A patient has a diagnosis of a sequestered small bowel. When the aircraft ascends to a cruising altitude of 4,000 feet mean sea level (MSL), Boyle's law could cause what?
An increase in volume within the sequestered bowel due to the decrease in atmospheric pressure
Your patient presents with jugular venous distention, distant heart sounds, and on chest x-ray has a widened mediastinum. Based on this information, the patient is likely presenting with what condition:
Cardiac tamponade
A patient’s blood pressure is 84/60. What is their current MAP?
68 mmHg
The average blood volume for an adult is how many milliliters per kilogram (mL/kg)?
70 mL/kg
A 70kg patient with second- and third-degree burns involving 45% total body surface area (TBSA) is being transferred 26 hours post-injury. The physician reports that the patient has had a total of six liters of fluid in a 24-hour period. Using the Parkland formula, how much fluid should this patient have received in the first 24 hours of burn care?
12,600 mL
You perform a needle thoracostomy on your neonate with a suspected “air leak.” After re-evaluating the neonate, which of the following would indicate that initial treatment was NOT successful?
A shift of the trachea away from the needle after the procedure
When pre-oxygenating a rapid sequence intubation (RSI) patient, the strategy for doing so is?
Causing nitrogen washout
Which of the following blood gas results would have you preparing to intubate and ventilate the multisystem trauma patient?
- pH 7.38, PaCO2 44, PaO2 68, HCO3 20
- pH 7.35, PaCO2 48, PaO2 80, HCO3 26
- pH 7.03, PaCO2 75, PaO2 50, HCO3 16
- pH 7.05, PaCO2 15, PaO2 158, HCO3 8
pH 7.03, PaCO2 75, PaO2 50, HCO3 16
Which of the following is a first-line drug for status epilepticus?
Midazolam
Ketamine
mannitol
Epi
midazolam
When keying up a radio that has a repeater system, it is essential to
Pause a moment before speaking
Which type of medication blocks the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAA) system to help with heart failure?
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor
Calculate the cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) with the following findings: BP 90/60, HR 110, RR 22, SpO2 98%, ICP 29, CVP 20, PA 32/14, PCWP 15.
41 mmHg
CPP = MAP - ICP
MAP = [(2 x DBP) + SBP] / 3
In this problem, the MAP = 70
CCP = 70 - 29 = 41 mmHg
The main focus when treating a patient with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is to
Correct the underlying pathology
Fractures of the 1st-3rd ribs should indicate a high index of suspicion for which injury?
Aortic dissection
The team is caring for an 18-month-old, 10 kg patient experiencing a heart rate of 230 beats per minute. The best medication for this patient is
Adenosine 0.05 to 0.1 mg/kg IV
A 33 year old male received seven units of blood products within the last hour due to a massive hemorrhage. He is beginning to have frequent ectopy on the ECG and has a core temperature of 35.5 degrees Celsius despite active warming measures. You should administer
Calcium gluconate 1 g IVP
Identify the following ABG:
pH 7.28, PaCO2 20, HCO3- 17, PaO2 80, BE -8
Partially compensated metabolic acidosis
The patient with cocaine toxicity is best treated initially with:
Benzodiazepine
The flight crew has responded to a mass causality event with 30 patients after a bus crash. There is a patient that cannot follow commands and demonstrating ataxia. You note a thready palpable radial pulse, with spontaneous respirations at 26 breaths per minute. Based on the START system, what would this patient be triaged as?
Immediate
Coronary artery perfusion is dependent upon?
Diastolic pressures
When calculating how PaCO2 affects pH, for every 10 mmHg change in CO2, the pH will change by __________ in the opposite direction?
0.08
Identify and diagnose the following CT scan. 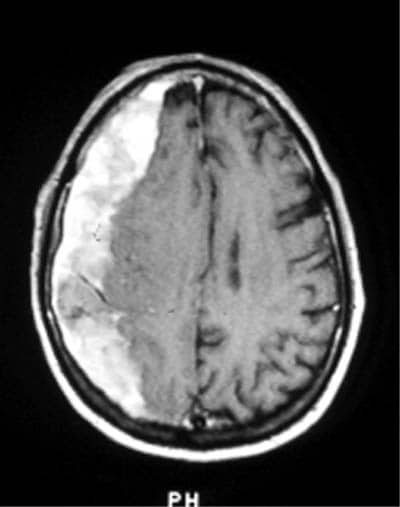
Subdural hematoma
In a patient with a diaphragmatic injury, what organ would also have a high suspicion of injury along with this?
Liver
You are preparing to transport a term neonate who has APGAR scores of 3 and 7. Her lungs are clear to auscultation, and she has normal pulses and no murmur auscultated. During assessment, her SpO2 drops from 97% to 72%. With oxygenation and ventilation using BVM, SpO2 increases to 90%. Which of the following is the most definitive treatment for this condition?
Administration of nitric oxide
You are caring for a pediatric burn patient weighing 20kg with second- and third-degree burns involving 45% total burn surface area (TBSA). The injury occurred two hours previously, and the referring facility administered 300 mL of LR thus far. Using the consensus formula, what would the fluid resuscitation amount be for the first 8 hours, taking into account volume already administered?
1,050 mL; 175 mL/hr
What acid-base imbalances would you anticipate in salicylate toxicity?
Respiratory alkalosis and metabolic acidosis
Which medication is an appropriate first-line intervention for the child with airway swelling due to croup?
Nebulized epinephrine
Dalton’s law demonstrates that the concentration of O2 at 18,000 feet mean sea level (MSL) is 21%. If the atmospheric pressure at 18,000 feet MSL is 380 torr, what would the partial pressure of oxygen be at that altitude?
79 torr
At sea level: 760 torr x 0.21 = PaO2 of 159
18,000 feet MSL: 380 torr x 0.21 = PaO2 of 79
Identify the underlying problem based on the following parameters:
- CVP 1
- CI 1.6
- PA S/D 12/8
- PCWP 5
- SVR 300
Septic shock
What is a normal SvO2 (central venous oxygen concentration) range?
60-80%
The sequela of sepsis can lead to multi-organ dysfunction. Which of the following organs is involved first?
Lungs
A patient who sustained extensive electrical burns is being transferred. Upon entering the room, there is brown urine noted in the foley bag, and myoglobinuria on the urinalysis. To prevent the development of acute tubular necrosis and further renal failure, what is the anticipated treatment?
Lactated Ringer's, sodium bicarbonate, and mannitol
The fetal heart monitor strip indicates what? 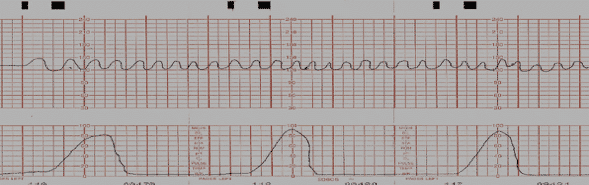
Sinusoidal
You are transporting an 80-kilogram patient who is being mechanically ventilated. Current SpO2 is 89%. The patient is currently chemically paralyzed, and lung sounds are noted to be diminished bilaterally in the lower lobes. Current ventilator settings are: SIMV 14, Vt 450, FiO2 0.8, PEEP 4, I:E 1:2. Manipulating which setting would be MOST beneficial to increase the patient's SpO2?
PEEP
When attempting to increase oxygenation in hypoxic patients, always increase FiO2 first and PEEP second. With the answers available, increasing PEEP would be the best choice.
A key component used in the management of an adult DKA patient is?
Aggressive fluid resuscitation
A 29 year old male self extricated himself from inside the building fire at a plastic plant. He has nausea and vomiting, tachypnea, bradycardia, and hypotension. You should administer
Hydroxocobalamin
What is the pitot tube on an aircraft used for?
Pressure measurement
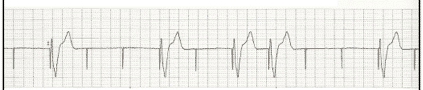
A patient complains of a recent syncopal episode with the following rhythm noted. What is the diagnosis?
Failure to capture
A patient has an intracranial pressure of 28, and blood pressure of 100/60. Their cerebral perfusion pressure is approximately what?
45 mmHg
CPP = MAP - ICP
MAP = [(2 x DBP) + SBP] / 3
Standard ICP = 0-15 mmHg
In this problem, the MAP = 73 [(120 + 100) / 3]
CPP = 73 - 28 = 45mmHg
A patient is ordered to have constant nasogastric tube suctioning. Based on this, what acid-base derangement is expected?
Metabolic alkalosis
A patient has sustained a gunshot wound to the left chest. The left chest has been decompressed with a needle. The patient is intubated and continues to desaturate. There is a noted increase in subcutaneous air. What would be the next best intervention for this patient?
Advance the endotracheal tube below the level of the injury
You arrive on the scene of a single rollover accident with a patient who is 28-weeks gestation. The patient is gravida 2, para 1. Assessment reveals palpation of fetal parts over the abdomen. What is your diagnosis?
Uterine rupture
A ground glass appearance is noted on a patient's chest film. Their current vent settings: SIMV 16, Vt 700, FiO2 0.80, and PEEP 5. Current ABGs: pH 7.34, PaCO2 38, PaO2 60, HCO3- 24. What pulmonary condition is suspected?
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
Interpret the patient's ABG: pH 6.91, PO2 86, PCO2 19, HCO3 13
Partially compensated metabolic acidosis
A 33 year old male received seven units of blood products within the last hour due to a massive hemorrhage. He is beginning to have frequent ectopy on the ECG and has a core temperature of 35.5 degrees celsius despite active warming measures. You should administer
a. Calcium gluconate 1 g IVP
b. Potassium 40 mEq IVP
c. Amiodarone 150 mg over 10 minutes
d. Lidocaine 100 IVP
a. Calcium gluconate 1 g IVP
For every 1,000 feet increase in altitude, the ambient temperature will _________ an average of _________ Celsius.
Decrease, 2º
The ambient temperature will decrease by 2°C for every 1,000 feet that is ascended in altitude
Upon review of a patient's labs, their potassium level is noted to be 3.1 mEq/L. When looking at their ECG, what would be expected?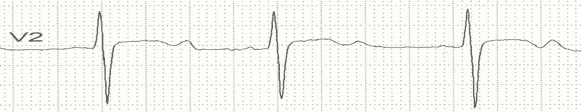
U waves
Hypokalemia can result in ECG changes including inverted T waves, ST segment depression, and prominent U waves.
What is a normal SvO2 (central venous oxygen concentration) range?
60-80%
Which of the following can be seen with hypocalcemia?
- Kehr's sign
- Grey-Turner's sign
- Trousseau's sign
- Brudzinski's sign
Trousseau's sign
Hypocalcemia can lead to numbness and tingling in the perioral area, muscle cramps/spasms, and irritability/fatigue. Two common physical exam findings associated with hypocalcemia include Chvostek's sign and Trousseau's sign.
After a multi-system trauma occurs, death within minutes is usually a result of which of the following?
- Multi-system organ failure
- Blood loss secondary to a pelvic fracture
- Great vessel laceration
- Head injury
Great vessel laceration
Great vessel laceration is a common cause of death in trauma patients. Aortic disruption is the most common cause due to the shearing injury that occurs from the deceleration seen in high force accidents.
Identify and diagnose the following chest x-ray.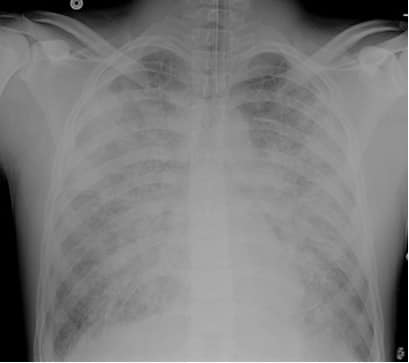
ARDS
Differentiating between ARDS and pulmonary edema can be difficult. Both will present with diffuse bilateral involvement. You may also see a "ground glass" appearance on the chest x-ray. Although "ground glass" does not discern between any disease process, it should alert you to an abnormality within the lungs.
A patient in severe hypothermia has an esophageal temperature that reads 28°C. You know that you should withhold cardiac medications until the core temperature reaches what?
30°C
A 6’ tall, 64-year-old male was intubated for COPD intubated exacerbation. An ABG on his current ventilator settings resulted with a pH of 7.30, PaCO2 70, PaO2 60, bicarb 36. Vent settings are mode AC, Vt 600, rate 16, PEEP 5 (auto-PEEP 9), FiO2 0.4, I-Time 1 second, Pplat 42. His vital signs are HR 94, RR 20, BP 146/88, SpO2 94%, and EtCO2 65. You should
Decrease his RR and I-time
A 38 year old female has a traumatic brain injury and imaging revealed a subdural hematoma with a 5mm shift. During transport, her intracranial pressure increases to 32 mmHg despite repositioning and increasing sedation. You should administer
a. Mannitol
b. Nicardipine
c. Lorazepam
d. Corticosteroids
a. Mannitol
Barodentalgia will most likely be exacerbated by ________?
Ascent
Barodentalgia will worsen on the ascent phase of flight. During ascent, a dull or severe pain will be experienced. The differences in pain will depend on whether it is a recent dental filling (severe pain) or an abscess (dull ache). Boyle’s law best explains this phenomenon.
Diagnosis of a left bundle branch block (LBBB) meeting Sgarbossa criteria uses which diagnostic indicator for an award of 5 points?
ST segment elevation equal to, or greater than, 1 mm that is concordant with the QRS complex
The ventilator is set to CMV: Vt 500, f 20, FiO2 1.0, PEEP 5. The delivered minute volume is:
10 L
A patient is diagnosed with pneumonia and resultant sepsis with the following vital signs: 102.3°F, BP 108/68, HR 124, and RR 28. What is the initial cardiovascular response to sepsis?
Increased cardiac output
Your patient has sustained traumatic injuries, with secondary hypovolemic shock. Which of the following would you also anticipate?
- Renal failure
- Pre-renal failure
- Post-renal failure
- Chronic renal failure
Pre-renal failure
Statistically, the type of hemorrhagic stroke that is associated with the most co-morbidities such as seizures, infection, ARDS is
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
A patient with a GSW to the torso presents with ipsilateral weakness and contralateral loss of sensation. These symptoms indicate which spinal injury?
Brown-Sequard Syndrome
The patient's ABG: pH 7.51, PO2 90, PCO2 20, HCO3 24. This represents the early stages of a patient with:
a.Aspirin overdose
b.Wood alcohol poisoning
c.Iron poisoning
d.Gapentin toxicity
a.Aspirin overdose
A 59 year old male who has heart failure is on NiPPV with setting of IPAP of 12 and EPAP of 7. Furosemide 80 mg IV has been administered and he remains alert and oriented. His vital signs are HR 82, RR 25, BP 190/110, and SpO2 is 94%. You should
a. Repeat furosemide dose
b. Intubate before transport
c. Increase the IPAP
d. Administer nitroglycerin
Administer nitroglycerin
Helicopter landing zones should be ______________ at a minimum.
100 feet x 100 feet
In addition to cardiovascular collapse; a beta blocker overdose may cause:
Hypoglycemia
The proper depth of a 3.5 endotracheal tube (ETT) would be?
10.5 cm
An excellent way to determine tube depth after watching it go through the cords is 3x the ETT size.
Which lab value corresponds with the findings on this chest x-ray?
a.BNP 14,000
b.Creatinine 1.8
c.Potassium 7.3
d.ALT 335
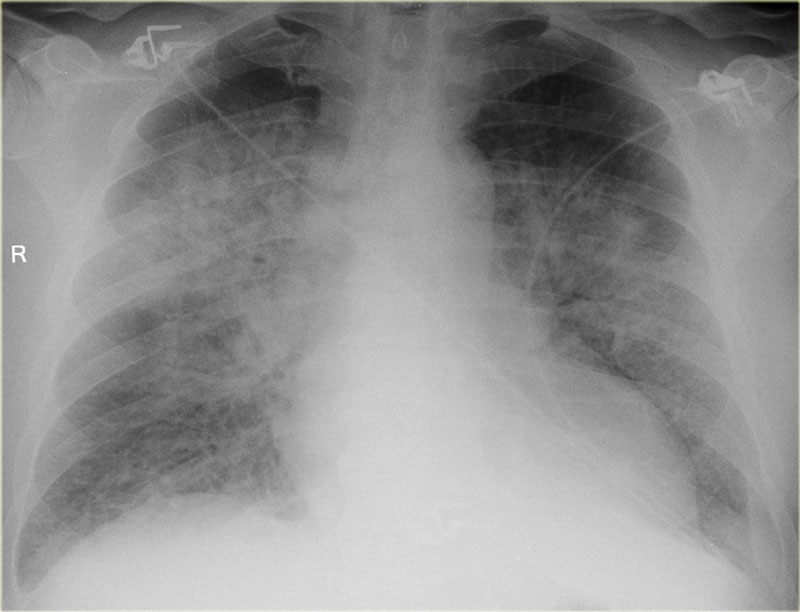
a.BNP 14,000
Which of the following is a classic manifestation of a digitalis overdose?
Yellow/green halos around objects
A patient with an umbilical cord prolapse should be
Placed in a knees-to-chest position
A 56 year old male experiencing a two-year midlife crisis recently had his 24 year old Eastern European bride divorce him and take half of his life savings. He decides to rebound by becoming an amateur mountain climber. Being very wealthy and ambitious, he decides to, with no experience, pay a group of Quechua guides to sherpa him up Aconagua (22,831 ft). While on the summit he experiences severe difficulty breathing, coughing up pink frothy sputum, and bilateral rales. Which of the following strategies should be employed to treat this patient?
Rapid descent, application of PEEP
A base excess of +4 indicates:
Metabolic alkalosis
You arrive to transport a 7 year old with a history of cardiac disease with pulmonary hypertension who is on a home medication of treprostinil. His mother advises he should remain on this medication at all times. You do not currently stock this medication. You should
a. Discontinue to medication
b. Refuse to transport him
c. Transport him with the medication infusing
d. Change out the medication for another medication
c. Transport him with the medication infusing
A SCUBA diver experiences severe joint pain upon rapid ascent to the surface. This phenomenon is an example of which gas law?
Henry's Law
The patient is a 56 year old male with syncope. Vital signs: HR 60, BP 74/50, R 22, SpO2 94%. In addition to the findings on the 12-lead EKG you also suspect:
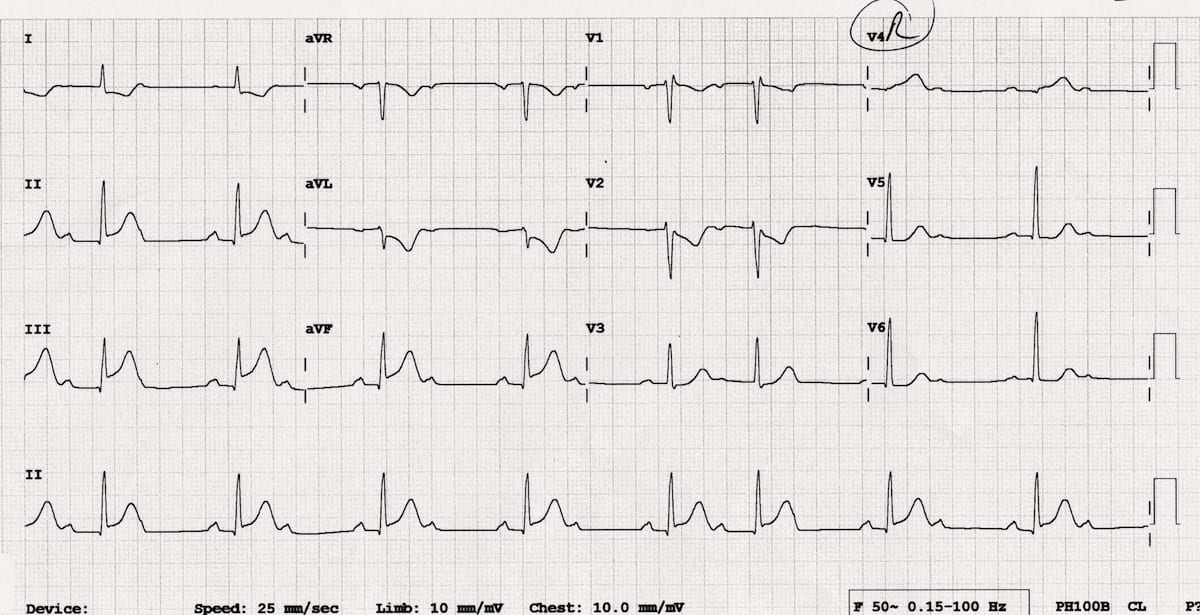
Right ventricular infarct
A calculated stroke volume for patient with the following values: HR 110, BP 90/69, CO 6.7 L/min, PCWP 8 mmHg is
a.54 mL
b. 61 mL
c. 75 mL
d. 89 mL
b. 61 mL
SV=HR/CO
In herniation, brain tissue is displaced:
Through the foramen magnum
Beck's Triad indicates a _____________ and consists of ________.
Pericardial tamponade; narrowed pulse pressure, JVD, muffled heart sounds
Pressing a patient's legs to her abdomen when shoulder dystocia is experienced during delivery is known as:
McRoberts Maneuver
You are transporting a patient with a lower GI bleed to a level 1 trauma center. She is receiving her third unit of PRBCs, first unit of FFP, and first unit of platelets. When her blood pressure cuff inflates to check an updated BP you notice her hand begin to spasm. You should consider:
Calcium administration
Interpret the patient's ABG: pH 7.38, PO2 90, PCO2 58, HCO3 22
Compensated respiratory acidosis
A 10-year-old child is rushed to the emergency department by parents who report “it is happening again”. The patient has had episodes of sweating and shortness of breath with feeling faint, but no diagnosis has been made.
Vital signs: P 208, BP 90/40, RR 24, SpO2 98%.
what medication would you give and what dose
Adenosine 0.1 mg/kg maximum 6 mg IV push
The flight crew is asked to respond to the scene of a pediatric trauma in an outlying area. The nearest available EMS unit is 45 minutes from the patient. The pilot is expressing concerns over taking this call due to the weather. Who has the final say when turning down a mission?
All crew members have an equal say
A pediatric patient was found down in the snow with a core temperature of 27°C. The following rhythm is identified, with no pulse present. What is the best treatment option?
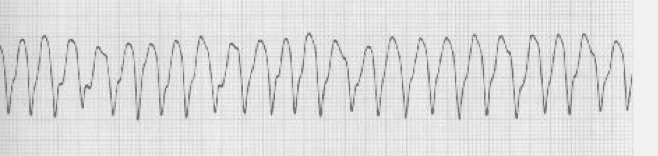
CPR until the core temperature is >30°C, shock
Calculate the Shock index from the following vital signs:
Heart rate: 115
B/P: 82/51
RR: 30
SPO2: 92% on room air
Temp: 36.9
BGL: 84
1.4
SI = Heart Rate / Systolic Blood Pressure
The team is caring for a 36-week pregnant patient who experienced an eight-foot fall, landing on the right side. Due to physiologic changes during pregnancy, this patient will present with:
Signs of shock may be delayed
It is important to remember that due to physiologic changes related to pregnancy, signs of shock may be delayed. This delay is due to the persistently elevated heart rate and increased blood volumes in the pregnant patient.
A multi-trauma patient undergoes fluid resuscitation with three liters of normal saline and five units of unwarmed packed red blood cells. They remain unconscious, intubated and ventilated with 100% oxygen. They have received sedation and remain immobilized on a backboard. Which of the following secondary complications should be of concern?
- Decreased clotting times due to the banked packed red blood cells
- Alkalosis due to the blood administration
- Hypothermia due to unwarmed blood
- Hypokalemia due to blood administration
Hypothermia due to unwarmed blood
The infusion of unwarmed or inadequately warmed intravenous (IV) fluids and cold blood may contribute to the many adverse consequences associated with hypothermia. These can include: cardiac arrhythmia, hemostasis abnormalities from impaired platelet function and slowed enzymatic reactions in the coagulation cascade, peripheral vasoconstriction, dehydration, decreased oxygen delivery to tissues, which impairs oxidative killing of bacteria by neutrophils and reduces the deposition of collagen during wound healing, increased red cell release of potassium, metabolic acidosis, and citrate toxicity (with blood component transfusion).
Identify the following chest x-ray: 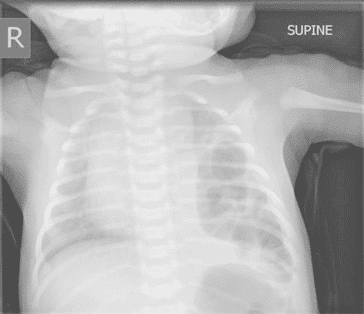
Diaphragmatic hernia
You will note the appearance of bowel and air in the upper left side of the chest x-ray. A diaphragmatic hernia is a significant defect and is often diagnosed in utero. A diaphragmatic hernia will cause secondary problems such as pulmonary hyperplasia, pulmonary hypertension, and CHF.
A patient with a tension pneumothorax is best treated by needle decompression at the following site:
- 2nd intercostal space, midclavicular, superiorly
- 2nd intercostal space, midclavicular, inferiorly
- 2nd intercostal space, midclavicular, apically
- 2nd intercostal space, midclavicular, laterally
2nd intercostal space, midclavicular, superiorly
A tension pneumothorax is best treated by a needle decompression at the second intercostal space, above the rib (superiorly). Other sites that can be used are the fourth or fifth intercostal space, mid-axillary and superiorly.
Classify the pH disorder based on the following ABGs:
pH 7.37, PaCO2 58, HCO3- 23, base deficit -2, PaO2 106
Compensated respiratory acidosis
You are infusing unmatched PRBC’s to a 35-year-old male when he complains of chest pain, shortness of breath, and burning in his arm. You notice blood oozing from the infusion site. He is hypotensive and febrile. You immediately stop the transfusion and administer Iv fluids wide open. You should next administer
Vasopressors and platelets