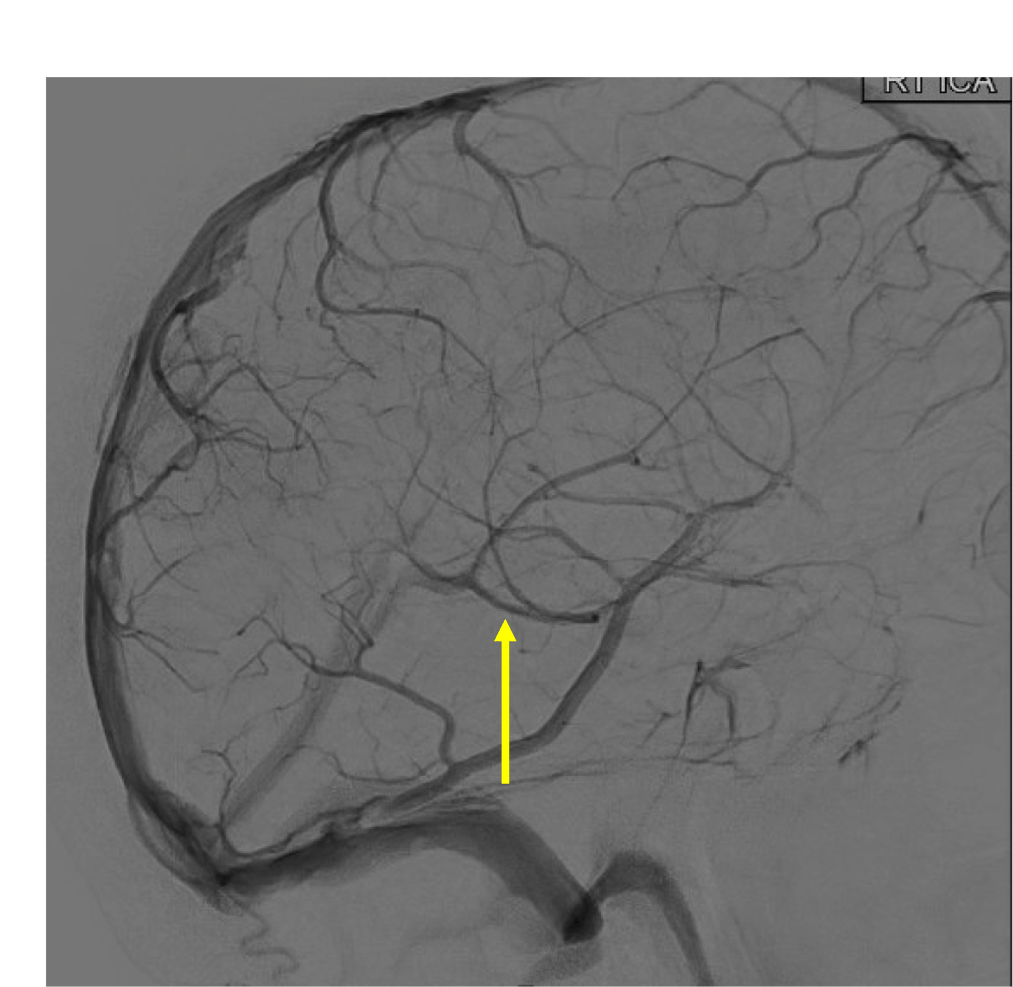
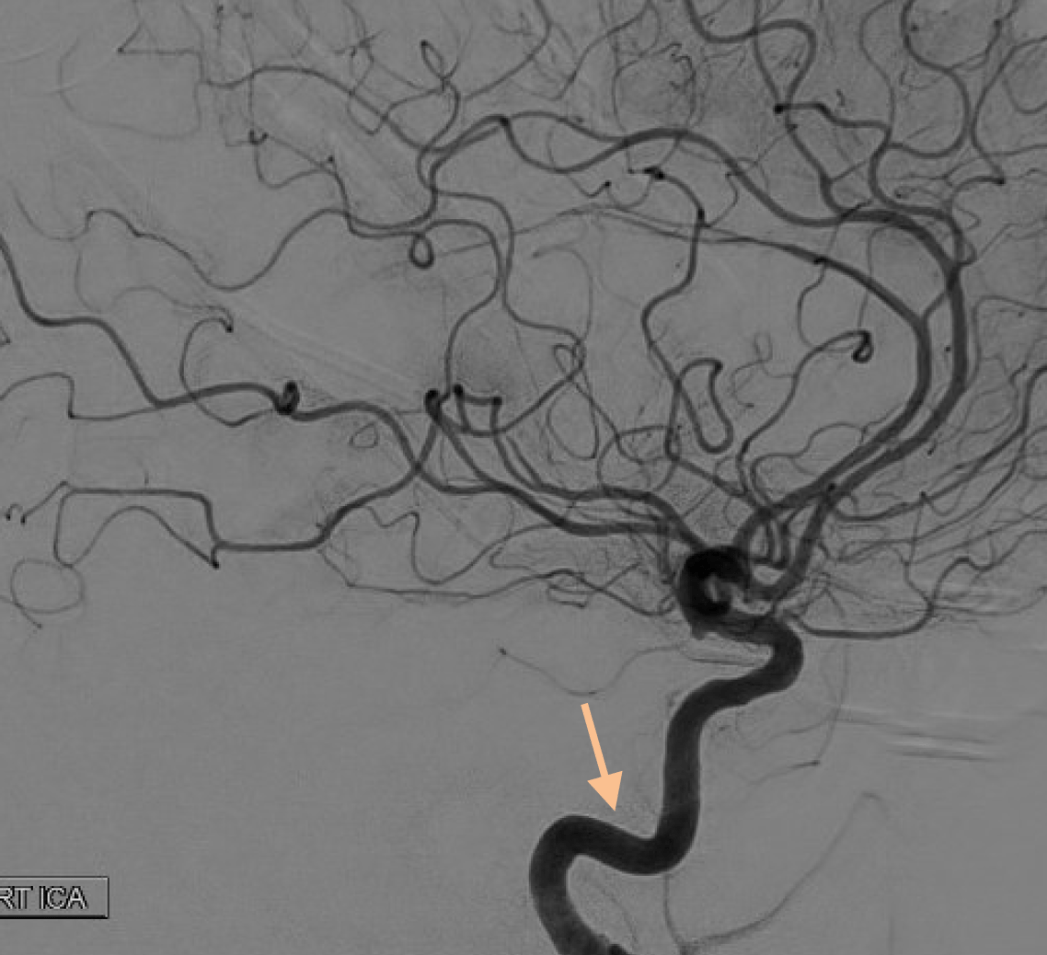
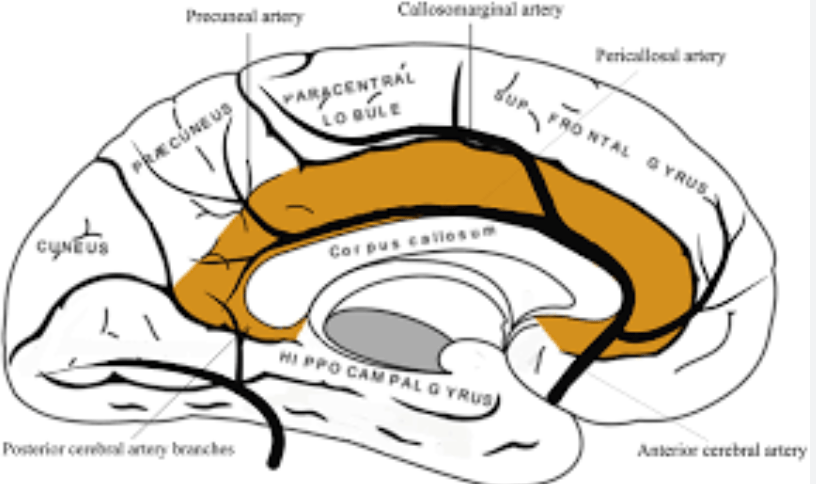
On this lateral view R ICA injection, name these two branches:
Pericallosal and callosomarginal arteries off the ACA
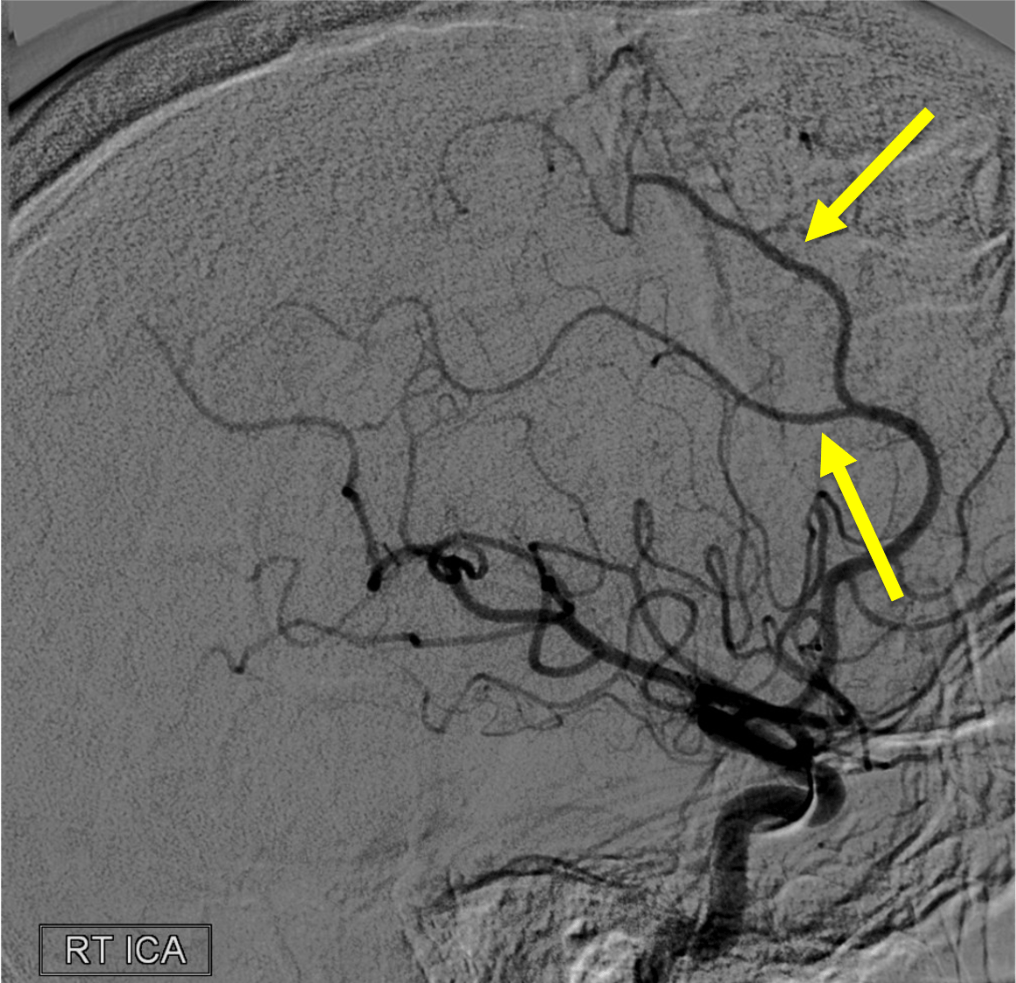
Name the highlighted artery
Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (PICA)
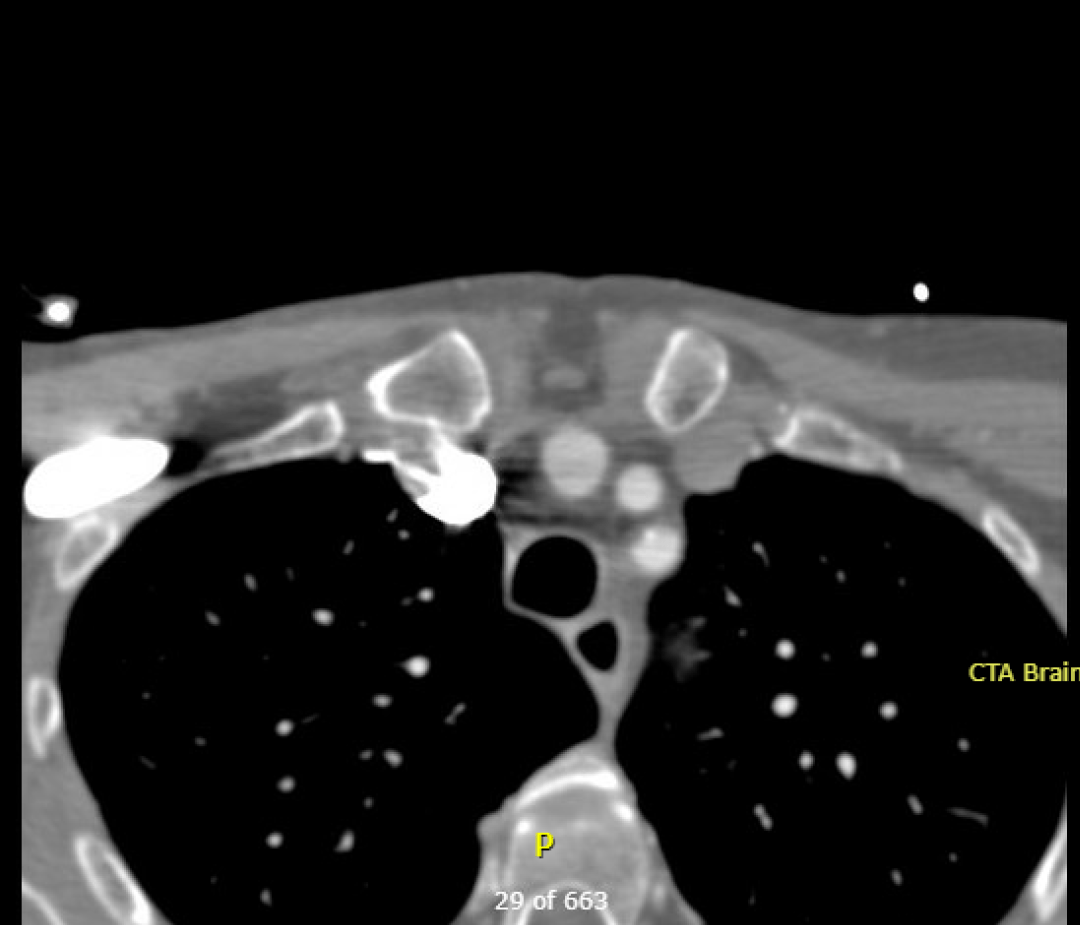
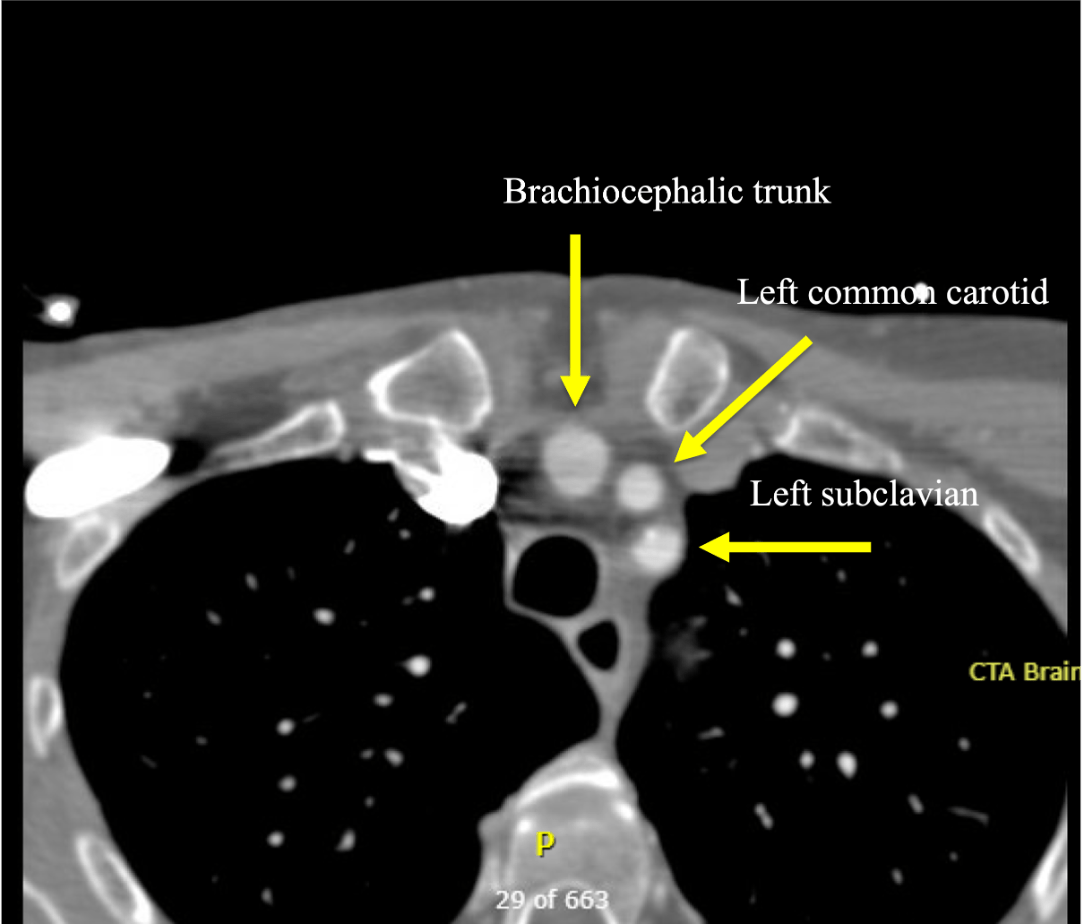
Name the three major branches off the aortic arch, as seen on this axial CTA:
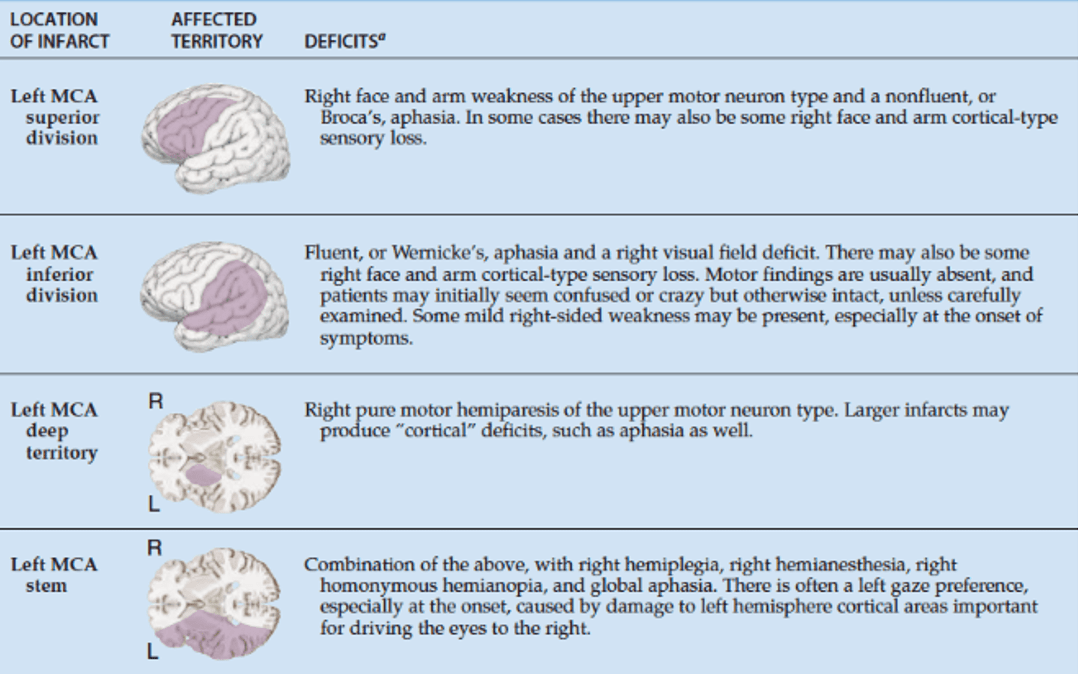
A patient presents with right-sided sensory loss and fluent aphasia. Classically, which territory is likely affected?
A) L MCA, superior division
B) L MCA, inferior division
C) L ACA, pericallosal branch
D) L ICA, anterior choroidal branch
B) L MCA, inferior division
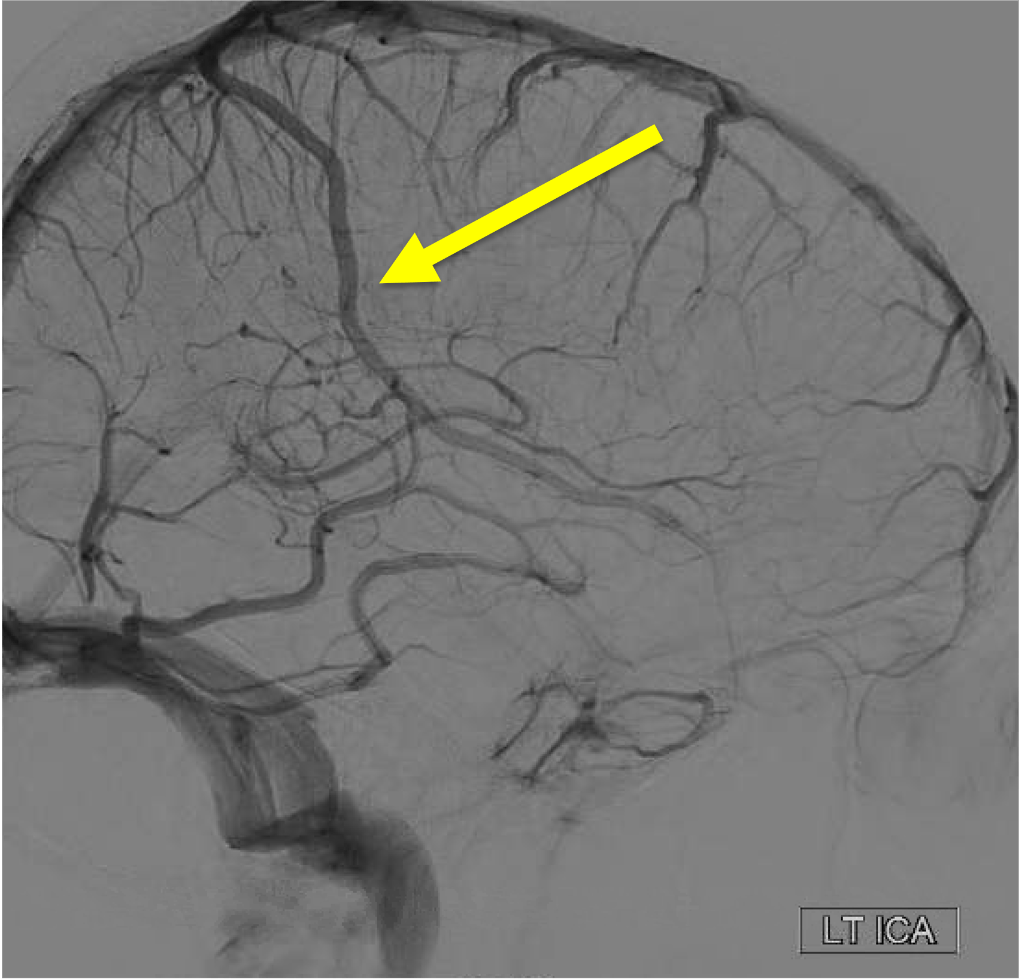
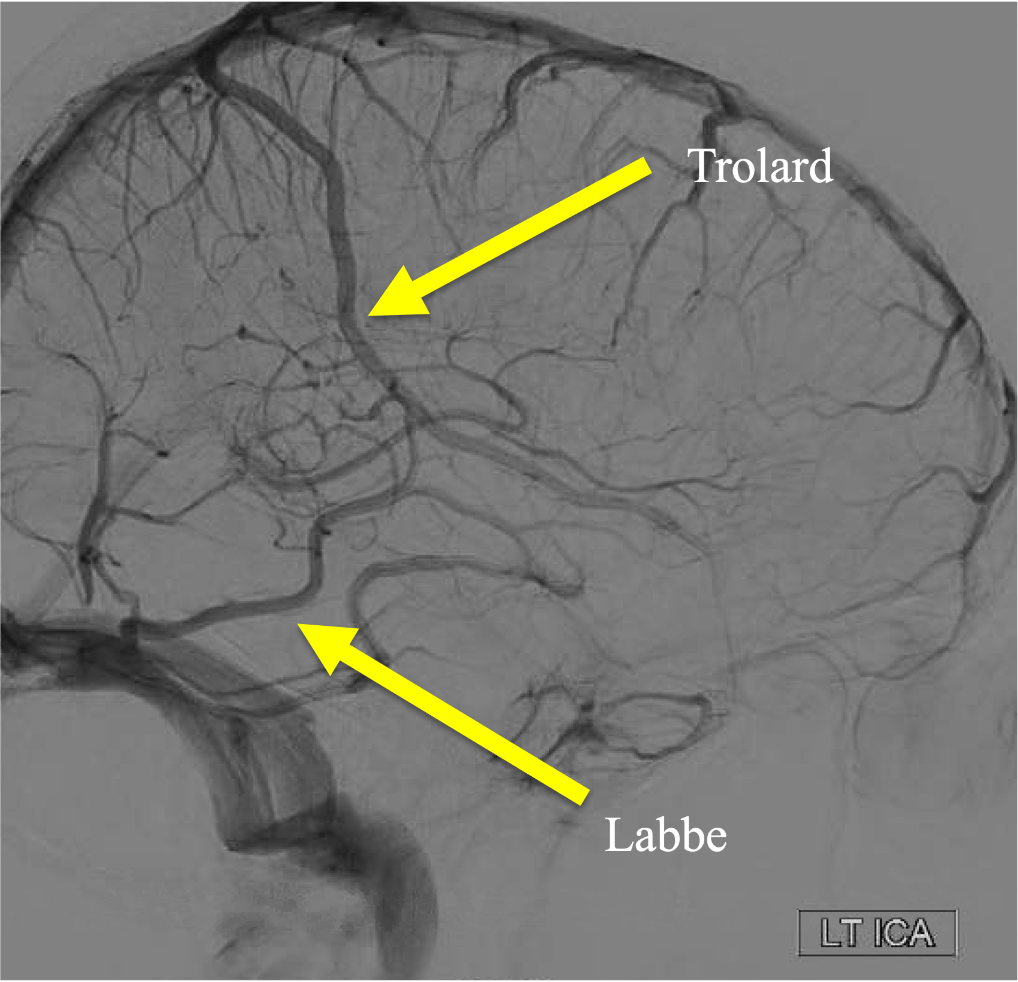
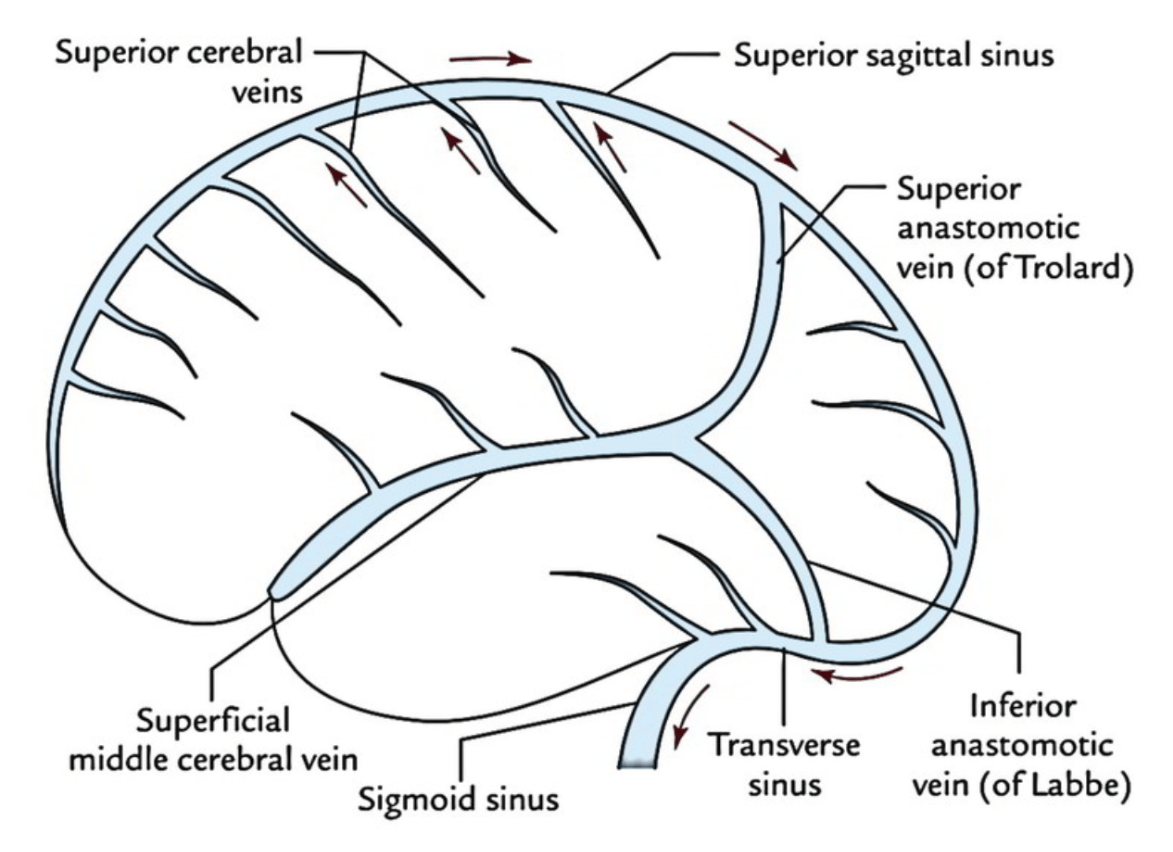
On the venous phase of this lateral L ICA injection, name the superficial vein:
Name this segment of the ICA:
Petrous segment

On this AP view right vertebral artery injection, name the following vessel(s):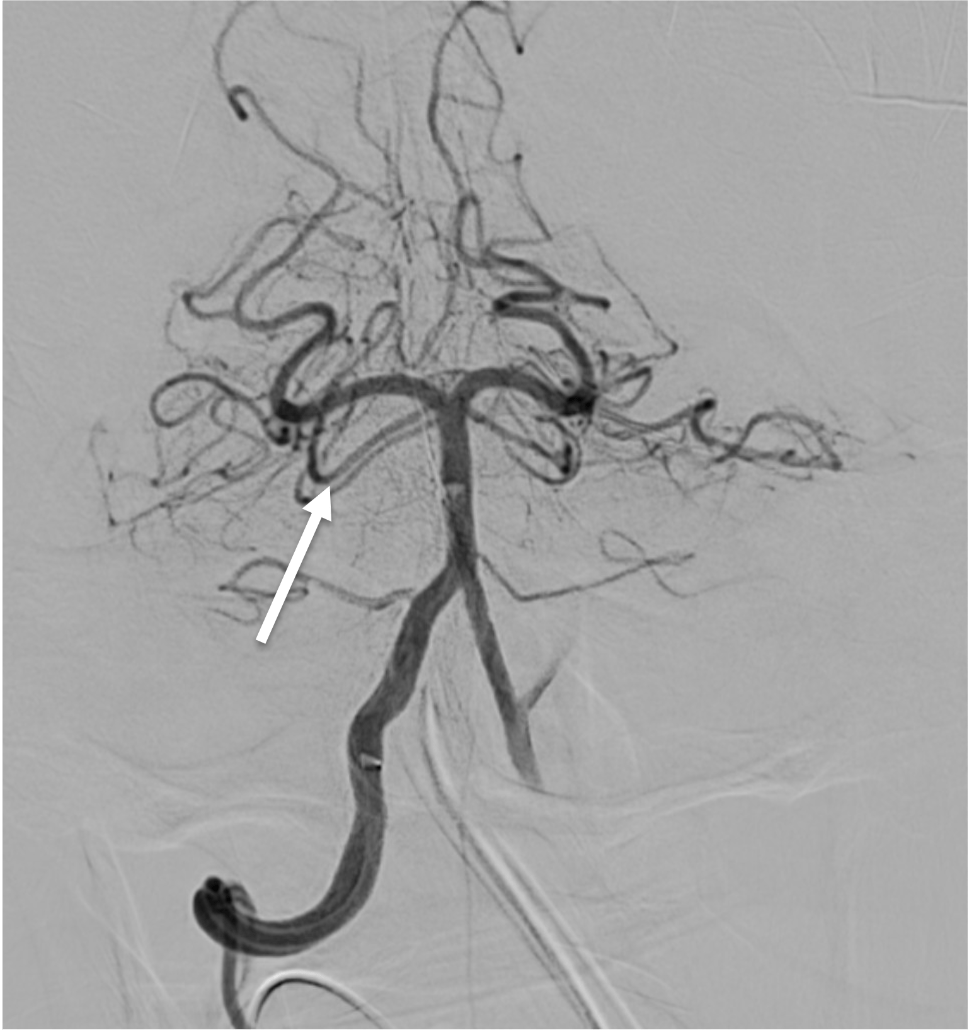
Superior cerebellar arteries (duplicated SCA)
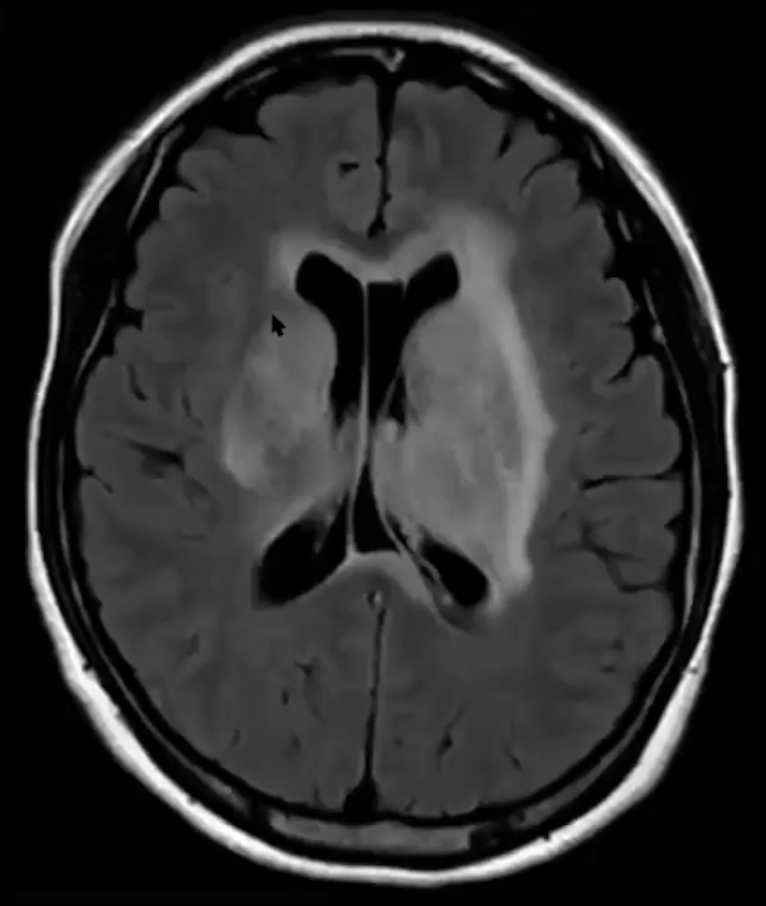
On this lateral view L ECA injection, name the vessel at the white arrow, which is the route of collateral between the ECA and ICA (yellow arrow) in this patient with longstanding ICA occlusion.
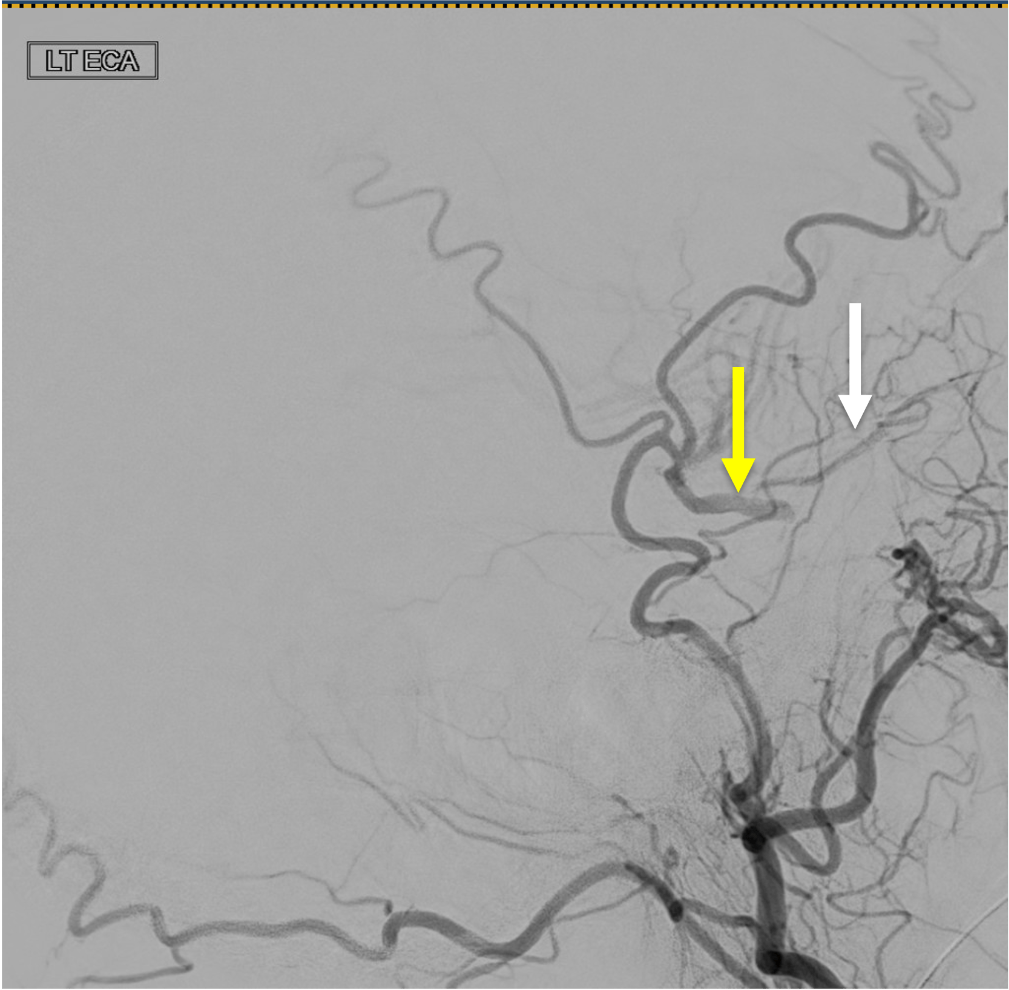
White arrow is the Ophthalmic artery-- here, likely collaterals from the ECA (through the internal maxillary artery --> ethmoidal artery) collateralize with the ICA through retrograde filling of the Ophthalmic

Strokes of the bilateral parietal lobes can lead to this syndrome characterized by optic ataxia, oculomotor apraxia, and simultagnosia.
Balint Syndrome
Optic ataxia is the lack of coordination between visual input and hand movements. For example, the patients can accurately touch their own body voluntarily, but when given a visually guided task, they are unable to complete it.
Oculomotor apraxia is the inability to voluntarily shift gaze despite the intact function of extraocular muscles.
Simultagnosia is the lack of ability to perceive more than a single object at a time. For example, when provided with a picture of a forest with trees, they are unable to see the forest, although they can see each individual tree
Pathologic early filling of this structure is seen on this AP view of the R CCA injection:
Cavernous sinus
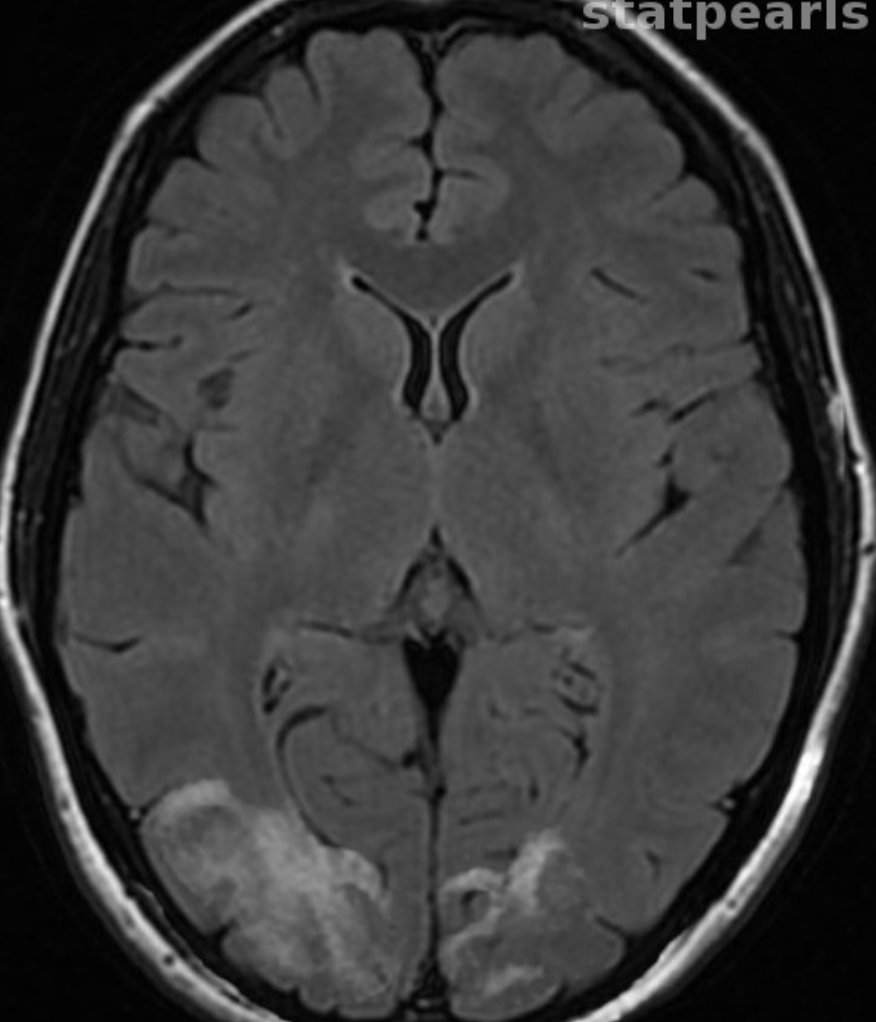
What vessel(s) caused this stroke?
Anterior Choroidal Artery
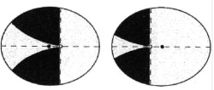
Interesting pearl: The homonymous hemianopsia appears as this:
Occlusion of which vessel(s) cause this stroke?
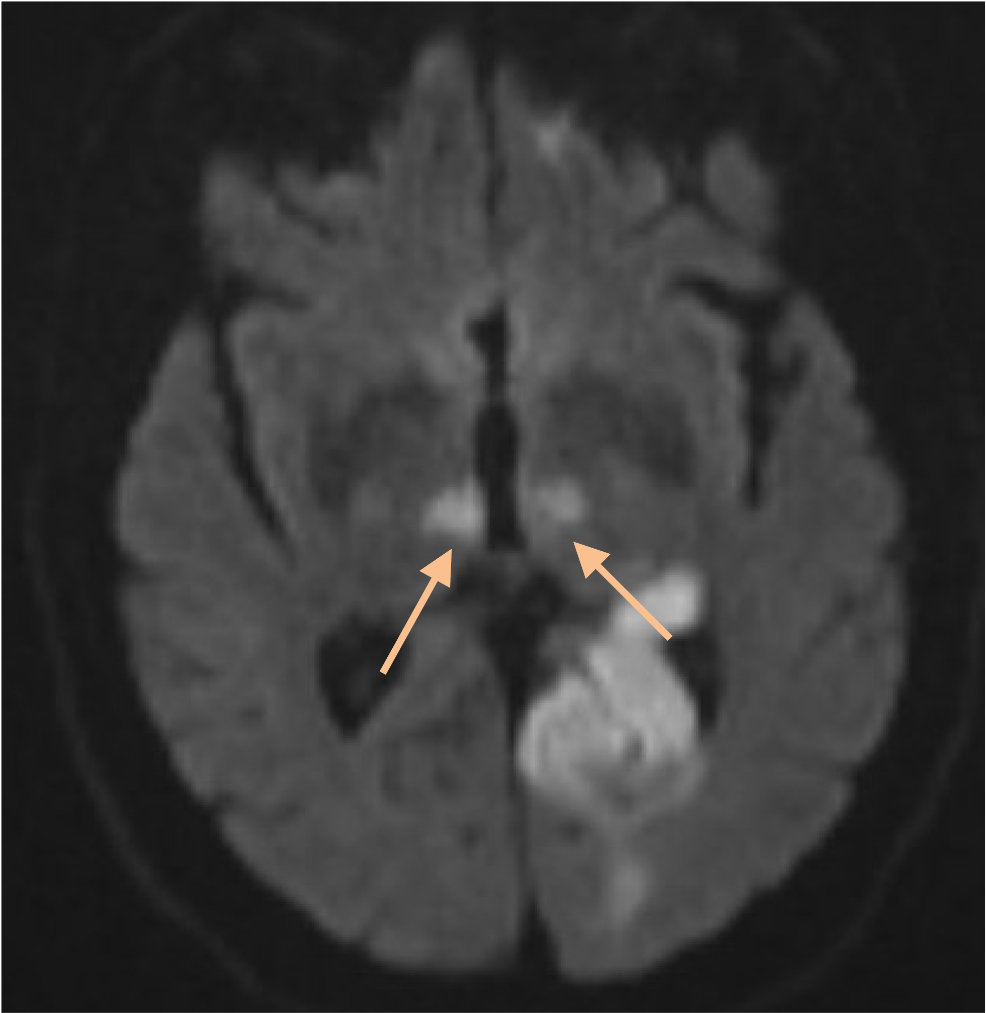
Artery of Percheron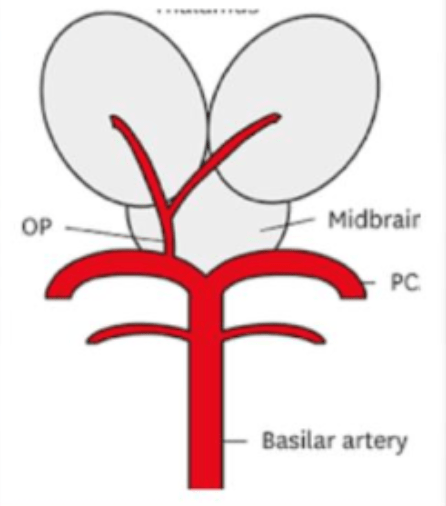
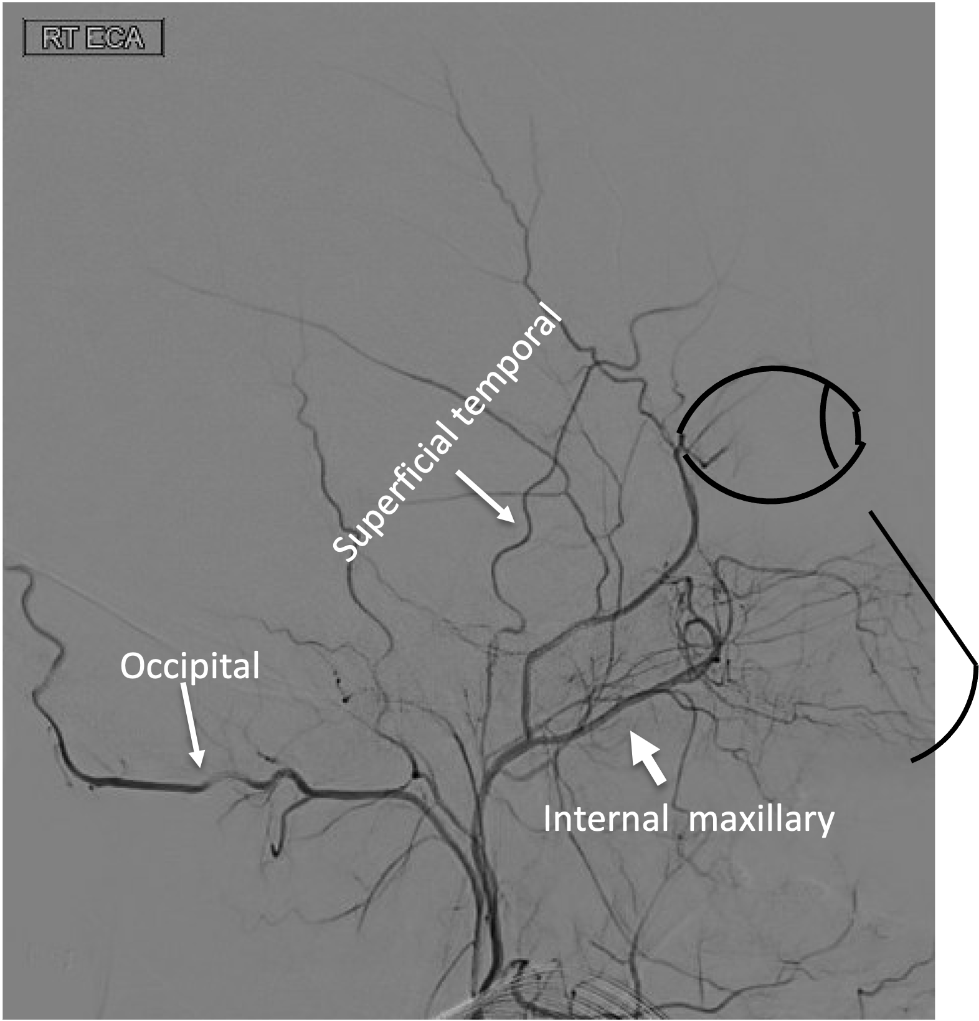
On this lateral view of the R ECA injection, name the following branch:
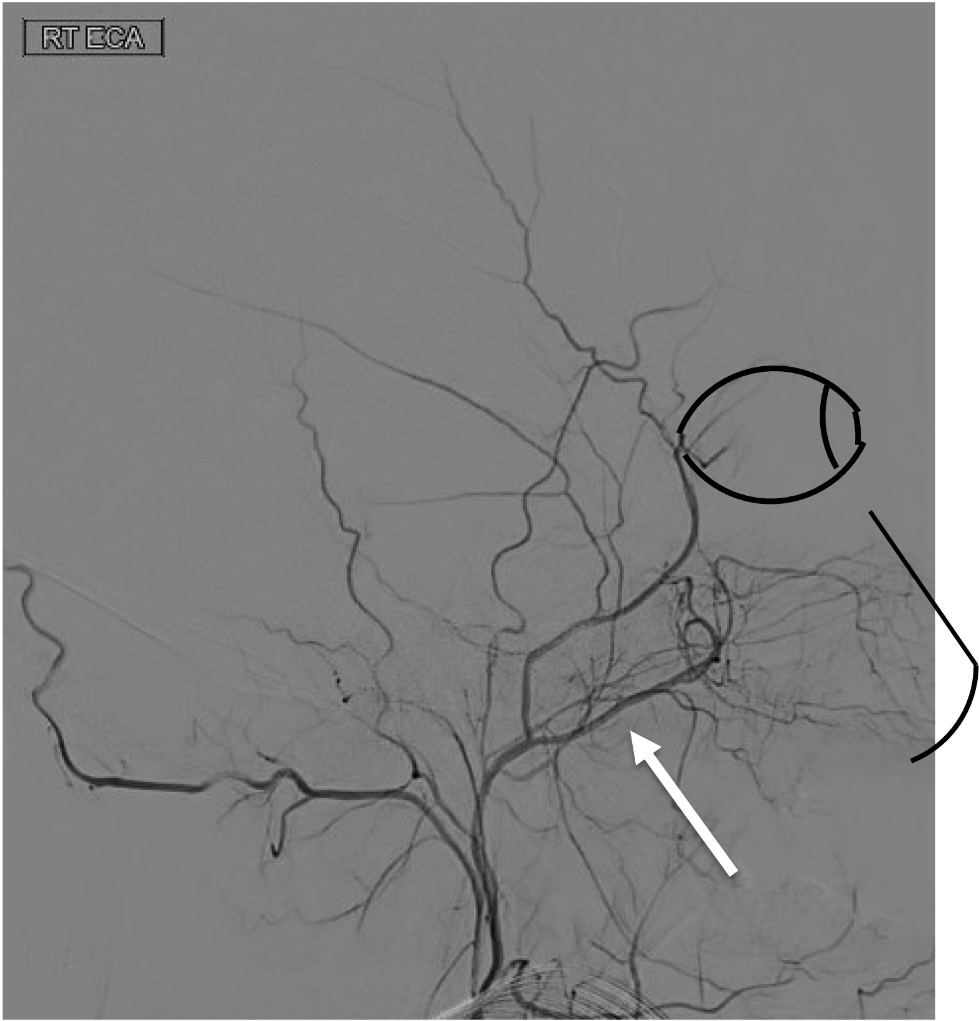
Internal maxillary artery
Name is the stroke site(s) which lead to alexia without agraphia
Splenium of the corpus callosum + left occipital lobe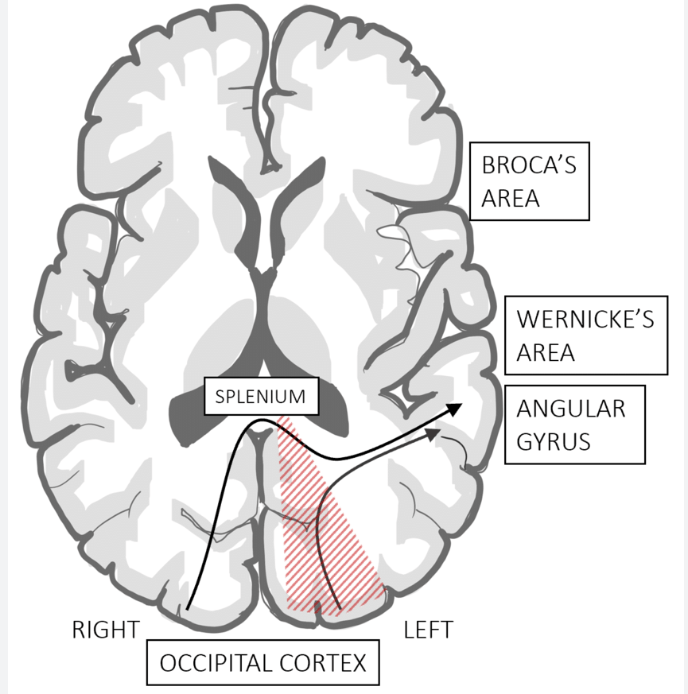
On the lateral view of the venous phase from this R ICA injection, name the following vein:
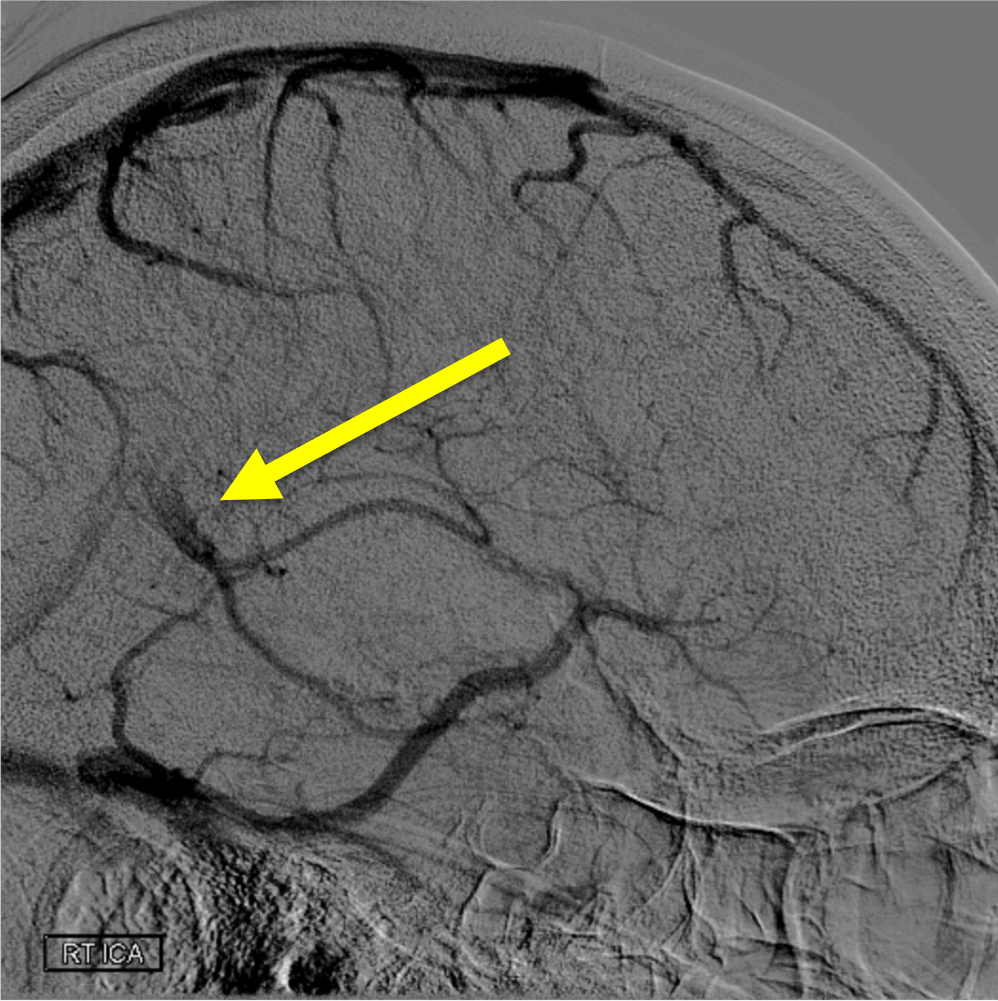
Vein of galen
Which vessel is the arrow pointing toward?
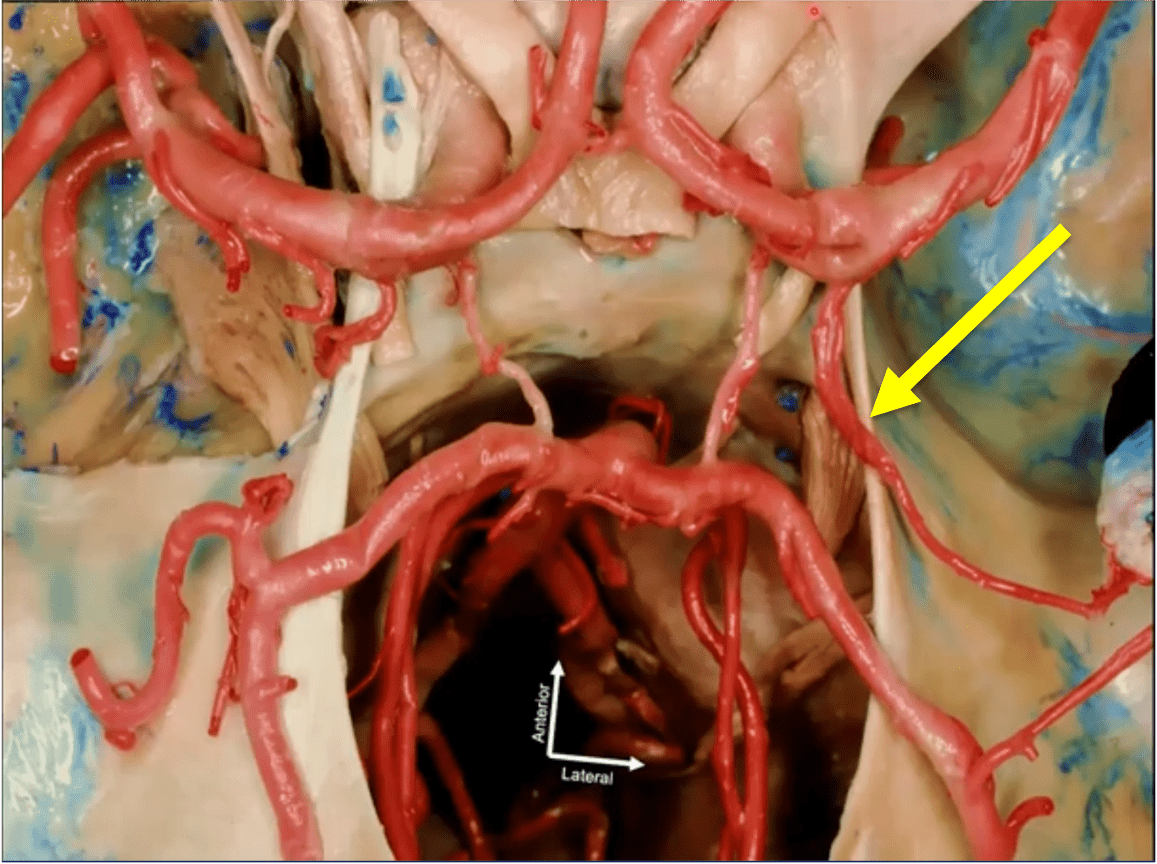
Anterior choroidal artery
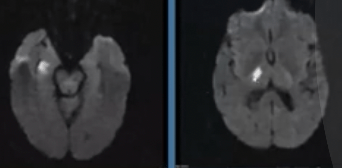
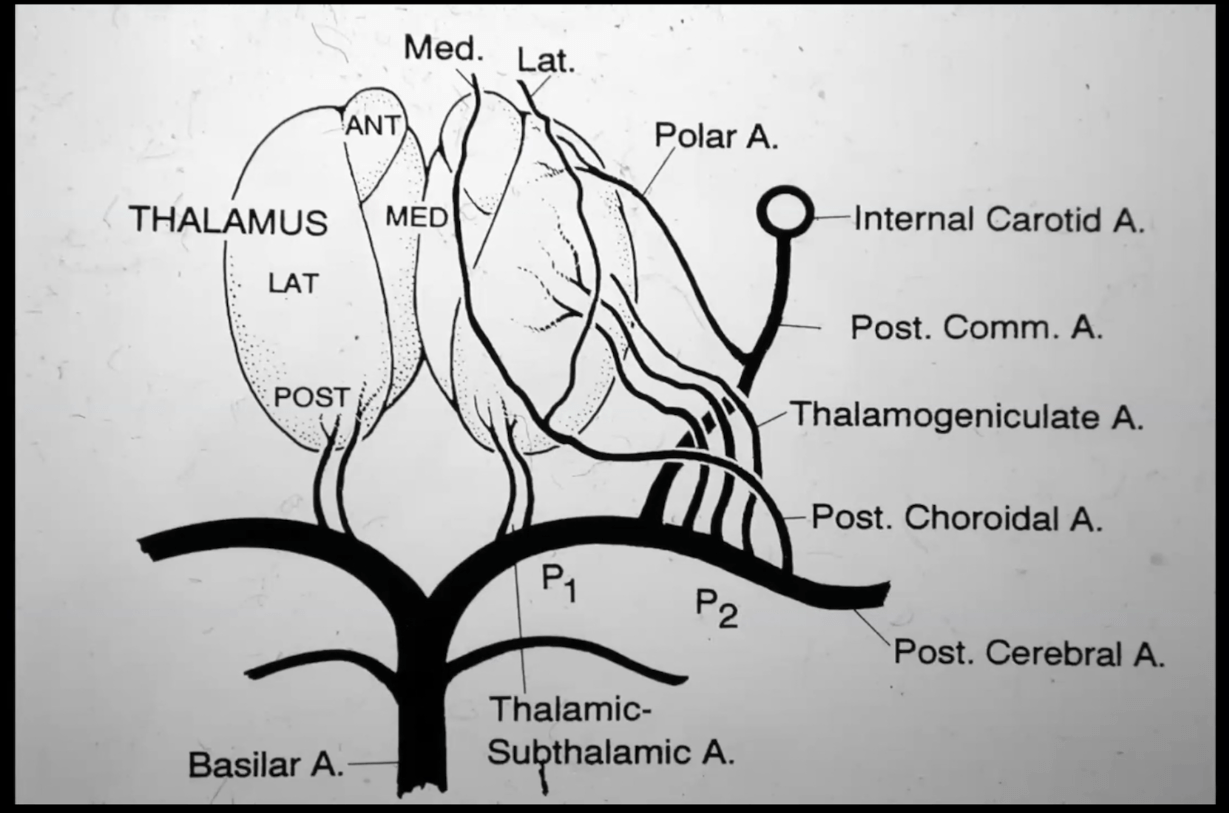
Lateral thalamic strokes, such as the R thalamic stroke shown below, are typically caused by occlusion of these perforating arteries that arise from the P2 segment of the PCA:
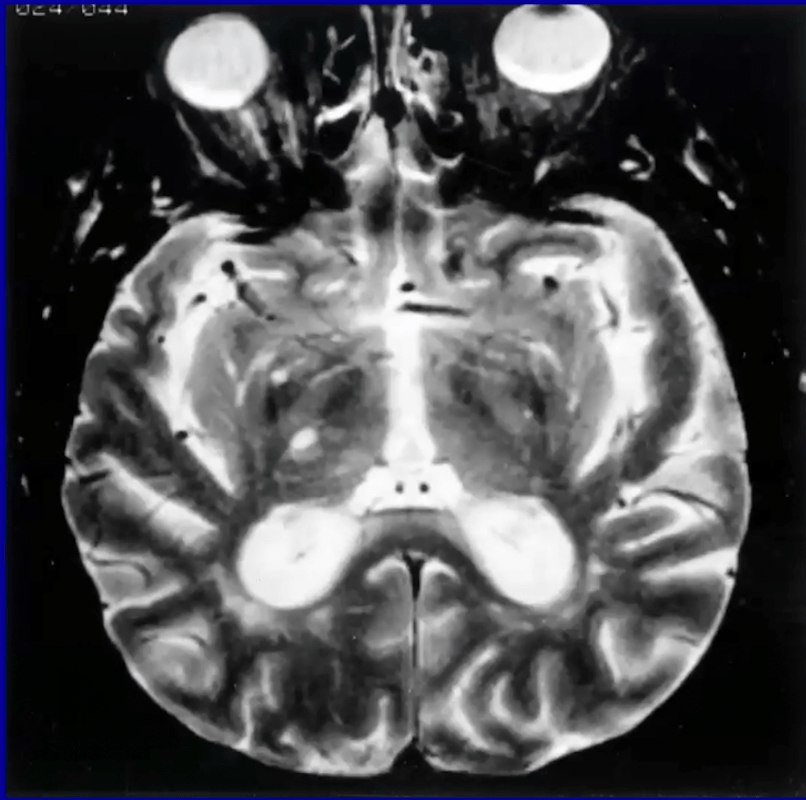
Thalamogeniculate branches
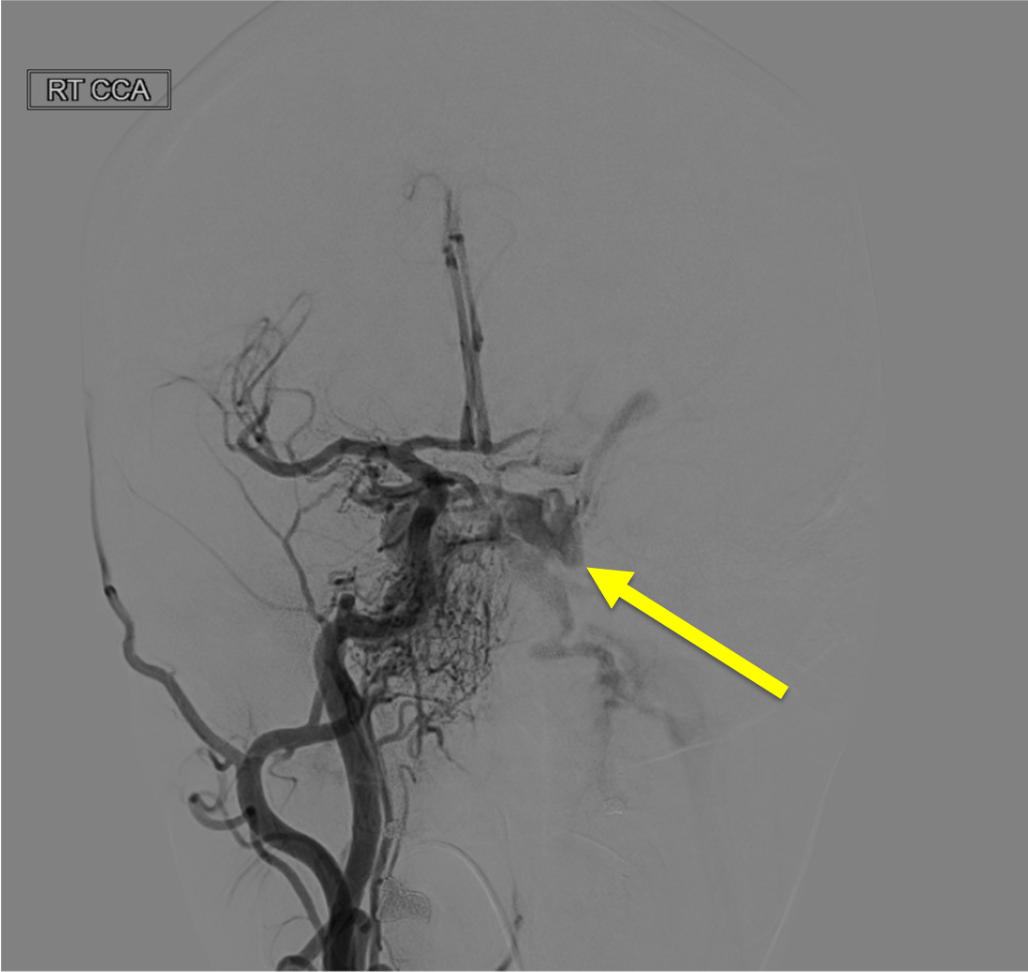
What is the name of this artery stemming from the cavernous segment of the ICA, seen here on the lateral view of this R ICA injection enlarged due to it feeding a dural AV fistula?
Meningo-hypohyseal trunk (specifically the artery of Brenasconi and Casanari)

A patient presents with R eye down and out, unsteady gait, with L arm tremulous movements. Which midbrain syndrome is this?
A) Weber
B) Benedikt
C) Claude's
D) Nothnagel's
B) Benedikt
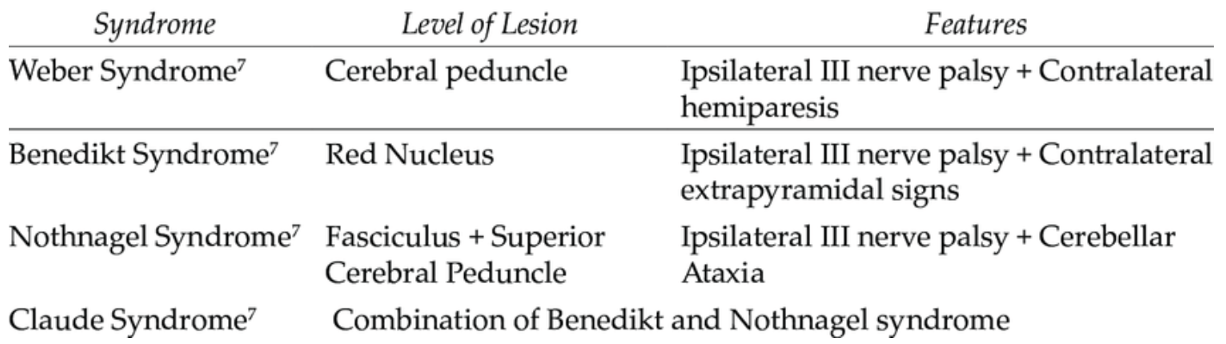
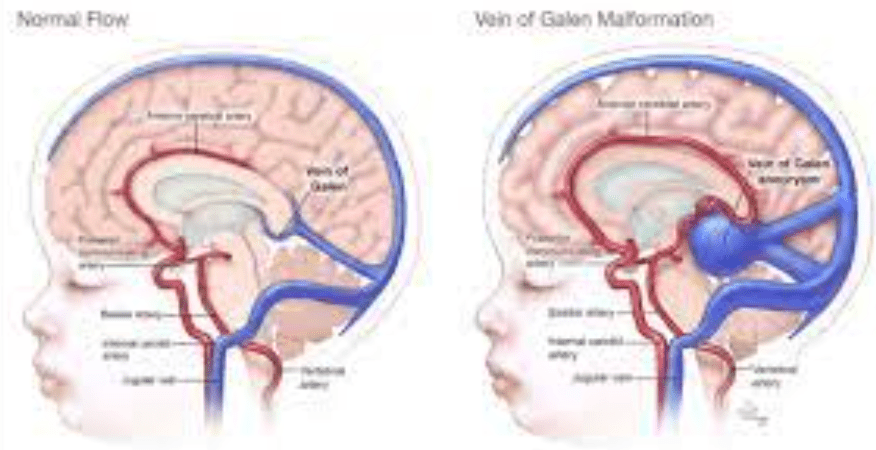
What vein is thrombosed, leading to the outcome below?
Bilateral internal cerebral veins or the vein of galen
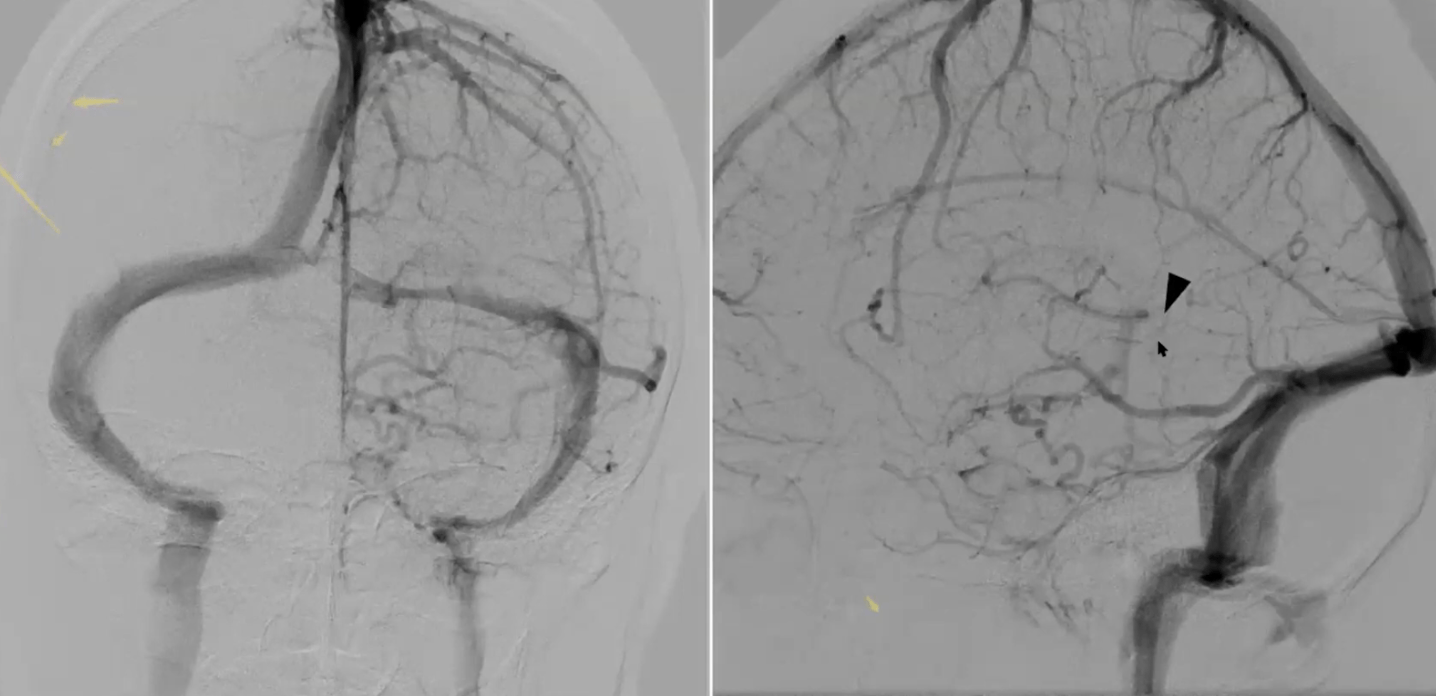
On this lateral view R ICA injection, what gyrus is located within the dashed lines?
The cingulate gyrus
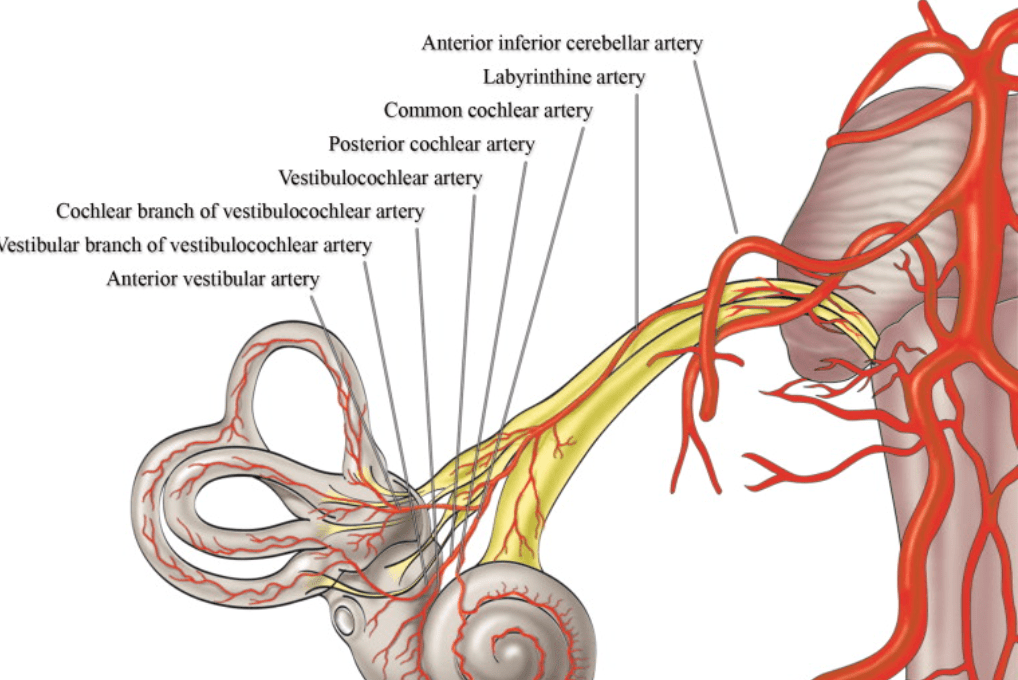
Occlusion of which artery can cause the rare manifestation of unilateral hearing loss in the setting of stroke?
Labyrinthine artery off AICA
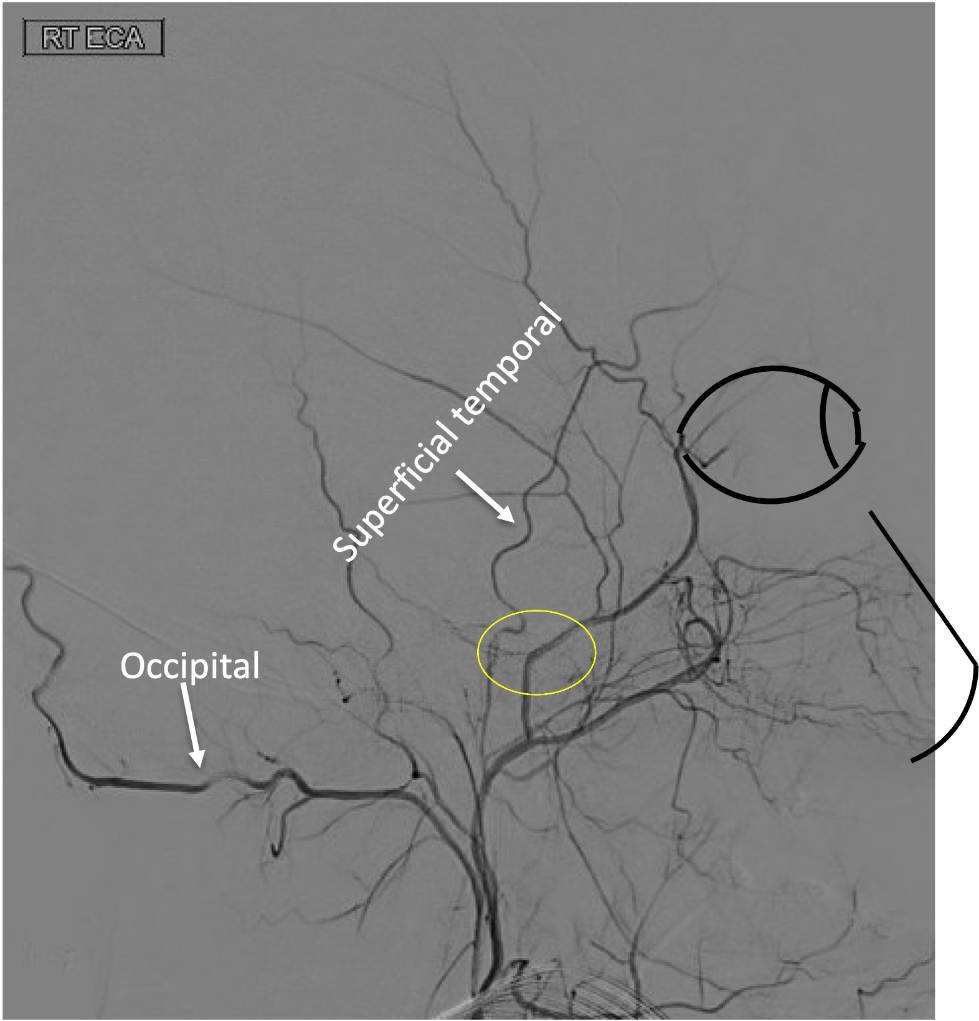
On this lateral view of the R ECA injection, name the circled foramen:
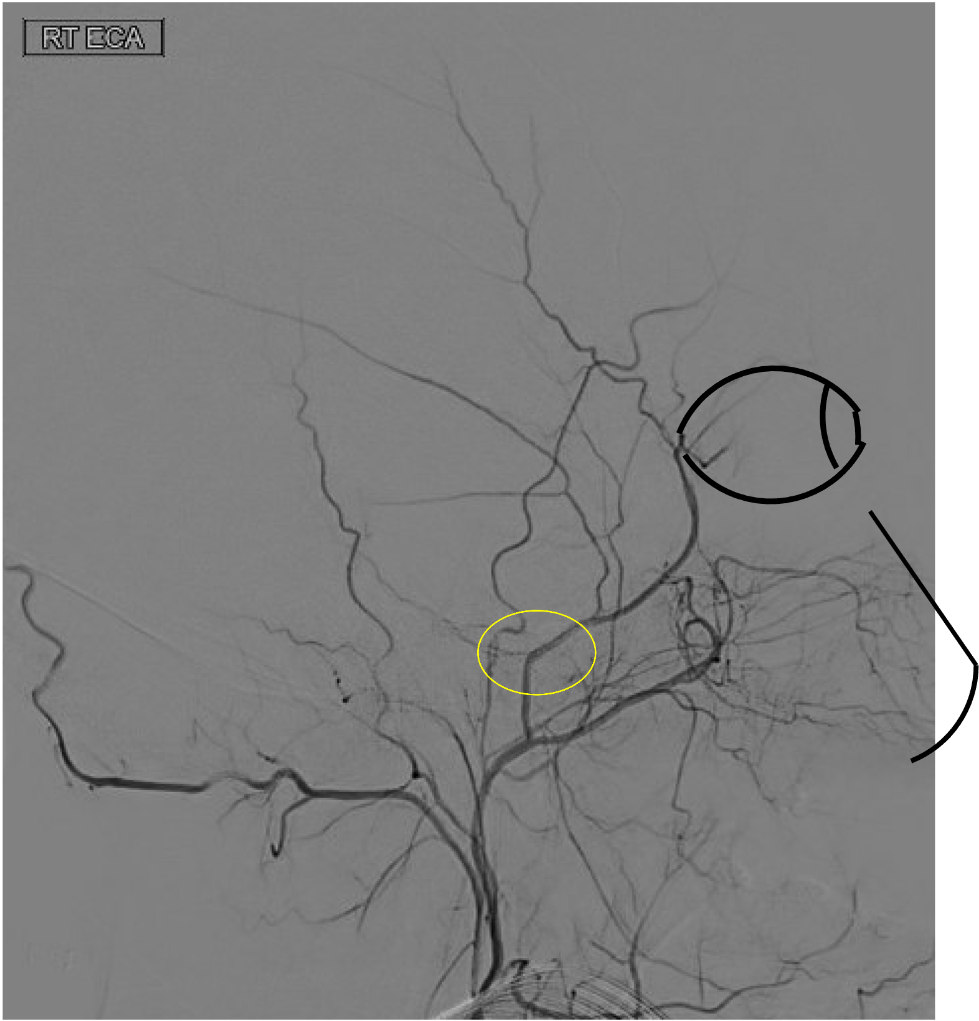
Middle meningeal artery through the foramen spinosum
Stroke of what vessel(s) leads to the following stroke: 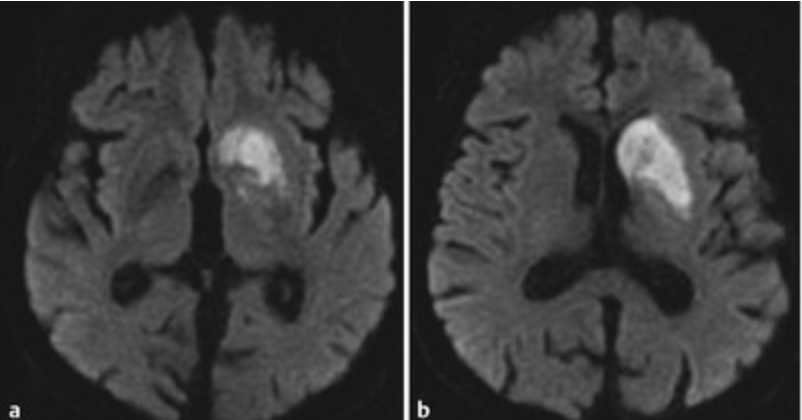
Recurrent artery of Heubner off the ACA feeds the head of the caudate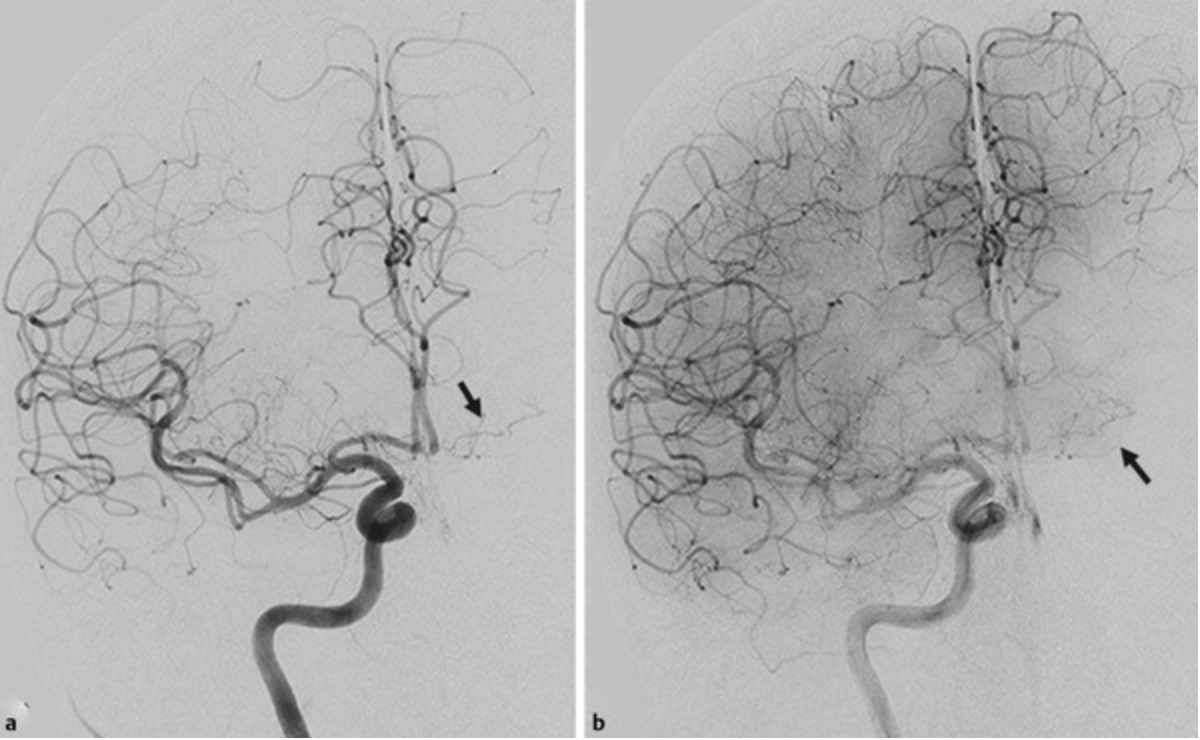
On the venous phase of this lateral R vert injection, name the purple arrow:
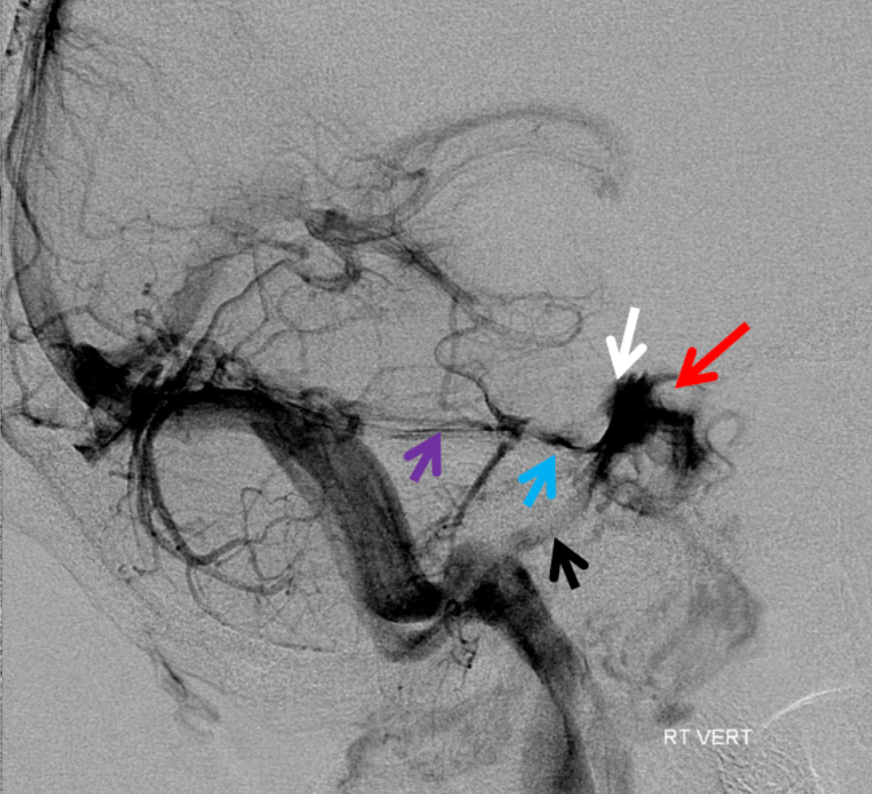
Superior Petrosal Sinus
petrosal veins (blue), cavernous sinuses (white), inferior petrosal sinus (black), silhouette of the ICA (red).
In this patient: 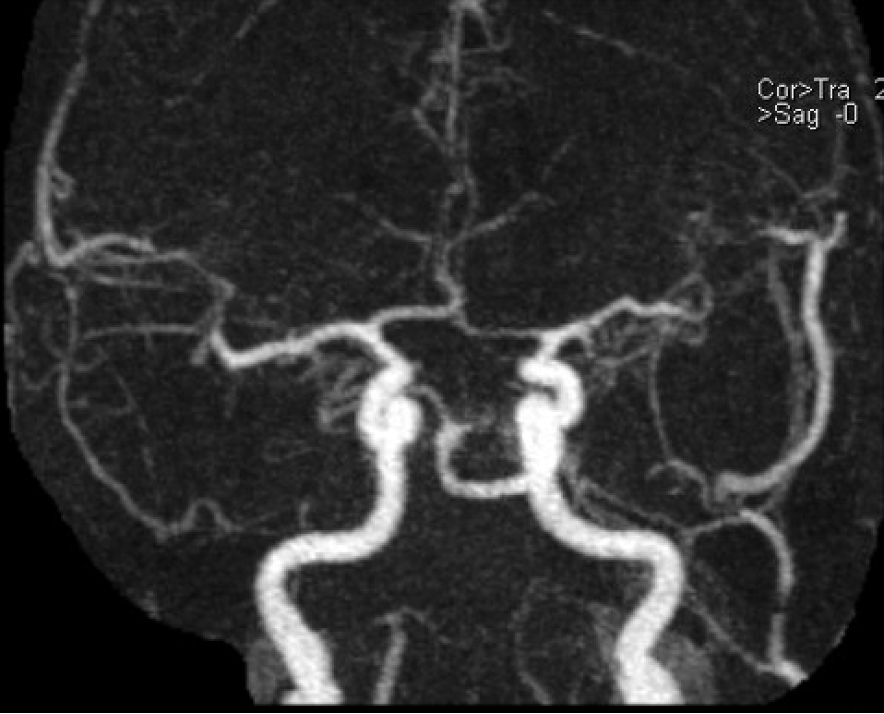
What is this artery:
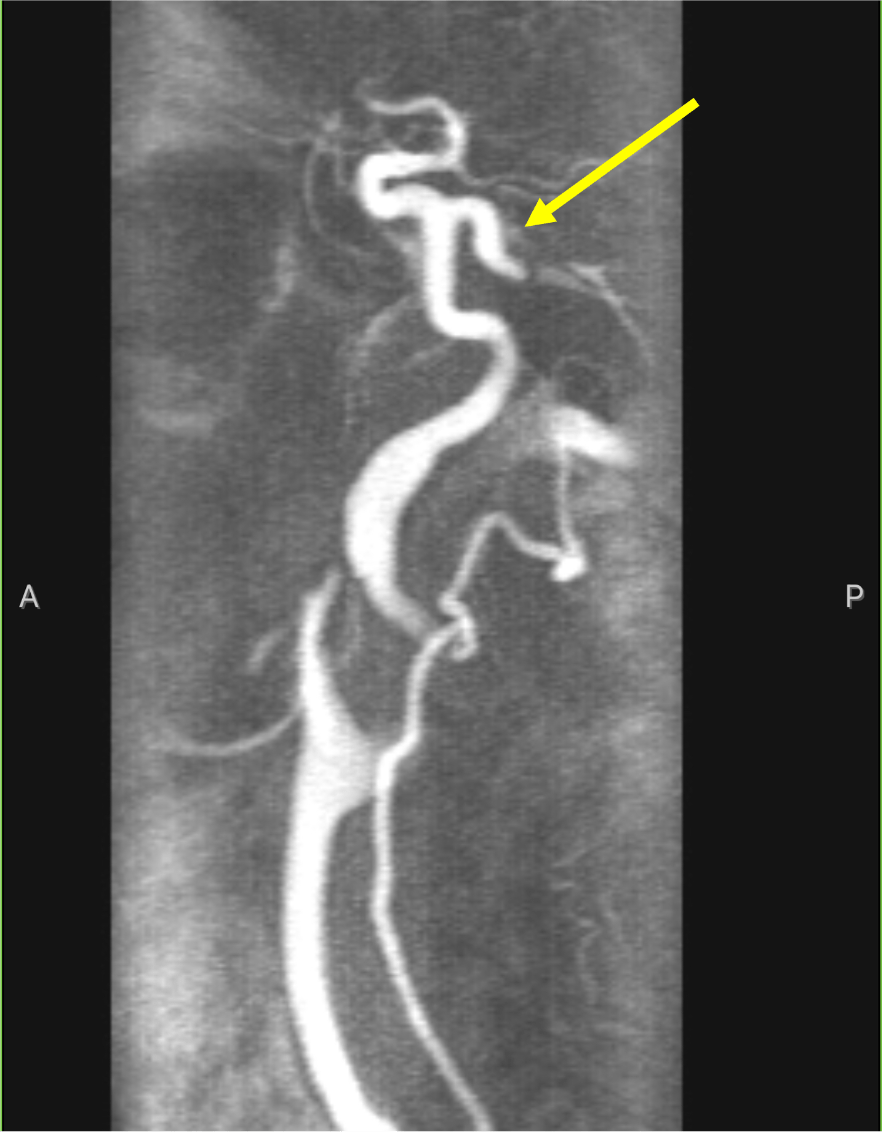
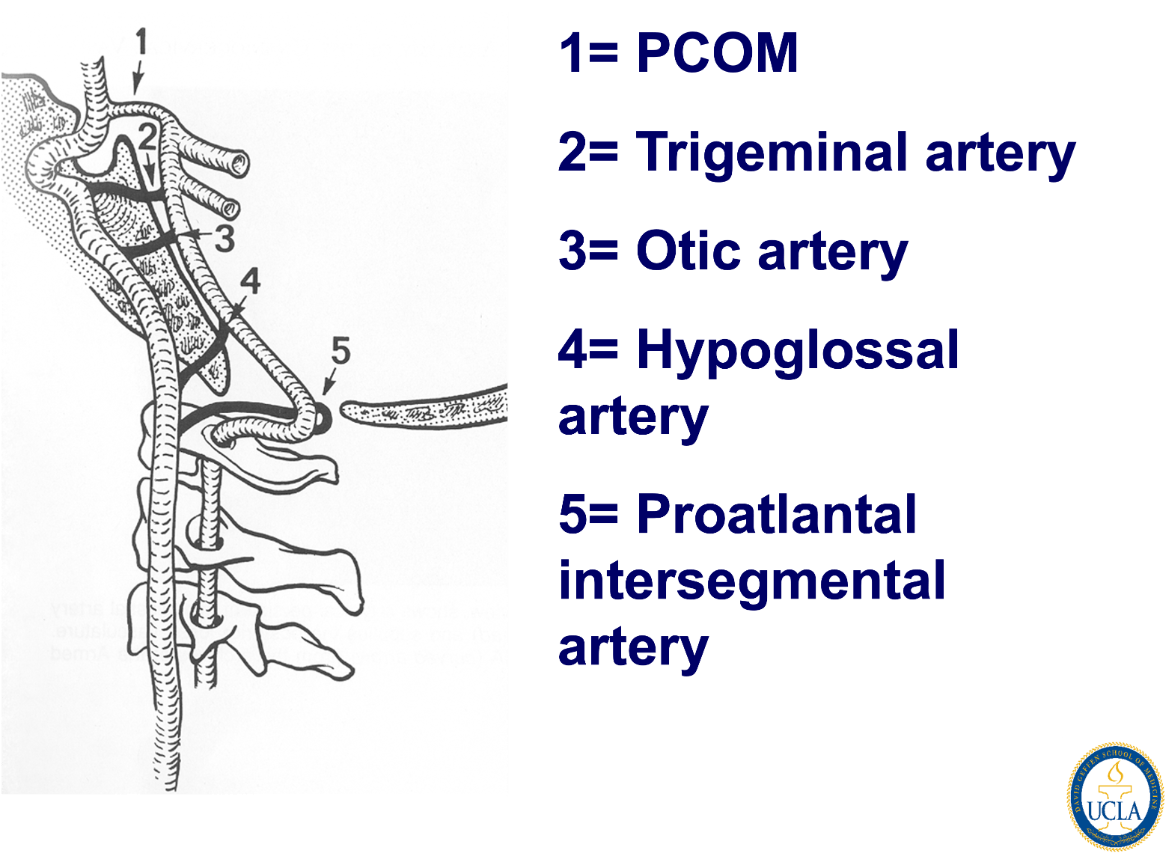
Persistent trigeminal artery!
Name the artery:
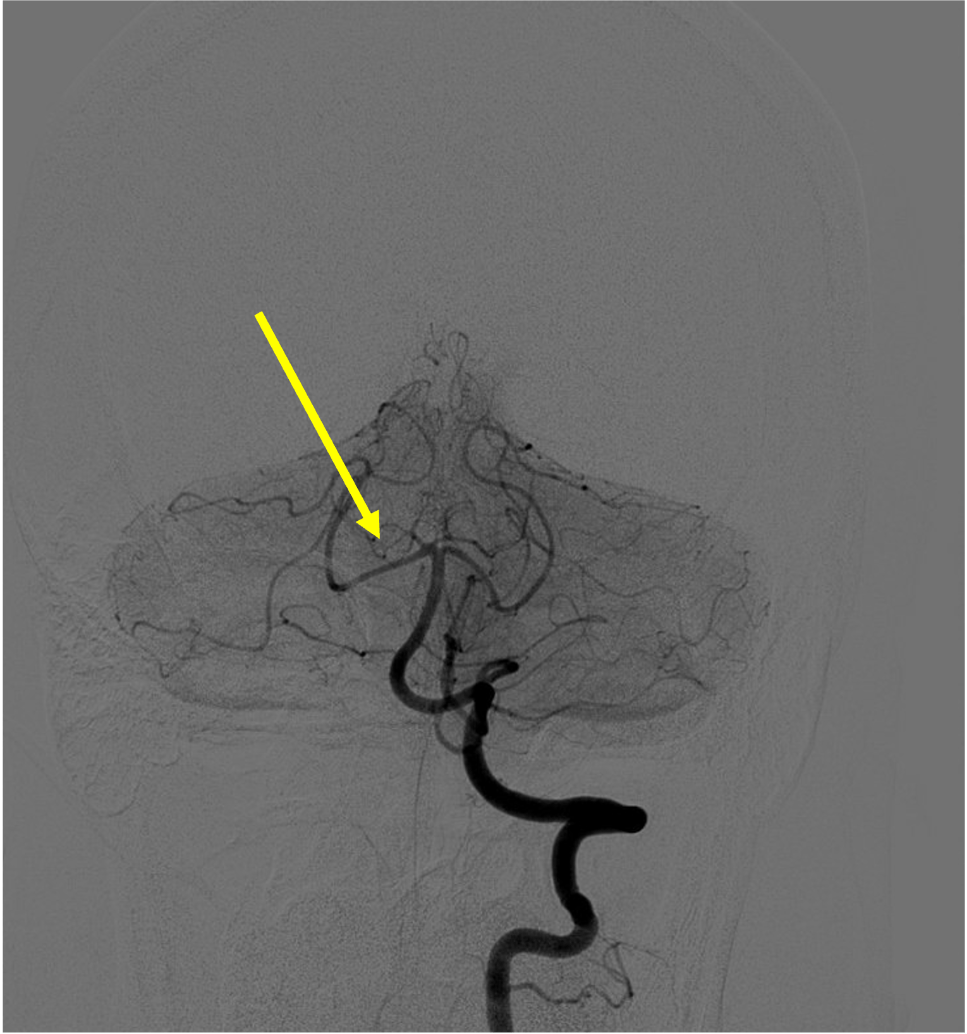
Superior cerebellar artery
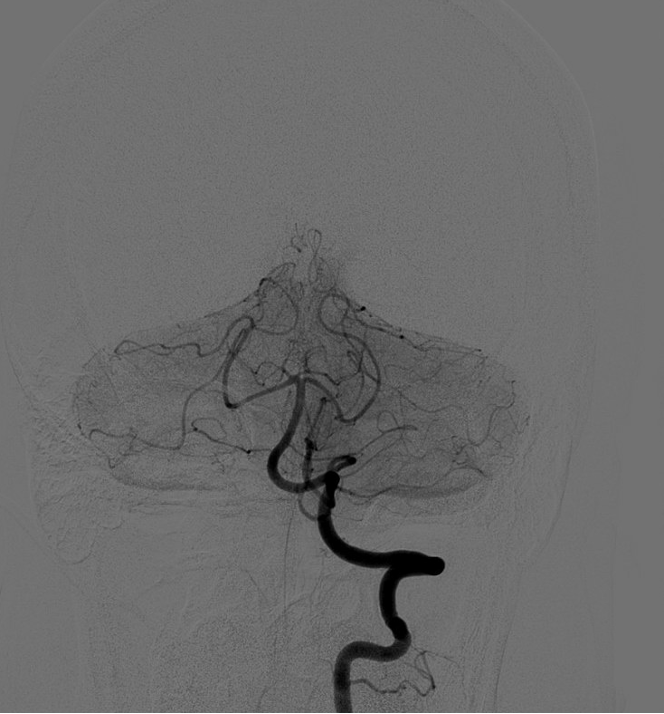
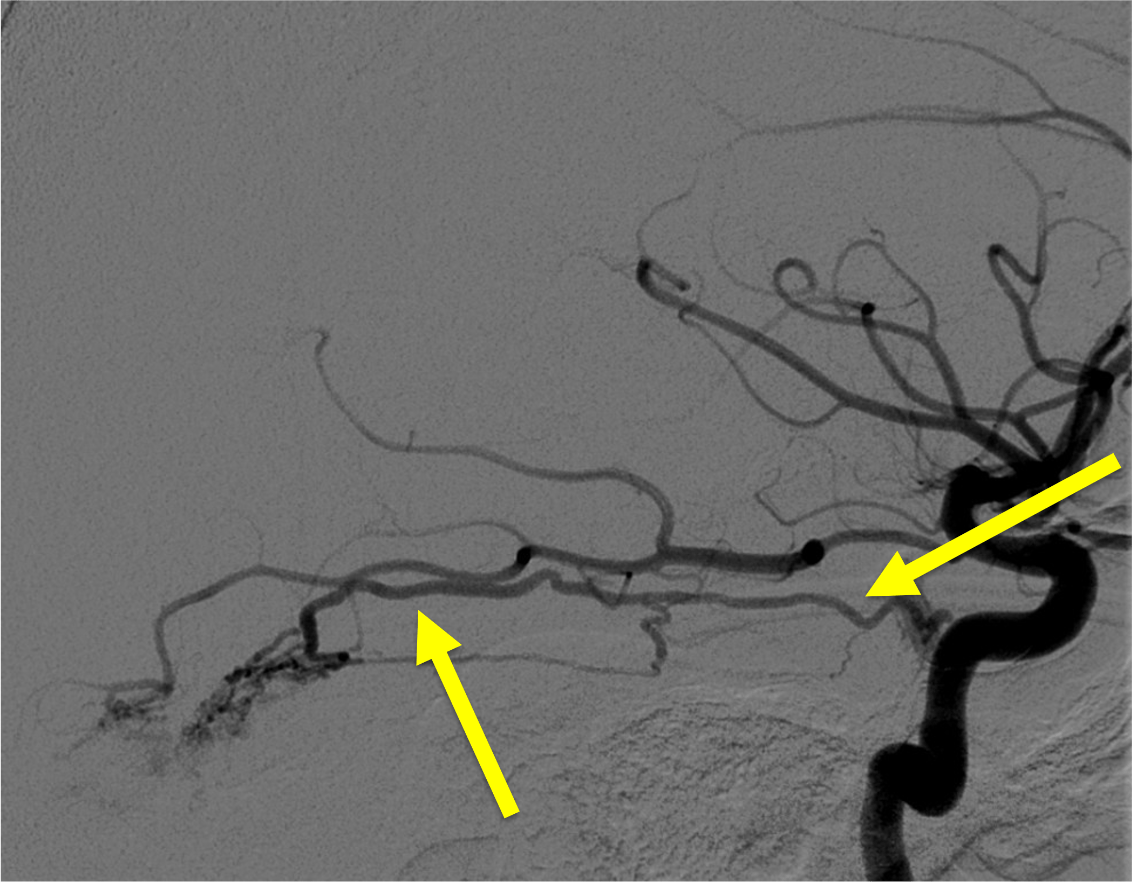
Name this ECA to ICA collateral: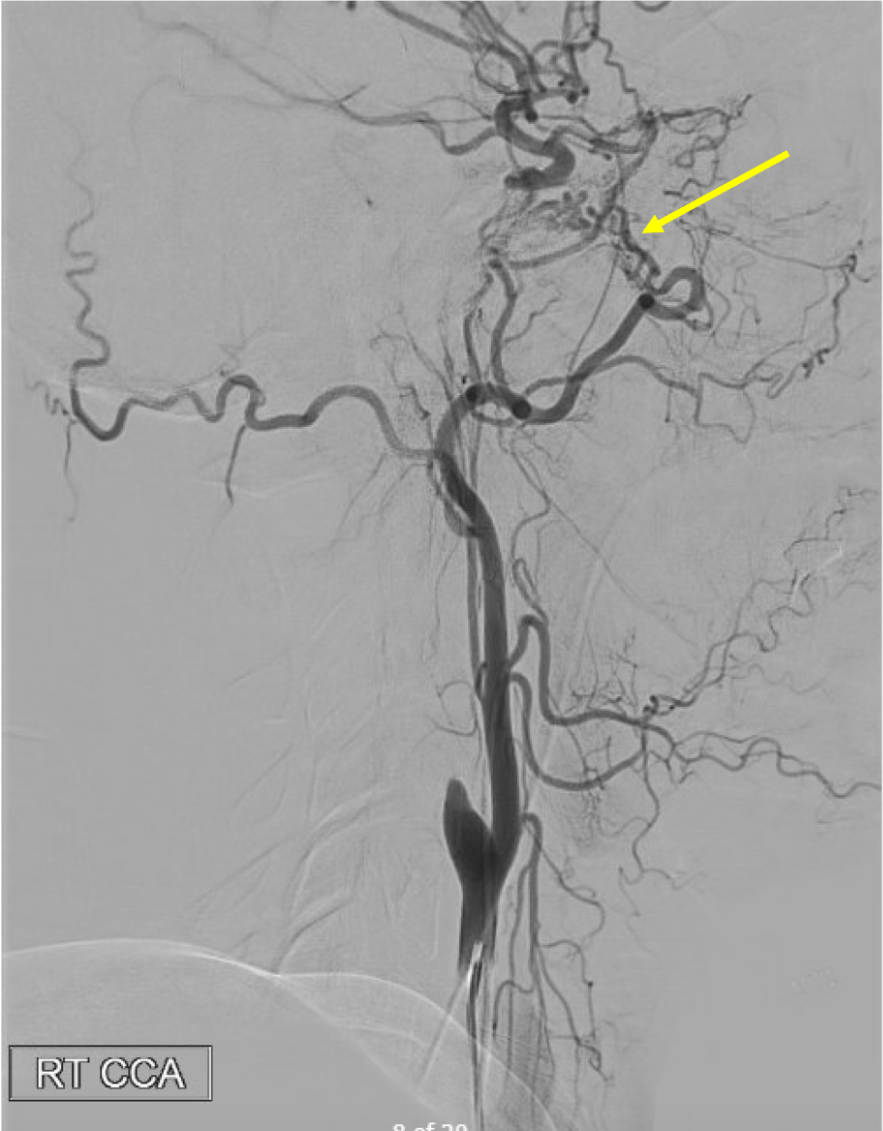
Gotcha! Do my teaching eval plz:

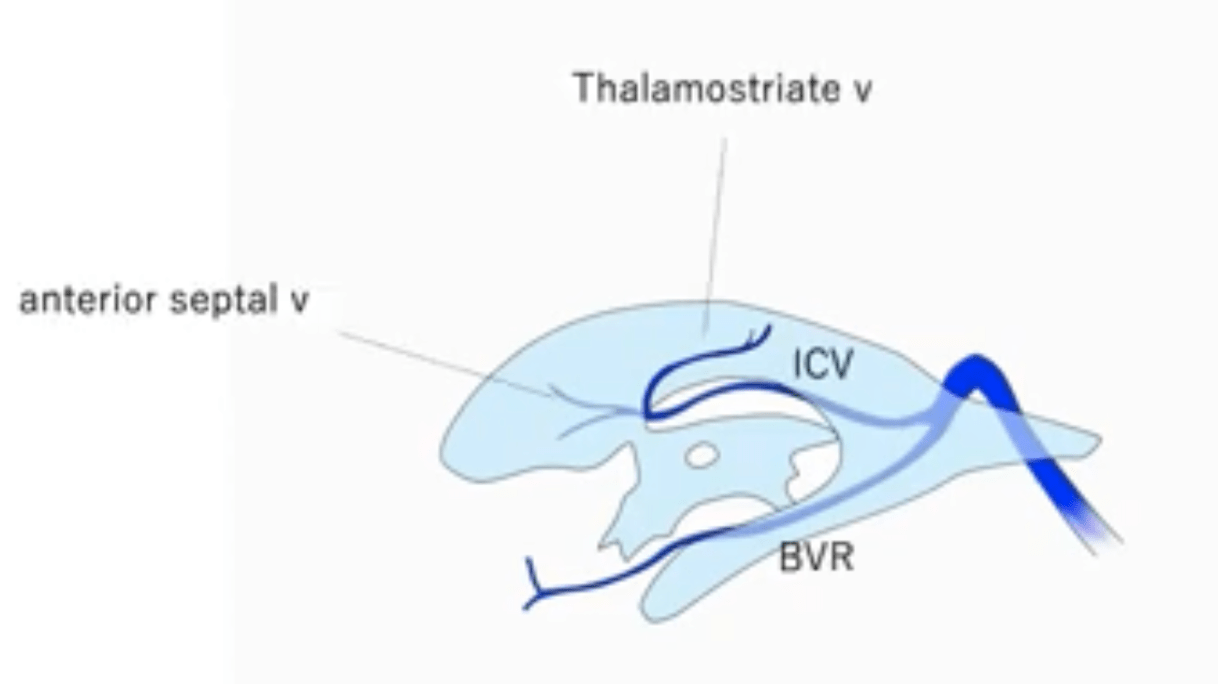
Name the vein
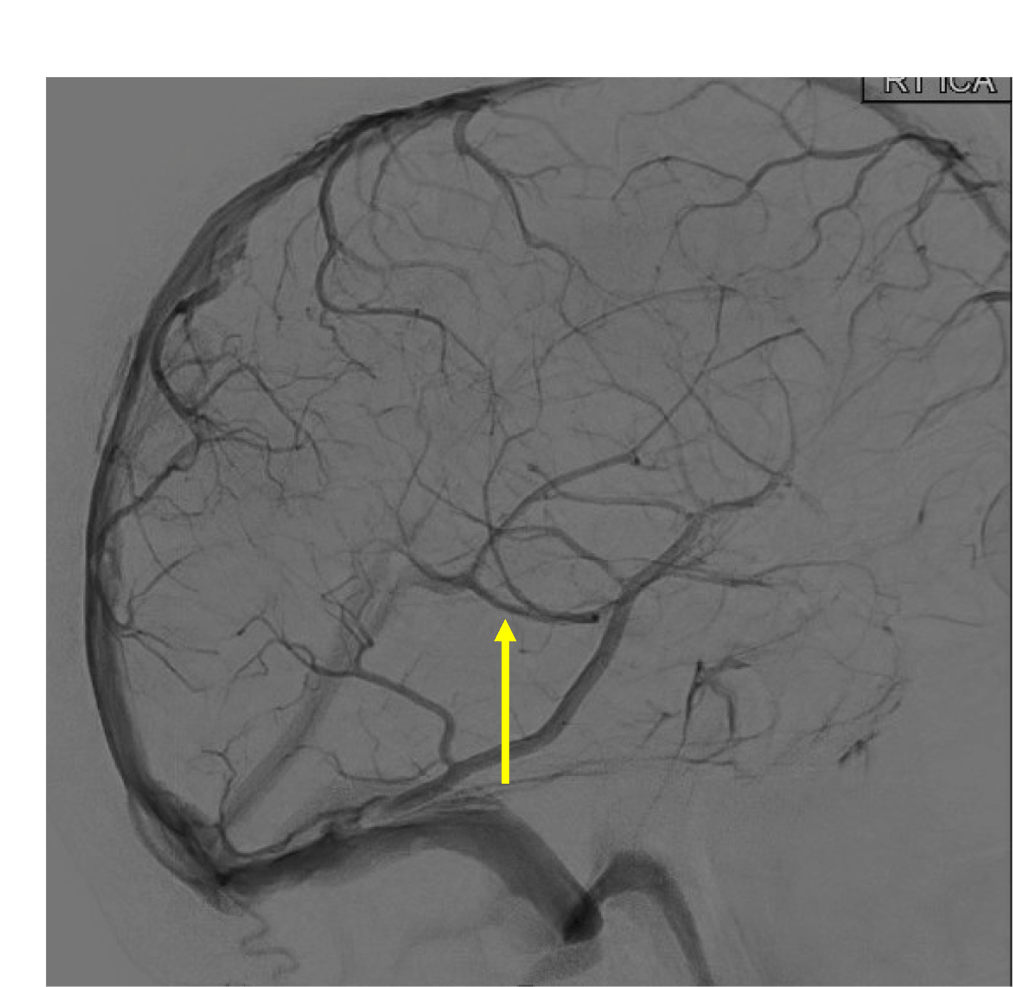
Basal vein of Rosenthal