This atmospheric condition is measured by how hot or cold something is.
What is temperature?
Two main types of possible weather fronts.
What are cold and warm fronts?

This month likely had the most thunderstorms with windy conditions. (Double points if you can explain why)
What is February?
Weather forecasts are made by collecting ____(1)____ about the current state of the ____(2)____.
What is (1) data/information & (2) atmosphere?
Cold fronts are identified by _______ on the weather forecast.
What are blue triangle?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1280px-Cold_front_symbol2222-7972964b6a7e4ef79c51957ea7d7f15b.jpg)
This atmospheric condition is measured by how much water is in the air.
What is humidity?
Cold fronts can be identified on maps using a thick line with ________(1)_______. Warm fronts can be identified on maps using a thick line with _______(2)_______.
What is a (1) thick line with triangles, and (2) semi-circles?
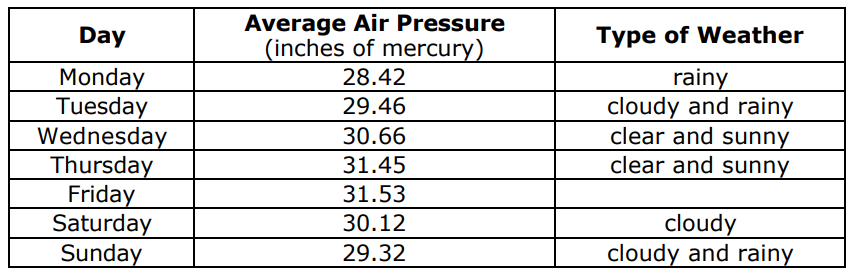
___________ type of weather is likey to occur on Friday.
What is clear and sunny?
What is heavy rainfall and thunderstorm?
Warm fronts are identified on a forecast by _____________.
What are red semicircles?

This atmospheric condition measures the "weight" of the air pushing down on the Earth's surface.
What is air pressure?
True or False:
During the summer, due to high temperatures, we can not have a cold front.
False: We still have cold fronts; the cold air mass is cooler than the warm air mass it moves into.
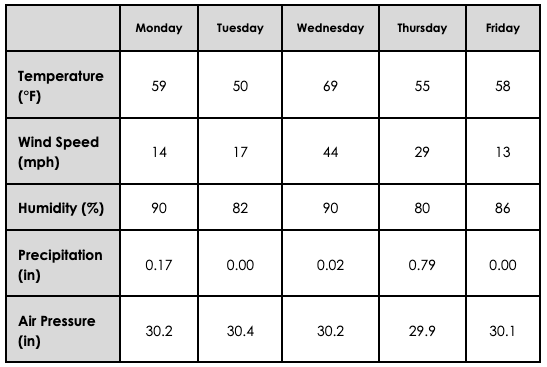
The precipitation _____(1)_____ and the air pressure ______(2)_____.
What are (1) increased & (2) decreased?

The breeze blows away from land when Charlie visits the beach in the winter because ____________________.
What is "The air is more dense over the land." ?
ONLY this type of front can produce thunderstorms.
What is a cold front?
These atmospheric conditions measure how fast the wind is blowing and the direction
What are wind speed and wind direction?
This slow-moving front forms when a moist, warm air mass slides up and over a cooler air mass.
This front creates thin and wispy clouds, and after the front, there are clearing skies, warmer temperatures, and higher humidity.
What is a warm front?
This is a ________ front, and can be identified by the rising temepture, low amount of precipitation and low wind speeds.
What is a warm front?
When examining information about a storm, you must consider these three sets of data.
What is before, during, and after the storm?
This is an imaginary line around the Earth, located at 0 degrees latitude, dividing the planet into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres
What is the equator?
The information about the different atmospheric conditions determines _______________.
What are where and how weather systems are moving?
What are weather patterns/systems?
This front forms when strong, upper-level winds push a cold, dense air mass into a warmer, lighter air mass, creating low-level clouds that appear thick and puffy, which cause heavy rain, hail, thunder, or lightning.
After this type of front, temperatures cool, rain stops, and there are clear skies.
What is a cold front?
This cold front can be identified by the rising _________, and decreasing _____________.
What are rising winds, precipitation, and decreasing temperature
A forecaster expects air pressure to ___________ as the cold front arrives.
What is the air pressure decreasing?
Atmospheric conditions that aid in forecasting the weather.
(Name at least 4 to get the points)
What is temperature, humidity, cloud coverage, air pressure, wind speed and wind direction.