This is the variable a scientist changes intentionally in an experiment.
What is the indepdendent variable?
This is what binomial nomenclature means.
What is the practice of referring to species by their genus and species name in Latin?
What is the difference between a prokaryote and a eukaryote?
What are:
Eukaryotes can be multicellular or unicellular; prokaryotes are only unicellular
Eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles, including a nucleus; prokaryotes do not have any complex structures in the cell.
Eukaryotes tend to have larger cells; prokaryotes have smaller cells
This is the difference between a density-dependent and density-independent factor.
Density-independent factors impact populations regardless of how dense they are in an area.
Density-dependent factors impact populations more if the population density is higher.
This is an organ that is no longer needed but still exists in an organism.
What is a vestigial organ?
This is something kept the same in all experimental groups.
What is a controlled variable?
List three characteristics of life.
What are: Made of cells, reproduction, has genetic material/DNA, made of CHNOPS, grow, develop and change, need energy to survive, maintain a stable internal environment, eventually die
These are four examples of eukaryotes.
What are animals, plants, fungi, and protists?
Give an example of a density-dependent factor and a density-independent factor.
Density-dependent: food availability, disease, predator density, competition
Density-independent: natural disaster, human influence and pollution, climate extremes
Provide an example of a homologous structure.
Answers will vary - needs to be something that two organisms share from a common ancestor
This is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory.
A hypothesis is a simple prediction that can be tested using an experiment.
A theory is a well-supported pattern that has been tested hundreds or thousands of times, with strong evidence behind it.
List the levels of classification of animals in order, starting with domain and ending with species.
What is:
Domain - Kingdom - Phylum - Class - Order - Family - Genus - Species
These are two examples of prokaryotes.
What are bacteria and archaea?
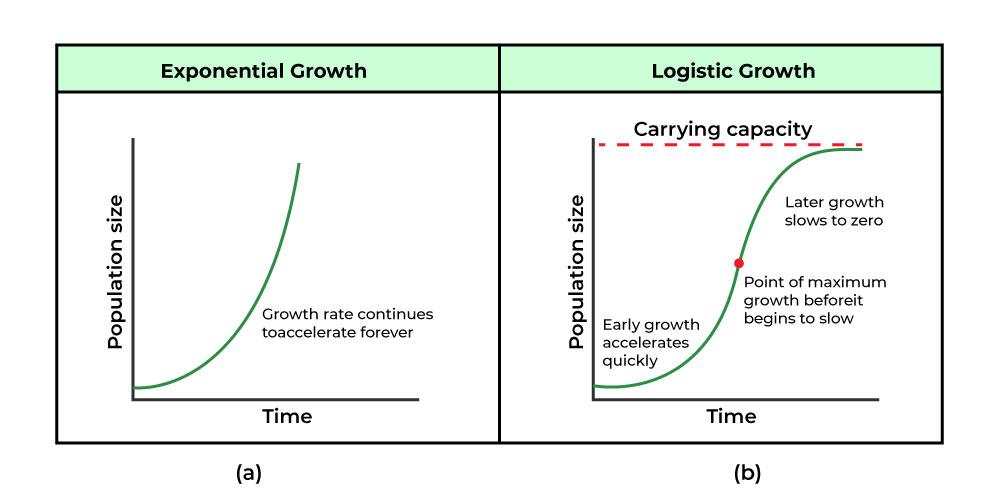
Draw a graph of logistic and exponential growth.
Draw a storyboard that shows how spoon-tongued lizards and straw-tongued lizards of the same species might change if spoon-tongued lizards can more easily access food.
Will do together
In an experiment, a scientist wants to measure the effect of sunlight on plant growth. Identify the independent, dependent, and controlled variables in this experiment. (Label all three!)
Independent variable: Amount of sunlight
Dependent variable: Plant growth/height of plants
Controlled variables: Type of plants, location, amount of water, etc.
Define "homeostasis."
What is the ability for organisms to maintain a stable internal environment?
In this phylogenetic tree, which organism shares the most recent common ancestor with prosimians?
What are humans?
Draw a graph that represents the relationship between the population of a predator and prey.
Provide two pieces of evidence supporting natural selection and how they support it.
Fossils: There are fossils that show gradual change of species over time in different geographical regions
Geographical distribution: Where species are located shows closer or more distant genetic relationships
DNA/genetic evidence: Shared DNA sequences show closer or more distant relationships based on the most recent common ancestor of extant species
Homologous structures: Different organisms have shared morphology that was inherited from a common ancestor
This scientific idea said that life could come from nothing.
What is spontaneous generation?
Provide two pieces of evidence that fire is alive and that fire is not alive.
Alive: consumes energy, grows
Not alive: No DNA, no CHNOPS
Draw a phylogenetic tree for this character table.

We will draw together
Draw a storyboard that shows how a population of bunnies would change over time if a new predator entered the area.
We will draw together.
List the three conditions required for natural selection.
What are:
Genetic variation
Inheritance of traits
Struggle for existence/variable survival

