider A/C.
Coupling of yawning and involuntary movement of a plegic arm
Parakinesia brachialis oscitans
(Lesions affecting pyramidal tracts. Proprioceptive input from anterior horn of c-spine during yawning may trigger reflex involving spinoarchocerebellar pathway)