The study of living organisms and the interactions that exist between them and their environment.
Ecology.
A relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is harmed.
Parasitism.
A single pathway of energy transfer through organisms in an ecosystem.
Food Chain.
A biome characterized by being semi-arid, having moderate rainfall, and the presence of animals such as coyotes, badgers, and bison.
Grassland.
The very first organisms to appear in an area of primary succession.
A community of living organisms and their physical environment. Contains both biotic and abiotic factors.
Ecosystems.
A relationship between two organisms in which they both benefit from the association.
Mutualism.
The top carnivore within this food chain.
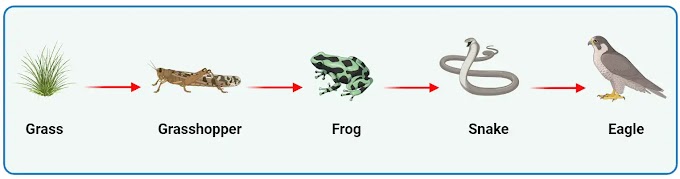
Eagle.
Typically found in the Yukon, NTW, Nunavut, and Northern Labrador.
Tundra.
The redevelopment of a previously existing community after a disturbance, such as a natural disaster.
Secondary Succession.
The transition area between two bordering ecosystems. They contain species from both ecosystems, thus creating higher biodiversity.
Ecotones.
The type of relationship found between bees and flowers.
Mutualism.
The type of consumer that receives 100% of the energy within a food chain.
Characterized by having four distinct seasons, year-round precipitation, and the presence of animals such as deer, raccoons, bears, and hawks.
Temperate Deciduous Forest.
The process by which an ecosystem develops on a previously barren landscape.
Primary Succession.
A system that can be maintained over time so to meet the needs of current and future generations.
Sustainable Systems.
An association between two organisms in which one benefits and the other neither benefits or is harmed.
Commensalism.
The omnivore within this food chain.
The frog.
The biome Newfoundland falls under.
Boreal Forest.
A type of competition seen when an owl and a hawk fight over a snake for food.
Interspecific.
The variety of all living things and their interactions in their environment.
Biodiversity.
The type of relationship between remora fish and sharks.
Commensalism.
Organisms that make their own food from nutrients, sunlight, or other non-living resources.
Autotrophs.
The type of biome shown here.
Temperate Deciduous Forest.
The type of competition seen here.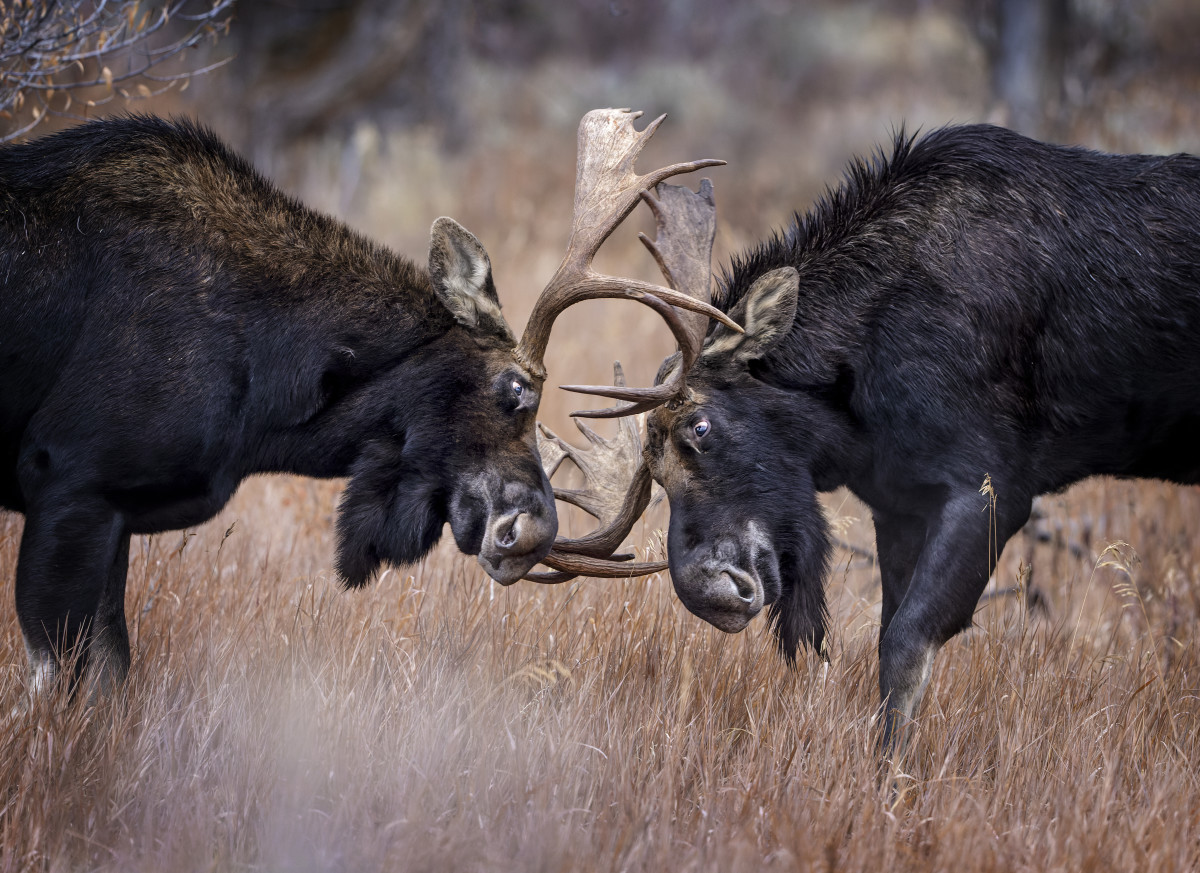
Intraspecific.