What is the function of parenchyma cells?
replicate to repair plants
The function of the root cap is...
to protect the root tissue.
List the following in the correct order from largest to smallest.
class, family, domain, species, kingdom, order, phylum, genus
What type of fruit is a pineapple?
multiple fruit
Which of the following is not a plant adaptation to land environments?
A- vascular tissue
B- cuticle
C- stomata
D- asexual reproduction
D- Asexual reproduction
If a sunflower plant lost all of its collenchyma cells, it would...
fall over.
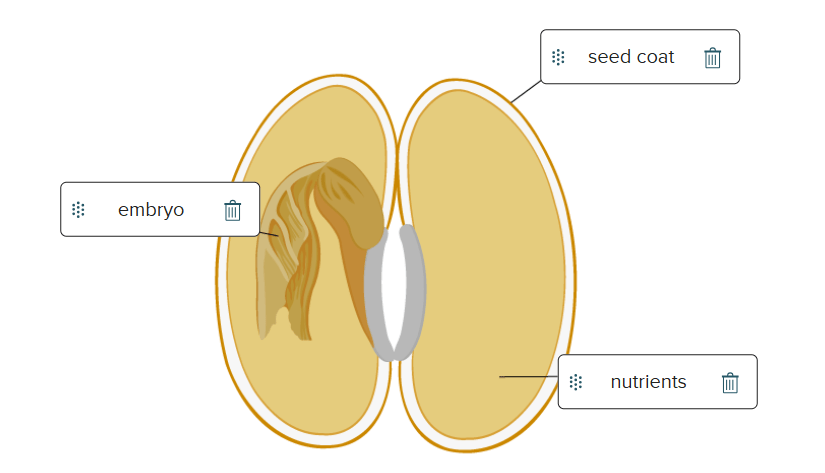
Draw a diagram of a seed and label the embryo, seed coat, and nutrients.
The second term in a scientific name is known as the _________________.
Species
What is the function of the cotyledons?
to store and absorb food.
How has the evolution of vascular tissues improved the adaptability of plants?
enabled plants to adapt to dry areas.
What structure enables the exchange of gasses?
stomata
Which vascular tissue transports water and minerals from roots to leaves?
Xylem
What do the fungi in lichens provide for their photosynthetic partners?
structural support
What is the function of the meristem?
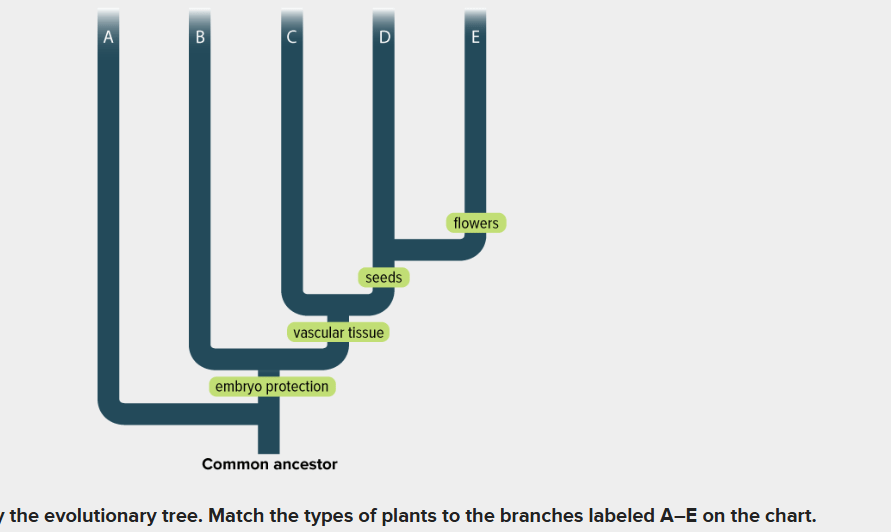
Draw the diagram above and match the type of plant to the letter where it belongs on the evolutionary tree. (Green Algae, nonvascular plants, angiosperms, gymnosperms, seedless vascular plants)
A-green Algae
B-nonvascular plants
C-seedless vascular plants
D-gymnosperms
E-angiosperms
What controls the movement of water vapor through the stomata?
guard cells
Which vascular tissue carries sugars from the leaves to other parts of the plant?
Phloem
What describes all organisms in the kingdom Fungi?
heterotrophic eukaryotes
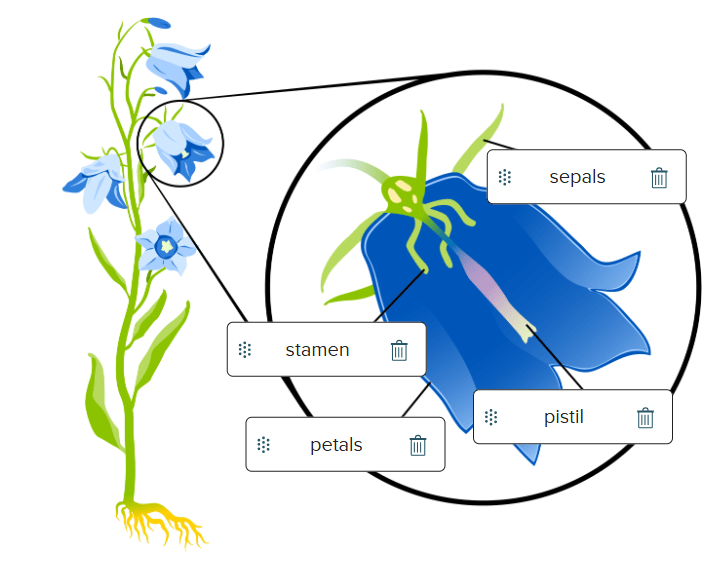
Draw a diagram of a flower and label the following parts. (sepal, petal, stamen, pistil)
Why is seed dispersal an important adaptation?
limits competition with parent plants
What are the three shapes of bacteria?
Spirochete, cocci, bacilli
What is the part of the embryo is the first part to emerge from the seed?
radicle
How are the three major groups of protists classified?
How they obtain nutrition.
Provides nourishment for the developing embryo in the seed.
The endosperm
How is a plant's vascular tissue related to its ability to live on land?
It provides a means to transport water and nutrients.